UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM
Annual Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended
or
Transition Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
Commission File No.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
||
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
|
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
|
|
|
||
(Address of principal executive offices) |
|
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
Trading Symbol(s) |
Name of each exchange on which registered |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports) and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
Accelerated filer |
☐ |
☒ |
|
Smaller reporting company |
|
Emerging growth company |
|
|
If any emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal controls over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report.
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates, based on the closing sales price of such stock on July 2, 2022 was $
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s common stock as of April 12, 2023 was
Restatement Background
On April 17, 2023, the Company’s management and the Audit Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Audit Committee”) reached a determination that the Company’s previously issued unaudited consolidated financial statements and related disclosures for each of the quarterly periods ended July 2, 2022 and October 1, 2022, should no longer be relied upon because of a material misstatement contained in those two quarterly unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements. The Company’s management and the Audit Committee discussed the matters with Frazier & Deeter, LLC, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the 2022 fiscal year, and with WSRP, LLC, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm during the second and third quarters in the 2022 fiscal year and prior fiscal periods since 2019, and determined to restate the Company’s unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements for the second and third fiscal quarters ended July 2, 2022, and October 1, 2022.
In connection with the Company’s preparation of its unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and related disclosures for each of the two referenced periods, the Company’s management and Audit Committee relied upon the report issued by a third-party valuation firm to determine the carrying value of the promissory note the Company had received from SPYR Technologies, Inc. (the “SPYR Note”), in connection with the Company’s sale of the assets of its GeoTraq, Inc. subsidiary to SPYR Technologies, Inc. in the first quarter of the Company’s 2022 fiscal year. The accounting treatment for the SPYR Note had financial statement implications to (i) two line items in the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets (specifically, Note receivable, net and Accumulated deficit), (ii) two line items in the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations And Comprehensive Income (Loss) (specifically, Gain on sale of GeoTraq, and Interest expense, net), resulting in a decrease in net income of approximately $1.8 million and a decrease in net loss of approximately $26,000 for the 13 weeks ended July 2, 2022 and October 1, 2022, respectively, and (iii) two line items in the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (specifically, Gain on sale of GeoTraq and Accretion of note receivable discount), resulting in decrease in net income of approximately $1.8 million for the 26 weeks ended July 2, 2022, and $1.7 million for the 39 weeks ended October 1, 2022. Further, in connection with the preparation of the Company’s Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q for those two quarterly periods that included those unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and related disclosures, the Company also received guidance from an additional third-party source in connection with the review of those unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. However, in connection with the Company’s 2022 fiscal year-end audit and the preparation of its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures for that fiscal year, the Company’s management and the Audit Committee concluded that the carrying value of the SPYR Note, as set forth in the aforementioned Quarterly Reports, should be restated. The initial carrying value of $11.2 million should be restated to be $9.4 million and reflect carrying value of $9.5 million as of July 2, 2022 and $9.6 million as of October 1, 2022. Each of these two quarterly restatements has an impact on net income (loss), but not on operating cash flows for any period.
Restatement of Previously Issued Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022 includes audited consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, as well as relevant unaudited interim pro forma financial information for the quarterly periods ended July 22, 2022 and October 1, 2022. The Company has not restated any information within this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the consolidated financial statements at December 31, 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, but did restate certain unaudited interim financial information for the quarterly periods ended July 2, 2022 and October 1, 2022.
See Note 28, Restatement, in Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, for such restated information on the quarterly unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements for the second and third quarters of the Company’s 2022 fiscal year.
i
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
Page |
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1. |
|
|
1 |
|
Item 1A. |
|
|
40 |
|
Item 2. |
|
|
52 |
|
Item 3. |
|
|
52 |
|
Item 4. |
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5. |
|
Market for Our Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
|
53 |
Item 6. |
|
|
53 |
|
Item 7. |
|
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
|
54 |
Item 7A. |
|
|
60 |
|
Item 8. |
|
|
61 |
|
Item 9. |
|
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
|
62 |
Item 9A. |
|
|
62 |
|
Item 9B. |
|
|
63 |
|
Item 9C |
|
Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
|
63 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 10. |
|
|
64 |
|
Item 11. |
|
|
67 |
|
Item 12. |
|
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters |
|
69 |
Item 13. |
|
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
|
70 |
Item 14. |
|
|
73 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 15. |
|
|
74 |
|
Item 16. |
|
|
74 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
|||
|
79 |
|||
ii
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
General
JanOne Inc. (formerly known as Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc.) and subsidiaries (collectively, “we,” the “Company,” or “JanOne”) is focused on being a clinical-stage pharmaceutical company committed to finding treatments for conditions that cause severe pain and bringing drugs to market with non-addictive pain-relieving properties.
One of the Company’s goals is to reduce the need for prescriptions for dangerous opioid drugs by treating underlying diseases that cause severe pain. The Company’s first drug candidate is a treatment for Peripheral Artery Disease (“PAD”), a condition that can cause severe pain and affects over 8.5 million people in the United States. The Company intends to champion new initiatives—digital technologies, educational advocacy, and revolutionary painkilling drugs that address what we believe is a multibillion dollar a year market—to help combat the opioid crisis, which claims tens of thousands of lives each year.
On December 28, 2022, we entered into a Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with Soin Therapeutics, LLC. Under the Purchase Agreement, JanOne acquired Soin Therapeutics and its LDN product, now known as JAN123. JAN123 is a novel formulation of 2.0 mg of LDN that results in a biphasic release of the product. The release properties of JAN123 provide for an immediate release of less than half the product with a slow, sustained release of the remaining product. Importantly, the rapid release of LDN has been reported to lead to vivid and lucid unpleasant dreams, which should be eliminated with the formulation of JAN123. Initially, a single tablet of JAN123 will be administered orally, once a day before sleep, with eventual titration up to two tablets (4 mg) before sleep.
The name of the Company, JanOne Inc., was strategically chosen to express the start of a new day in the fight against the opioid epidemic. January one is the first day of a New Year—universally considered as a day of optimism, resolution, and hope. JanOne stands by its strategic commitment to fresh thinking and innovative means to assist in ending the worst drug crisis in our nation’s history.
Through March 8, 2023, the Company operated its legacy businesses, ARCA Recycling, Inc. (“ARCA Recycling”) and Customer Connexx, LLC (“Connexx”), in its Recycling segment. ARCA Recycling recycles major household appliances in North America by providing turnkey appliance recycling and replacement services for utilities and other sponsors of energy efficiency programs. Connexx is a company that provides call center services for recycling businesses. On March 9, 2023, we entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement with VM7 Corporation, a Delaware corporation under which the Buyer agreed to acquire all of the outstanding equity interests of (a) ARCA Recycling, Inc., a California corporation, (b) Customer Connexx LLC, a Nevada limited liability company, and (c) ARCA Canada Inc., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada. The principal of the Buyer is Virland A. Johnson, our Chief Financial Officer.
The information contained in or accessible from our website is not incorporated into this Annual Report on Form 10-K (the “Form 10-K”), and it should not be considered part of this Form 10-K. We have included our website address in this Form 10-K solely as an inactive textual reference.
The Company was incorporated in Minnesota in 1983, although, through its predecessors, began operating its legacy recycling business in 1976. In 2018, the Company reincorporated in the State of Nevada. The Company's principal office is located at 325 E. Warm Springs Road, Suite 102, Las Vegas, Nevada 89119.
1
Biotechnology
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on becoming the leader in identifying, acquiring, licensing, developing, partnering, and commercializing novel, non-opioid and non-addictive therapies to address the large unmet medical need for the treatment of pain and addiction. JAN101 (formerly known as TV1001SR), is a potential treatment for PAD, a vascular disease that affects more than 8.5 million people in the U.S. and more than 60 million people worldwide. We expect to commence Phase IIb/III clinical trials for the treatment of PAD in 2024.
JAN101
Generally
JAN101, formerly known as TV1001SR, JAN 101, is a patented oral, sustained release pharmaceutical composition of sodium nitrite that targets poor blood flow to the extremities, such as those with vascular complications of diabetes or PAD and treats pain. A conclusion from a round of human studies found JAN101 prevents the prevalent reports of headaches by patients treated with an immediate release formulation of sodium nitrite. In a previous study of patients with PAD, a 40 mg BID treatment with immediate release sodium nitrite led to a statistically significant reduction in reported pain, while an 80 mg BID treatment had a more pronounced effect on bioactivity and Flow Mediated Dilation, a measure of vascular function. However, a number of subjects in both treatment groups reported headaches and dizziness following treatment. Although this did not result in subjects discontinuing treatment, JAN101 was developed to overcome this side effect. JAN101 was tested in a bridging study of diabetic neuropathy subjects and, during that bridging study, the subjects did not report headaches or dizziness. Subjects in this bridging study also reported less pain following treatment and improvements in bioactivity (quantitative sensory testing, a measure of nerve function) were similar to the PAD study, where the 80 mg dosing group had the greatest improvement in Flow Mediated Dilation. The ability to alleviate pain with BID treatment of JAN101 offers promise for a new non-addictive, non-sedating treatment of chronic pain.
Clinical Studies in Humans JAN101 Attributes
JAN101 does not mask pain, but instead treats the cause of pain by improving tissue and vascular function.
Benefits of Sodium Nitrite on Vascular Health
In initial research studies, sodium nitrite effectively restored ischemic tissue blood flow and was effective in a wide range of pathologies involving alterations of angiogenesis – development of new blood vessels – including diabetes, wound healing, and tissue necrosis. Beneficial effects include enhancing angiogenesis, endothelial cell proliferation, and arteriogenesis. There is also a strong association between reduced circulating nitrite levels and cardiovascular diseases in humans. We describe some of the associations and beneficial effects of sodium nitrite/nitrite below.
2
Plasma nitrite levels are negatively correlated to cardiovascular disease

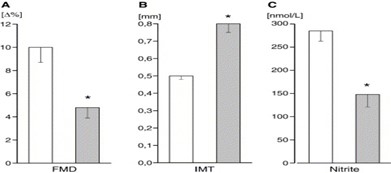
Plasma nitrite levels were inversely related to number of cardiovascular risk factors a subject had and decreased plasma nitrite was associated with decreased flow mediated vasodilation (FMD) and increased intimal medial thickness (IMT) (both are indicators of vascular pathology). Kleinbongard, et al. (2006) Free Radic Biol and Medicine 40:295-302.
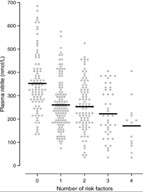
Plasma nitrite levels are reduced in diabetic and PAD patients
3
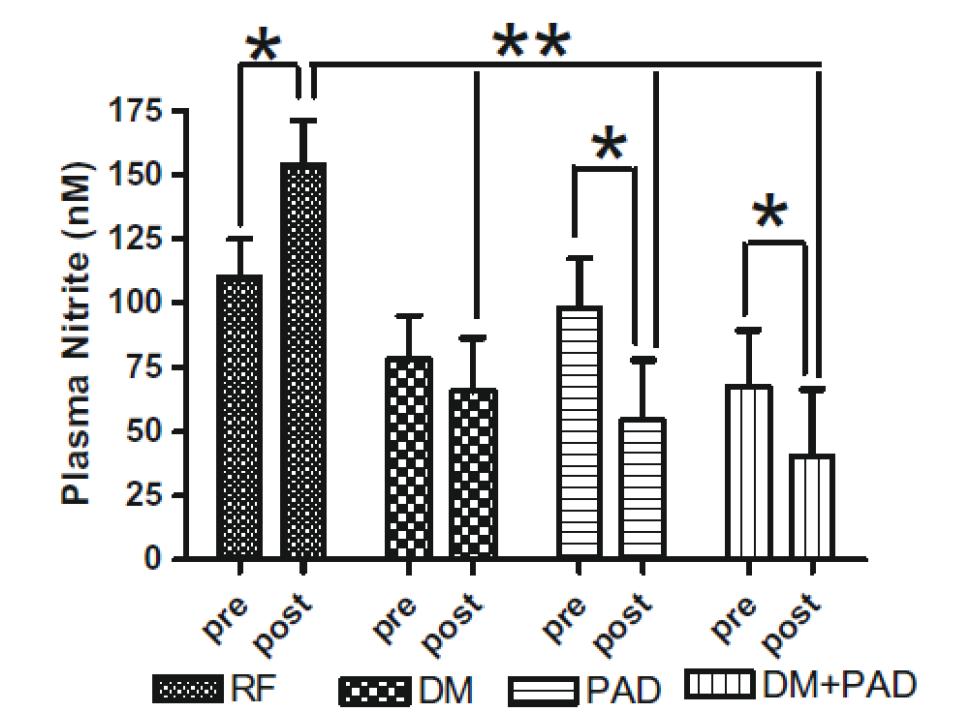
Exercise is a well-known stimulator of endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity, an enzyme that enhances nitric oxide (NO) production, which leads to increased plasma nitrite. In the study by Allen, et al., these authors revealed that baseline plasma levels of nitrite were less in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) or DM + PAD. Importantly, increases in plasma nitrite levels were not observed in either DM, PAD or DM + PAD patients after supervised exercise. These data reveal that baseline nitrite availability is compromised in DM patients and that supervised exercise is unable to increase plasma nitrite levels but actually results in a decrease in nitrite, highlighting a physiological efficiency of this molecule. Allen, et al., Nitric Oxide 2009 20:231-2377.
Skeletal Muscle Nitrite and Metabolite Levels are Reduced in Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI) Patients
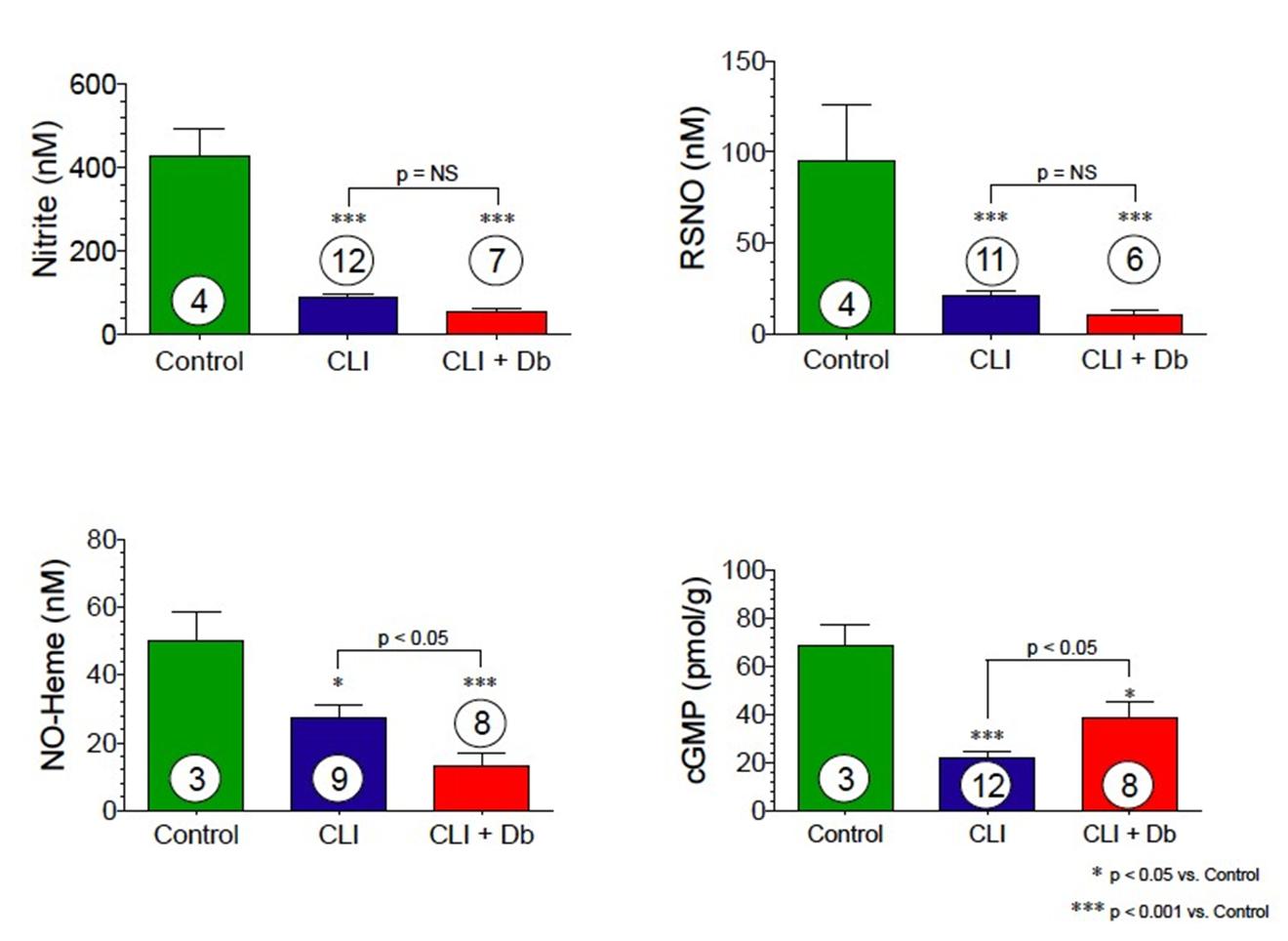
Skeletal muscle nitrite, nitrosothiol (RSNO), nitric oxide-heme, and cGMP are all significantly reduced in CLI (the most severe form of PAD) patients. Diabetic patients with CLI show even further nitrite reductions.
In summary, nitrite levels in various cardiovascular and vascular diseases appear to be inversely related to the severity of the disease in humans:
Given the association between low levels of circulating nitrite and human diseases, supplementation with sodium nitrite has been studied preclinically in animals. Below are summaries of some of the more important findings:
4
From Arya, et al.
Nitrite Therapy Selectively Increases Ischemic Tissue Vascular Density in a NO-dependent Manner
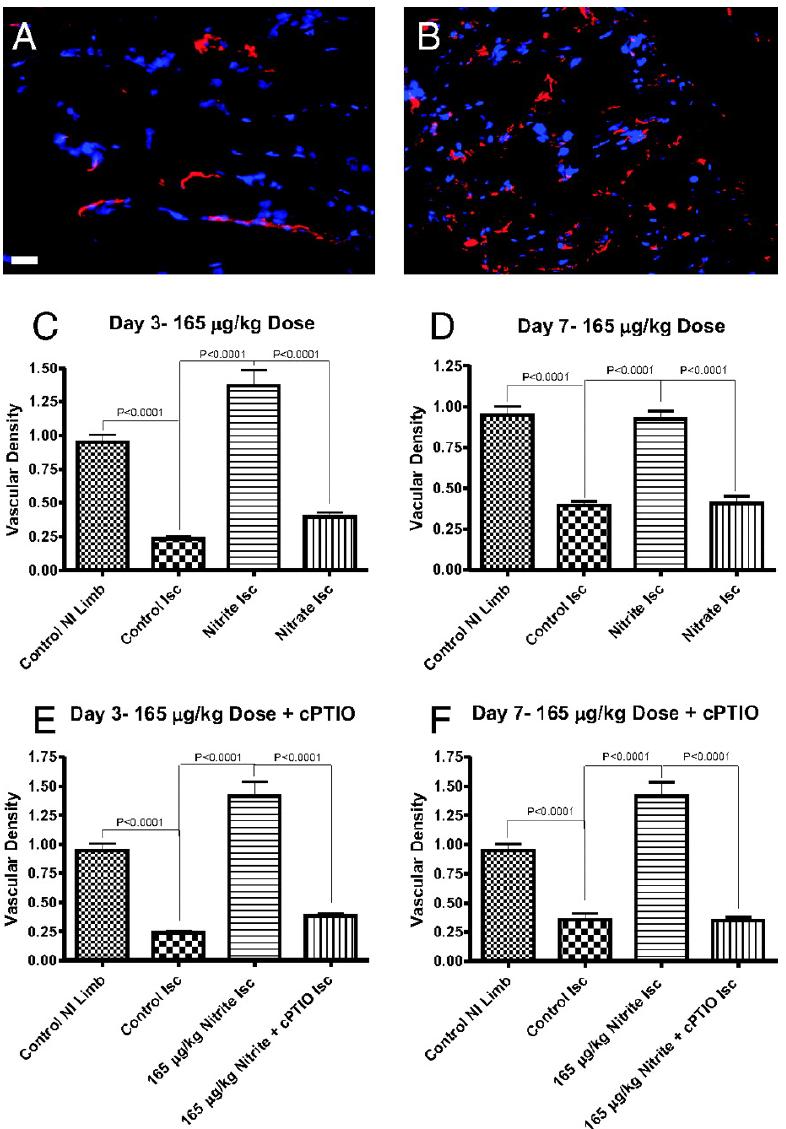
Chronic sodium nitrite therapy increases ischemic tissue vascular density in a NO-dependent manner. A and B show representative images of CD31 (red) and DAPI nuclear (blue) staining from sodium nitrite and sodium nitrate ischemic gastrocnemius muscle tissue at day 7. C and D report the vascular density of ischemic gastrocnemius muscle tissue at days 3 and 7 for 165 μg/kg sodium nitrite and nitrate treatments, respectively. E and F demonstrate the vascular density of ischemic gastrocnemius muscle tissue at days 3 and 7 from 165 μg/kg sodium nitrite plus carboxy PTIO. (Scale bar, 150 μm.) n = 10 mice per treatment group. Kumar D., et al., PNAS; 2008; 105:7540-7545.
5
Nitrite Therapy Augments Arterial Perfusion of Ischemic Tissue
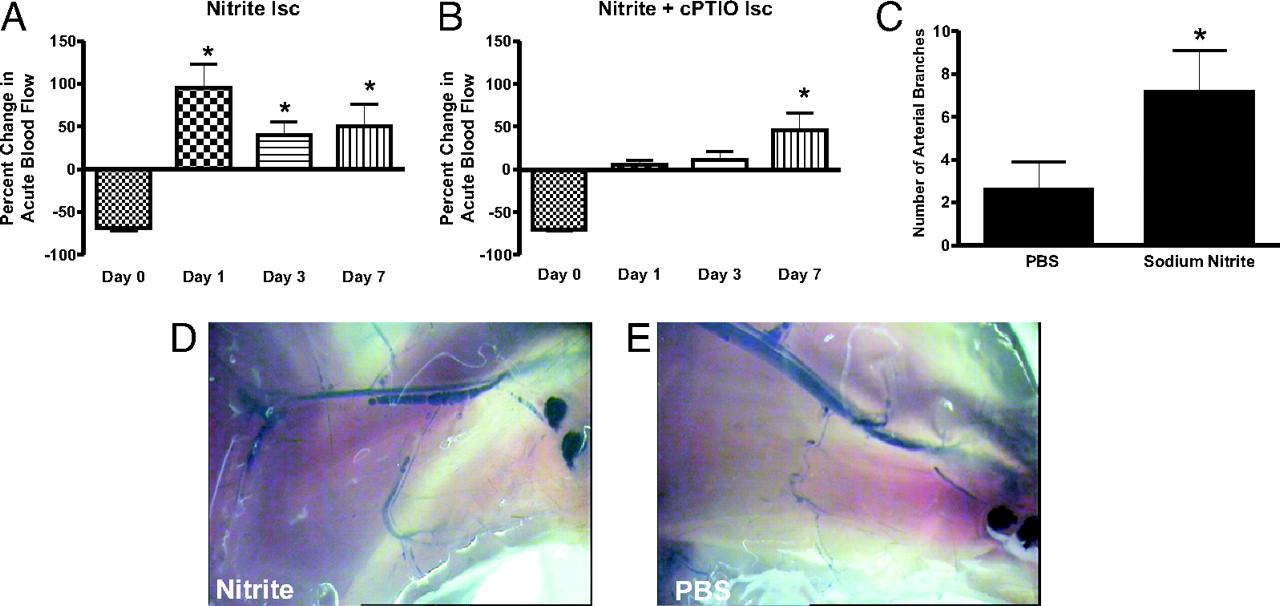
Chronic sodium nitrite therapy acutely increases ischemic tissue blood flow and stimulates arteriogenesis. A and B report 165 μg/kg sodium nitrite-induced acute changes in blood flow of chronically ischemic tissues at various time points with or without cPTIO, respectively. C reports the number of arterial branches between PBS and nitrite therapies. D and E illustrate vascular casting of the arterial vasculature in ischemic hind limbs of day 7 nitrite or PBS-treated mice, respectively. *, P < 0.01 vs. sodium nitrate. N = 10 mice per treatment group. Kumar D., et.al., PNAS;2008; 105:7540-7545.
Nitrite Therapy Restores Diabetic Ischemic Hind-Limb Blood Flow and Promotes Wound Heal
6
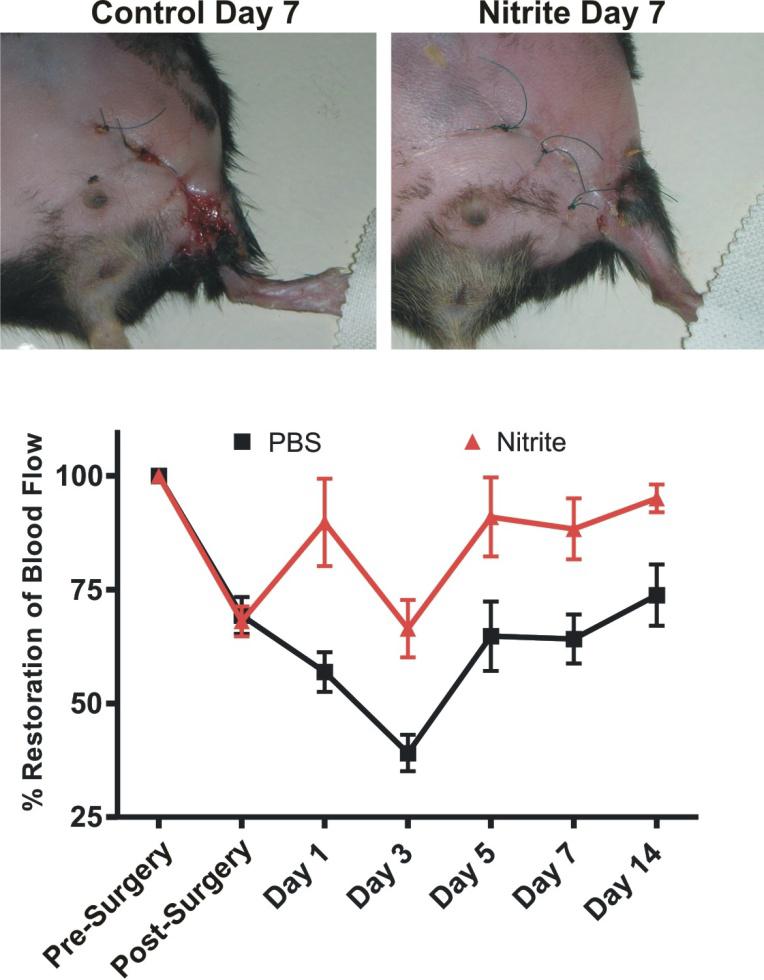
Unilateral femoral artery ligation was performed on 18-20 week old male Db/Db mice. Mice were randomized to PBS or sodium nitrite (165 μg/kg) therapy twice daily via I.P. injection. Laser doppler flowmetry was performed at the indicated time points. Increased wound dehiscence was noted in the PBS treated animals at day 7 but not in nitrite treated animals. (Bir, et al., Diabetes 2014, 63(1):270-81).
Nitrite Therapy Increases Diabetic Ischemia Induced Angiogenesis
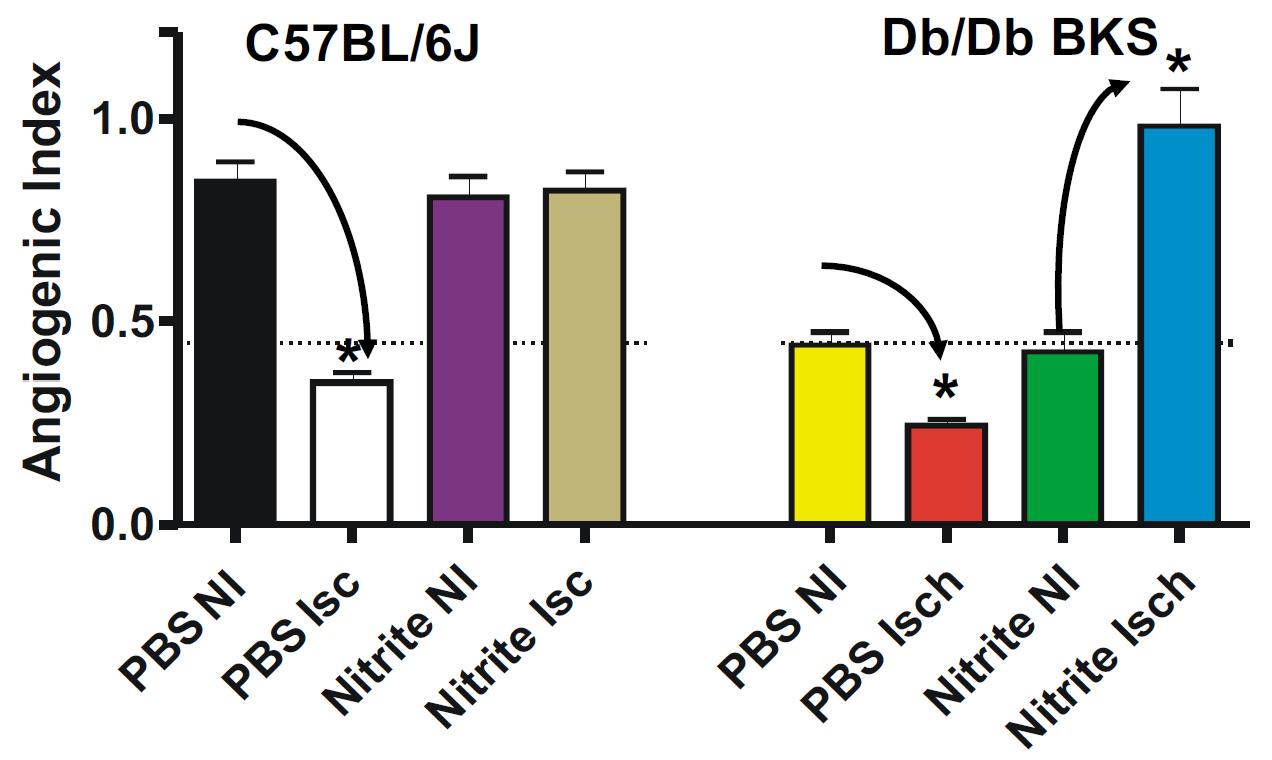
Nitrite therapy prevented ischemia mediated endothelial cell density loss in normal C57BL/6J ischemic limbs. Nitrite therapy significantly restored endothelial cell density in ischemic limbs of diabetic mice to normal C57BL/6J levels compared to PBS therapy of non-ischemic and ischemic conditions. These data suggest that nitrite therapy may be useful in attenuating microvascular rarefaction due to loss of nitric oxide that is observed during metabolic dysfunction (Frisbee JC AJP Integr Comp Physiol 2005 289(2):R307-16; Stepp et al Microcirculation 2007 14(4-5): 311-6).
7
Delayed Nitrite Therapy Restores Ischemic Hind-Limb Blood Flow
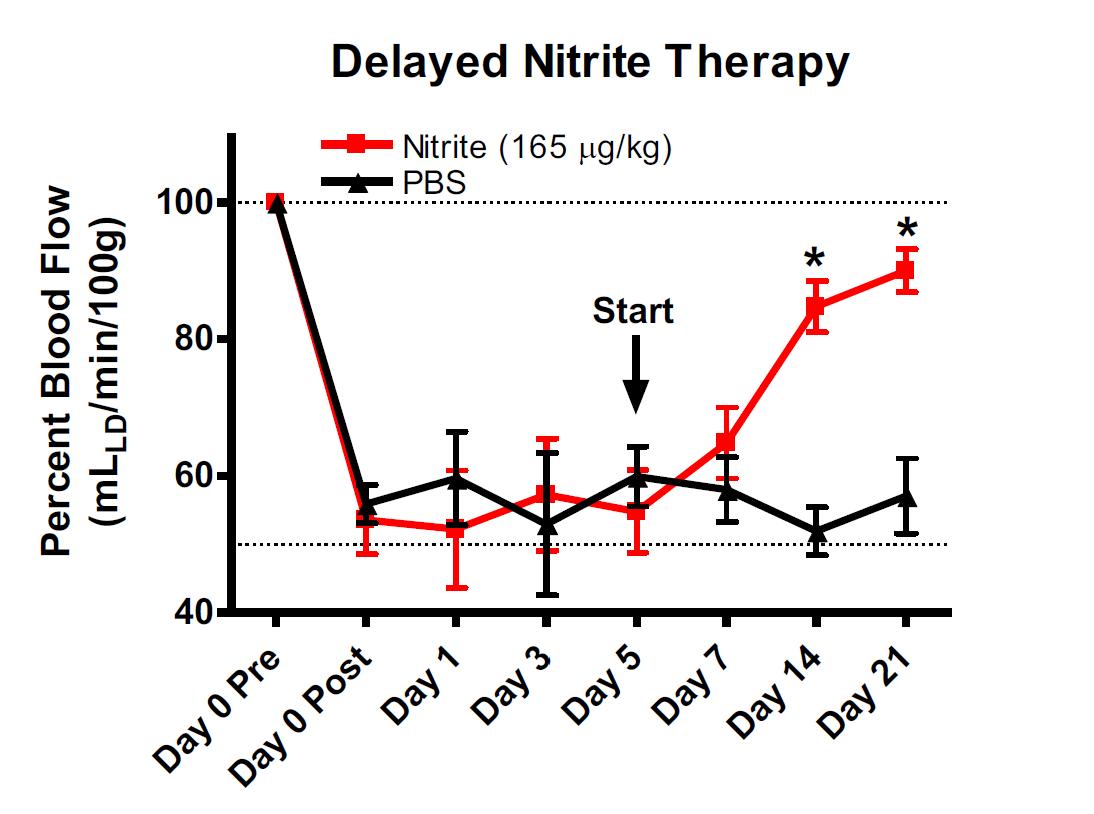
Studies were performed to determine whether nitrite mediated therapy would be effective in tissue that had been left ischemic for 5 days after femoral artery ligation. Femoral artery ligation was performed in C57BL/6J mice and the animals randomized to either PBS or sodium nitrite therapy 5 days after artery ligation. Treatments were given b.i.d. via I.P. injection. Ischemic limb blood flow was measured using laser doppler flowmetry. (Bir, et al., Diabetes 2014, 63(1):270-81).
8
Delayed nitrite therapy increases SPY angiogram arteriogenesis
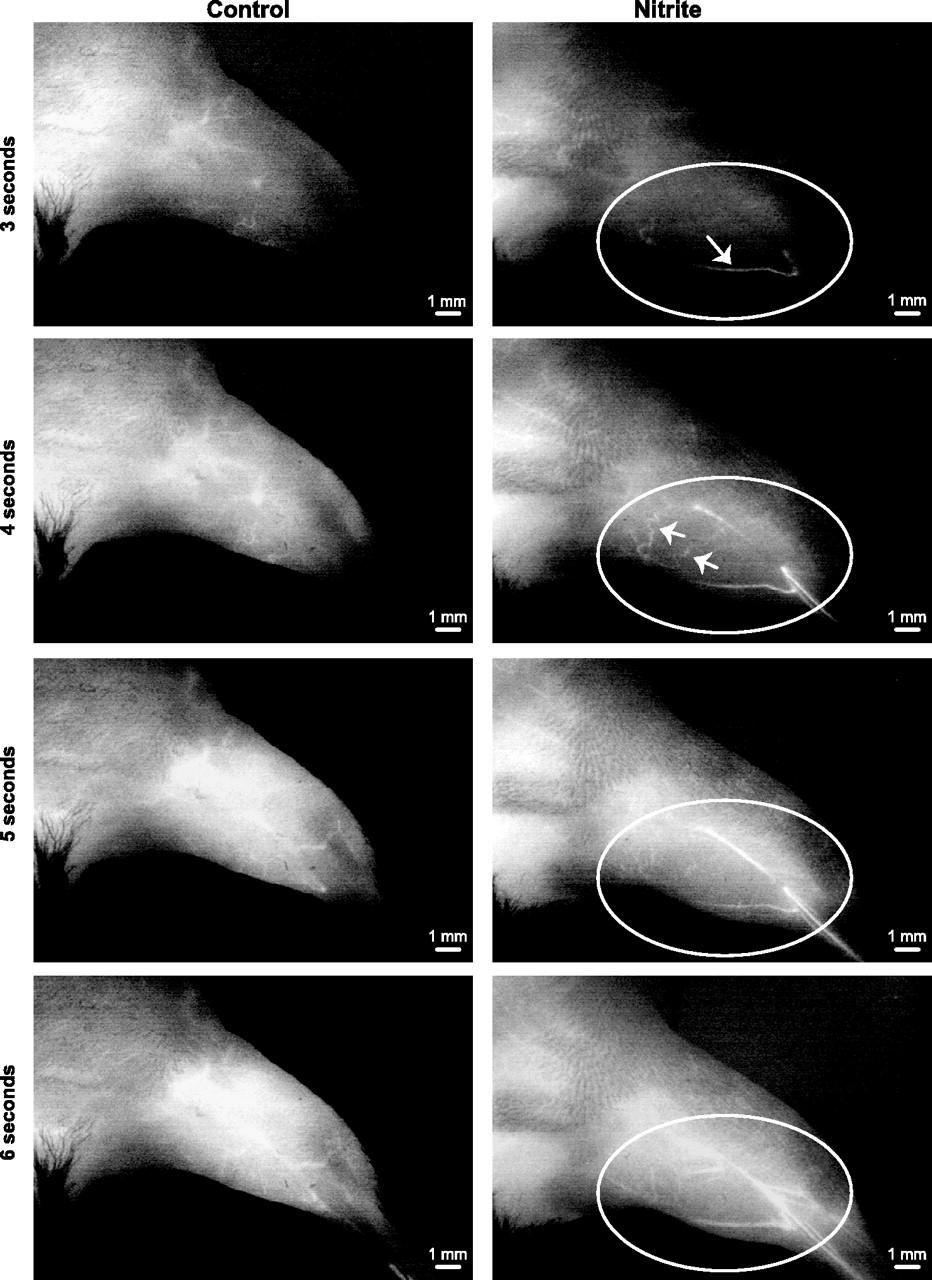
Delayed nitrite therapy increases SPY angiogram arteriogenesis. Representative temporal SPY angiogram image stills (3–6s) are shown at 11 days following ligation and 6 days after beginning therapy (either PBS or sodium nitrite). Left: PBS control angiogram. Right: sodium nitrite angiogram following injection of ICG. n = 5 animals per cohort. Circles identify limb anatomical regions of vascular blush, whereas arrows indicate perfused vessels that progressively occur over time.
Bir, et al., Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2012;303:H178-H188.
9
Nitrite Therapy Prevents Tissue Necrosis in Aged Db/Db Mice
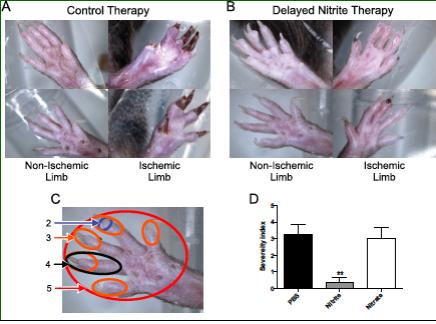
Delayed sodium nitrite (165 ug/kg) or control PBS therapy was stated 5 days post-femoral artery ligation in nine-month old Db/Db mice. Nitrite therapy significantly prevented tissue necrosis (panel B) compared to control PBS therapy (panel A). Panel D reports tissue necrosis severity as a function of degree of limb and digit involvement. Nitrite therapy, but not PBS control or sodium nitrate, significantly prevented tissue necrosis. (Bir, et al., Diabetes 2014, 63(1):270-81).
Nitrite and Hind Limb Ischemia Summary
Sodium nitrite has long been known to be a potent vasodilator (transiently increasing blood vessel diameter) that can lead to a drop in blood pressure when given acutely. The above studies indicate that chronic administration at low doses promotes angiogenesis, unlike one-time nitrite therapy, which does not stimulate angiogenesis. In addition, these studies and a large number of other studies not reviewed above show:
JAN101
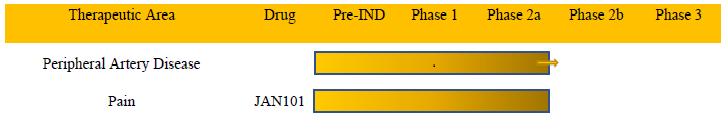
JAN 101 is designed to treat diseases associated with poor vascular function. The following table summarizes our current product candidate:
Therapeutic Area Peripheral Artery Disease Pain COVID-19 Drug JAN101 Pre-IND Phase 1 Phase 2a Phase 2b Phase
10
Pain
Pain is a protective reaction that alerts the body to the presence of actual or potential tissue damage so that necessary corrective responses can be mounted. The National Institutes of Health (the “NIH”) defines chronic pain as pain that persists beyond the normal healing time of an injury or that persists longer than three months. It is estimated that chronic pain affects 100 million individuals in the United States and over 1.5 billion people worldwide; thus, more people suffer from chronic pain than diabetes, heart disease, and cancer combined (Cowen Therapeutic Categories Outlook, March 2019). Chronic pain exacts a tremendous cost in terms of direct treatment and rehabilitation expenditures, lost worker productivity, prevalent addiction to opioid-based drugs, and emotional and financial burden for patients and their families. According to an Institute of Medicine of the National Academies report, pain is a significant public health problem in the United States that costs society between $560 billion and $635 billion annually. Despite the magnitude of the pain problem, innovation in the development of therapeutic solutions has been largely absent. Since 2010, there have been 20 approvals by the FDA for the treatment of pain, of which 12 were opioid variants, one was an extended-release generic corticosteroid, five were variants of aspirin, and two were variants of other existing drugs. We are developing a novel product candidate designed to overcome the limitations of current treatment options for patients with PAD who suffer from chronic pain. According to a research study by Stanford University, more than 24% of patients with PAD are at risk of high opioid use. By treating pain at the source and presenting patients and physicians with better and safer treatment alternatives, we expect to minimize opioids at the prescription pad. Given the properties of JAN101, we have made the strategic decision to focus initially on pain associated with PAD by treating the underlying cause of PAD.
Peripheral artery disease
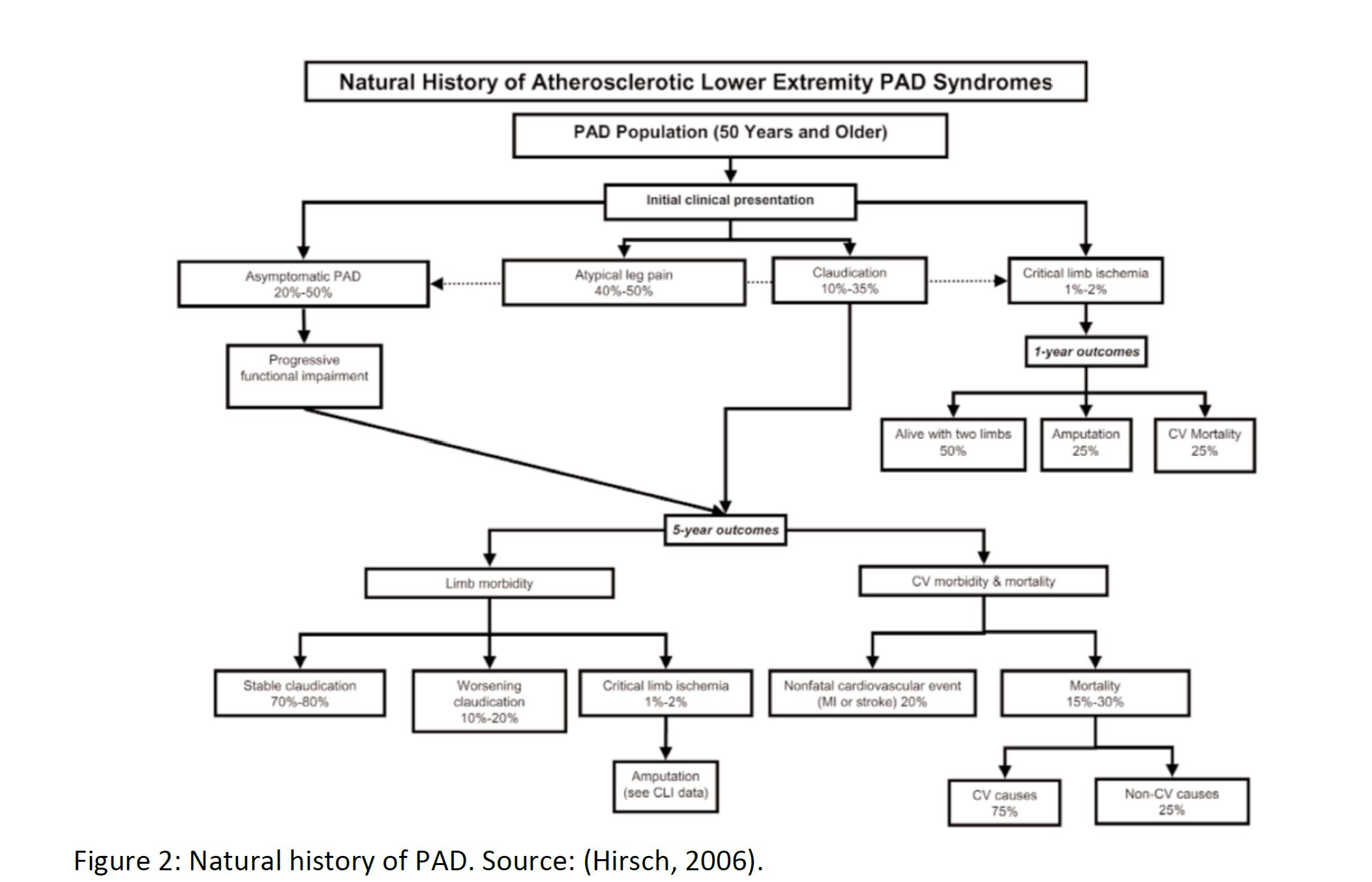
Peripheral artery disease (“PAD”) is a general term for conditions in which arterial blood flow to the limbs is partially blocked. When there is less blood present in the extremities relative to demand, muscle pain and fatigue result, especially in the calf, which is also known as “intermittent claudication.” In many patients, pain and fatigue are relieved through rest. Roughly half of patients with PAD are asymptomatic. The most common cause of PAD / intermittent claudication is atherosclerosis. Diabetes, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and smoking are all risk factors that can increase the likelihood of PAD. In atherosclerosis, fat deposits (plaques) build up along arterial walls, resulting in a reduction in blood flow in the legs. This same process can cause strokes if the arteries leading up to the brain are affected.
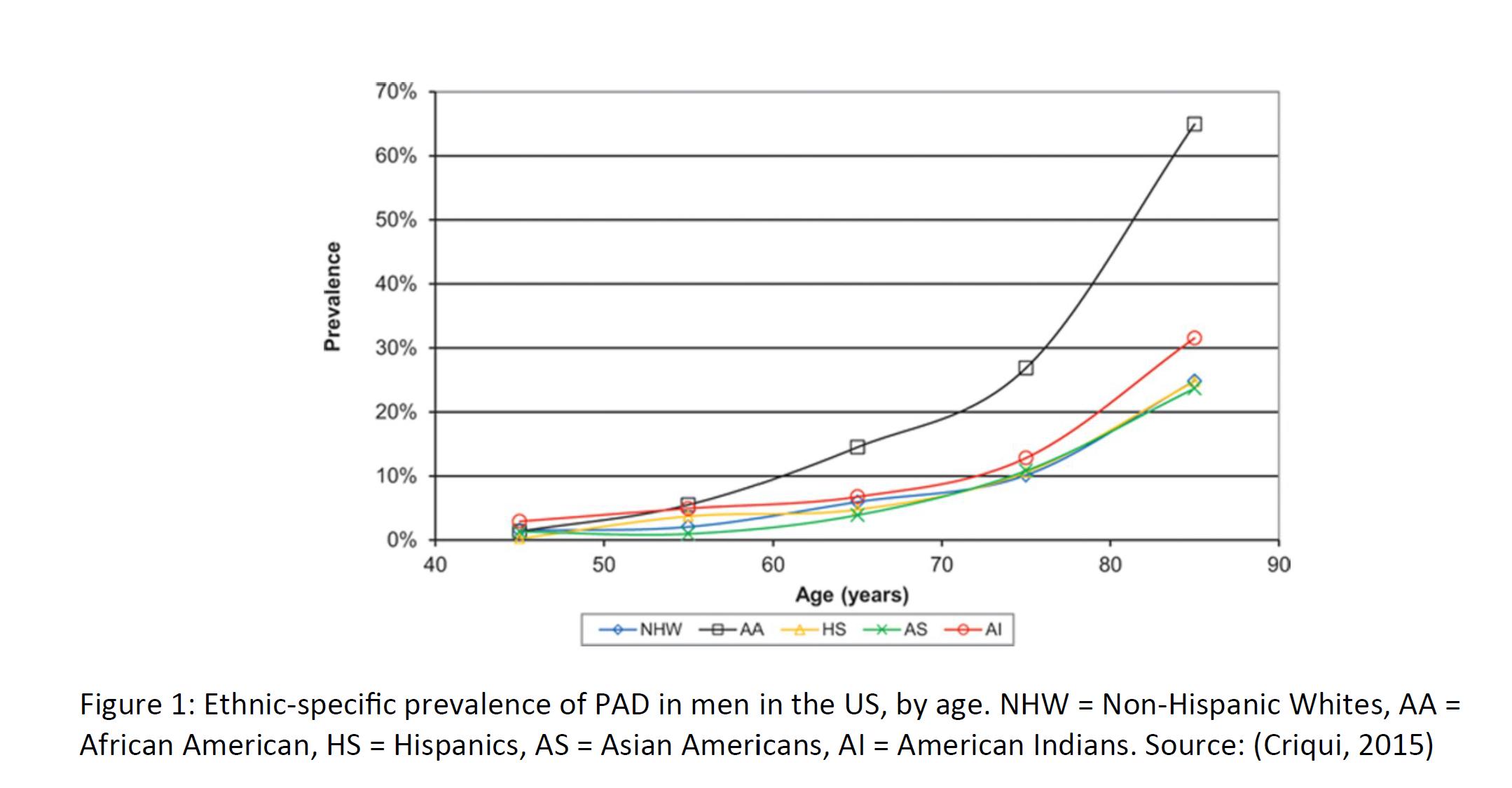
Because of the high rate of asymptomatic patients, prevalence figures vary widely. Some estimate that up to 200 million people worldwide have PAD, ranging from asymptomatic disease to severe. Prevalence increases as a function of patient age, rising sharply after the age of 60. Thus, in countries with an aging population, it is expected that the prevalence of PAD will only increase. There is also a strong ethnic and racial component to PAD prevalence, which may be due to cultural differences in diet and exercise, along with genetic differences. Some suggest a prevalence of eight to 12 million in the United States alone, with roughly one-third experiencing pain when walking, which improves upon resting. The diagnosis of PAD usually begins with patient complaints of pain in the extremities. If the patient is already being treated or monitored for diabetes or other risk factors, then the physician will check for a weak or absent pulse in the extremity. Decreased blood pressure, poor wound healing, and whooshing sounds (via stethoscope) in the legs are also tell-tale signs of PAD / intermittent claudication. Angiograms, electrocardiograms, and ultrasounds can also be used to image and confirm the diagnosis.
11
The non-drug treatment of PAD / intermittent claudication may be divided into four general categories:
The underlying condition is not addressed by surgery. Surgical approaches will not, in the long run, improve exercise capacity and walking distance. Only exercise itself, coupled with lifestyle changes and drug approaches, has this benefit.
Prescription drugs for the treatment of the underlying PAD may be divided into multiple categories, depending on the underlying condition and severity:
12
The lack of any truly effective treatment of PAD, along with encouraging early trial results using JAN101 on both improving vascular function and reducing pain in PAD patients, has created an opportunity potentially to treat this large unmet medical need. By improving vascular function, JAN101 has the potential to reduce associated pain and improve PAD patients’ quality of life.
Our Strategy
Our focus is to develop and commercialize novel, non-opioid, and non-addictive therapies to address, safely and effectively, the significant unmet medical need of chronic pain or treat conditions that cause pain. The principal elements of our strategy to achieve this mission are the following:
13
Chronic Pain
The NIH defines chronic pain as pain that persists either beyond the normal healing time of an injury or longer than three months. We believe that chronic pain represents a significant public health crisis. It is estimated that chronic pain affects 100 million individuals in the United States and over 1.5 billion people worldwide; thus, more people suffer from chronic pain than diabetes, heart disease, and cancer combined (Cowen Therapeutic Categories Outlook, March 2019). Chronic pain exacts a tremendous cost in terms of direct treatment and rehabilitation expenditures, lost worker productivity, prevalent addiction to opioid-based drugs, and emotional and financial burden for patients and their families. According to an Institute of Medicine of the National Academies report, pain is a significant public health problem in the United States that costs society between $560 billion and $635 billion annually. Chronic pain is the leading cause of long-term disability in the United States, and approximately 23 million adults in the United States experience severe pain over a three-month period. Globally, the prevalence of chronic pain is even larger, with over one billion people worldwide affected each year. Common types of chronic pain include those of neuropathic and inflammatory origin and may involve the skin, muscles, joints, bones, tendons, ligaments, and other soft tissues. Chronic pain is associated with a variety of clinical conditions including, but not limited to, arthritis, spinal conditions, cancer, fibromyalgia, diabetes, surgical recovery, visceral injury, and general trauma.
Pain is a necessary protective reaction that alerts the body to the presence of actual or potential tissue damage so that necessary corrective responses can be mounted. Pain is signaled by specialized cells in the peripheral nervous system called nociceptors, or pain-sensing fibers. These pain-sensing fibers normally transmit information about stimuli that approach or exceed harmful intensity from different locations in the body to the brain, which registers this information as a sensation of pain. In the case of tissue injury due to trauma or infection, pain accompanies the associated inflammation, persists for the duration of the inflammatory response, and aids healing by inhibiting use of the affected body part.
14
Pain also can modify the central nervous system such that the brain becomes sensitized and registers more pain with less provocation. This is called central sensitization. When central sensitization occurs, the nervous system goes through a process called wind-up and gets regulated in a persistent state of high reactivity. This persistent, or up-regulated, state of reactivity lowers the threshold for what triggers the sensation of pain and can result in the sensation of pain even after the initial injury might have healed.
When there is dysfunction in pain signaling, injury to the nervous system, or an unhealed injury, pain becomes no longer just a symptom, but a disease in itself.
Current Therapeutic Approaches to Treating Chronic Pain and Their Limitations
NSAIDs
Some of the most widely used therapies to treat chronic inflammatory pain are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (“NSAIDs”). NSAIDs can have significant side effects that include gastrointestinal bleeding, gastritis, high blood pressure, fluid retention, kidney problems, heart problems, and rashes. On April 7, 2005, the FDA announced a decision to require boxed warnings of potential cardiovascular risk for all NSAIDs.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, or steroids, also possess anti-inflammatory properties and are commonly used in the practice of pain management, either systemically or locally, depending on the condition. Steroids work by decreasing inflammation and reducing the activity of the immune system. While steroids are commonly used, they may have numerous and serious side effects. These side effects may include allergic or hypersensitivity reactions, increased risk for infection, adrenal insufficiency, diabetes or decreased glucose tolerance, hypertension, loss of bone density, and loss of joint cartilage volume. In addition, steroids should not be administered when there is an infection present because steroids can inhibit the body’s natural infection-fighting immune response. Also, if a joint is already damaged or is subject to chronic deterioration, intra-articular, or IA steroid injections are not likely to provide any long-term restorative benefit. For the above reasons, IA steroid injections are generally recommended to be administered no more often than every six weeks and not more than three to four times per year.
Opioids
Opioids are some of the most widely prescribed therapeutics for chronic and acute pain, and sales of these drugs have quadrupled between 1999 and 2010.According to a National Survey on Drug Use and Health report, in 2016 more than one-third of adult Americans were prescribed opioids and 230 million opioid prescriptions were written that year in the United States. Opioids act by binding to specific receptors located on neurons in both the central and peripheral nervous system throughout the body including in the brain, spinal cord, and other nervous tissue. Although they can be effective in providing pain relief, the increased medical use of opioids has been accompanied by an increase in the abuse and misuse of prescription opioids. In addition, for most patients, chronic opioid use is a poor option due to an intolerance to the many side effects, including nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, and constipation, and the propensity for opioids to become less effective with long-term use. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (the “CDC”), almost two million individuals abused or were dependent on prescription opioids in 2014. CDC figures show that the number of opioid-related overdose deaths has quadrupled between 1999 and 2010, and currently approximately 40% of opioid overdose deaths in the United States involve a prescription opioid. This increase in prescription opioid-related deaths in the United States prompted former President Trump to declare the opioid crisis a national Public Health Emergency in October 2017. Opioid abuse has become an epidemic in the United States, ranking as the nation’s second most prevalent illegal drug problem. These major issues create the need to find new approaches to treating chronic pain.
Our Approach to Treating PAD and Chronic Pain
The unmet medical need for treating PAD and chronic pain reflects the historic failure to develop novel classes of analgesics with comparable or greater efficacy, an acceptable level of adverse effects and a lower abuse liability than those currently available. Some of the reasons for this include the heterogeneity of chronic pain and its related conditions, and the complexity and diversity of the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms for pain. However, recent advances in the understanding of the neurobiology of pain are beginning to offer opportunities to identify new drug targets and develop new therapeutic strategies.
15
We have taken an innovative and targeted approach to identifying treatments for chronic pain that leverages our understanding of the pathophysiology of pain. Pain is variable. For example, it can be inflammatory or neuropathic in nature, and it may be localized to a specific area of the body or it may be generalized throughout. We believe that the most effective way to treat chronic pain is through therapies that specifically target the origin of the pain signal. We strive to maximize JAN 101’s potential based on its unique mechanism of action related to the origin of the pain signal.
A Randomized, Double-Blind Study of the Effects of a Sustained Release Formulation of Sodium Nitrite (SR-nitrite) on Patients with Diabetic Neuropathy
Background: Sodium nitrite has been reported to be effective in reducing chronic peripheral pain.
Objectives: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of 40 and 80 mg, BID, of an oral sustained release formulation of sodium nitrite (SR-nitrite) in patients suffering from diabetic neuropathy, and to determine whether SR-nitrite would reduce the frequency of headaches reported previously by subjects receiving the same doses of an immediate release formulation. Study Design: Phase II, single-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial. Setting: The Ohio Pain Clinic and Kettering Medical Center.
Methods: Twenty-four patients were randomized to 40 mg or 80 mg SR-nitrite or placebo twice daily for 12 weeks. The primary objective was to determine whether headaches would be reduced using SR-nitrite. The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean difference in the change of the Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory (NPSI) pain score from baseline to that reported after 12 weeks of treatment. Secondary endpoints included changes from baseline for the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) Scale, the RAND 36 questionnaire, Short-Form McGill Questionnaire, daily patient reported score for neuropathic pain, changes in HbA1c, PulseOx, and quantitative sensory testing. Results: The number of subjects reporting adverse events and the number of adverse events did not change with dose. There were no reports of treatment-related headaches. Although no significant differences were identified in patient responses to the questionnaires, a trend was observed. In the NPSI assessment, patients in the 40 mg and 80 mg dosing groups reported a 12.7% and 22.0% reduction in pain, respectively, compared to an 8.4% reduction by patients in the placebo group. A trend was also observed with the BPI total severity score. However, the 40 mg dosing group reported the greatest reduction in pain using the McGill Pain index and via patient logs of daily pain scores, where the mean of pain scores reported by subjects in the 40 mg group dropped by day 41 and generally stayed lower than the mean of scores reported by subjects in either of the other two groups. Patients in the 80 mg SR-nitrite group had an improvement in both Nerve Sensory Conductance and Nerve Sensory Velocity. No changes were observed in HbA1c levels or PulseOx.
Limitations: Small sample size.
Conclusion: Sustained release sodium nitrite prevents the prevalent reports of headaches by patients treated with an immediate release formulation of sodium nitrite. In a previous study of patients with peripheral arterial disease (PAD), 40 mg BID treatment led to a statistically significant reduction in reported pain. Similar trends were observed at the end of the trial period for most of the pain questionnaires used in the study. The 80 mg BID treatment had the more pronounced effect on bioactivity (quantitative sensory testing), which was similar to the PAD study, where this dosing group had the greatest improvement in Flow Mediated Dilation . The ability to alleviate pain with BID treatment of SR-nitrite offers promise for a new non-addictive, non-sedating treatment of chronic pain and warrants further study.
Microcirculatory injury, which is common in diabetic patients, can lead to a number of problems. Prominent among these is diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). About 10% of patients will have evidence of DPN at the time they are initially evaluated, and almost 50% of diabetic patients will ultimately develop DPN. Of diabetic patients with DPN, 40% to 50% suffer from chronic pain, as well as paresthesia, sensory loss, and weakness, and have at least an eight-fold increased risk of undergoing a distal lower extremity amputation compared to similar non-diabetics. Endothelial cells play an important part in the regulation of microcirculation, as they maintain vascular tone by secreting both vasodilators and vasoconstrictors. A central feature of diabetic microvascular disease (MVD) is endothelial dysfunction, which, in turn, plays an important role in the development and progression of DPN. The pathophysiological factors leading to endothelial dysfunction in diabetes include chronic hyperglycemia and protein glycosylation, insulin resistance, inflammation, and increased oxidative stress. Studies have now shown a close relationship between endothelial dysfunction and diminished nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability. Endogenously produced NO has a half-life measured in seconds, and is rapidly oxidized to nitrite (NO2–) and nitrate (NO3–)
16
end-products, the latter of which is biologically inert. In the presence of microcirculatory ischemia and endothelial cell dysfunction, however, endogenous NO production by eNOS is much more limited. In such circumstances, circulating NO2 can be non-enzymatically reduced to increase NO availability. In addition to serving as a circulating NO reservoir, nitrite itself has also been shown to have direct and potent vasodilatory effects in vitro and in vivo. The findings that NO2– mediates vasodilatation, both directly and through NO generation, has led to growing interest in the potential effectiveness of nitrite as a therapeutic agent in conditions associated with DPN and endothelial dysfunction. Such conditions include diabetic microvascular disease, DPN, and retinopathy, in which low levels of NO and NO2–, as well as elevated levels of nitrate (NO3–), suggest that the complete oxidation of NO occurs during diabetes with insufficient NO2– reserves to restore NO bioavailability. Previous human studies with an oral formulation of NaNO2 have shown that administration twice daily improves vascular function. In the peripheral arterial disease study, subjects who received the lower dose of NaNO2 reported a significant reduction in pain. Although side effects were minimal, headaches and dizziness were reported by a large number of subjects, likely due to the rapid release of NaNO2 leading to vasodilation. An oral, sustained-release formulation of NaNO2 (SR-nitrite) was developed in an attempt to overcome these problems and was tested in a porcine model of metabolic syndrome with critical limb ischemia. SR-nitrite-treated animals showed increased myocardial NO bioavailability, diminished oxidative stress, and cytoprotection in ischemic tissue. Importantly, 24-hour telemetry recordings of blood pressure showed no evidence of vasodilation. In the above study, we hypothesized that the SR-nitrite would reduce or eliminate headaches reported in patients following administration of the immediate release formulation. Given the promising results on reducing pain in diabetic patients with PAD reported in the previous study, patients with diabetic neuropathy were utilized in this study to determine whether any trends in reducing pain could be observed. The study design was a randomized, placebo controlled, double-blind phase II study was carried out to investigate the safety and potential biological activity of multiple doses of an oral, sustained-release formulation of sodium nitrite (SR-nitrite; TheraVasc Inc., Cleveland, OH, USA), BID in doses of 40 mg and 80 mg over a 12-week treatment period, in human subjects with diabetes and neuropathic pain in the lower extremities and feet. The trial was approved by the Copernicus Group Institutional Review Board and listed on ClinicalTrials.gov: www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02412852. The study was funded by TheraVasc Inc. (“TheraVasc”).
JAN101—Regulatory Strategy
Sodium nitrite has been previously approved as one of the active components of cyanide poisoning antidote. This means the approval path for JAN101 is through a 505(b)(2) (“NDA”), which we intend to pursue.
JAN101—Commercial Strategy
We currently intend to use third-party providers and manufacturers to support the commercialization JAN101, if we are successful in obtaining FDA approval. We believe that we can promote JAN101 to the patients suffering from PAD in a cost effective manner. We anticipate our commercial operation will include outside sales management, outside sales support, distribution support, and an internal marketing group. Additional requisite capabilities will include focused management of key accounts, such as managed-care organizations, group purchasing organizations, and government accounts. We intend selectively to partner with third parties with vast experience in the space, as we have been partnering for every aspect of development.
17
Competition
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are characterized by extensive research and development efforts, rapidly advancing technologies, intense competition, and a strong emphasis on proprietary products. We are currently focused on the development and commercialization of our asset pipeline of novel, non-opioid, and non-addictive therapies for PAD. The number of patients suffering from chronic PAD is large and growing. While we believe that JAN 101 and our Chief Scientific Officer’s development experience and scientific knowledge provide us with competitive advantages, we face potential competition from many different sources, including pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and specialty pharmaceutical companies that market or develop therapeutics to treat chronic pain. Academic research institutions, governmental agencies, as well as public and private institutions are also potential sources of competitive products and technologies. Our competitors may have significantly greater financial resources, robust drug pipelines, established presence in the market, and expertise in research and development, manufacturing, pre-clinical and clinical testing, obtaining regulatory approvals and reimbursement, and marketing approved products than we do. These competitors also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified clinical, regulatory, scientific, sales, marketing, and management personnel, establishing clinical trial sites and patient registration for clinical trials, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs. Smaller or early-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies. The key competitive factors affecting the success of JAN 101 (as well as other subsequent product candidates), if and when approved, is likely to be its efficacy, durability, safety, price, and the availability of reimbursement from government and other third-party payors.
Significant competition exists in the PAD pain field. Although we believe our approach to developing novel treatments for pain is unique from most other existing or investigational therapies, such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and opioids, we will need to compete with all currently available and future therapies within the indications where our development is focused. With respect to JAN101, the main classes of marketed products that are available for the treatment of PAD pain include NSAIDs and opioids. Furthermore, numerous monoclonal antibodies targeting nerve growth factor, or NGF inhibitors, are in clinical development, including two product candidates in Phase III.
There are a number of companies developing or marketing therapies for the treatment and management of pain that may compete with JAN 101, including many major pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
Intellectual Property
Our success depends in large part upon our ability to obtain and maintain proprietary protection for our products and technologies, and to operate without infringing or otherwise violating the proprietary rights of others. We endeavor to protect our products using a combination of intellectual property protections and available government regulatory and marketing exclusivities afforded to new medicines. For example, we endeavor to protect our products by, among other methods, filing United States and, potentially in the future, foreign, patent applications related to our proprietary technology, inventions, and improvements that are important to the development and implementation of our business. We also use other forms of protection, such as confidential information, trade secrets, and know-how, and trademarks to protect our intellectual property, particularly where we do not believe patent protection is appropriate or obtainable.
The proprietary nature of, and protection for, JAN 101, processes, and know-how are important to our business. Our policy is to pursue, maintain, and defend intellectual property rights, and to protect the technology, inventions, and improvements that are commercially important to our business.
Trade Secrets and Other Proprietary Information
In addition to patents, we rely on trade secrets and know-how to develop and maintain our competitive position. For example, we have developed methods for more efficient manufacture of sustained released sodium nitrite tablets. We seek to protect our proprietary information, in part, by confidentiality agreements and invention assignment agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors, contractors, and commercial partners.
18
License Agreement
On November 19, 2019, we entered into a Patent and Know How License Agreement (the “License Agreement”) with UAB Research Foundation (“UABRF”), TheraVasc, and the Board of Supervisors of Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, acting on behalf of LSU Health Shreveport, together with UABRF and TheraVasc, the “Licensors”). Under the License Agreement, the Licensors have agreed to grant to JanOne an exclusive, worldwide license, including the right to sublicense, to the Licensors’ patent rights and know-how related to the Licensors’ sustained release formulation of sodium nitrite. Under the License Agreement, we have agreed to pay a non-refundable upfront license fee and certain milestone payments upon the achievement of certain milestones of up to approximately $6.5 million and certain royalty payments and annual license maintenance fees. The License Agreement requires us to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize JAN101.
Soin Therapeutics
JanOne acquired Soin Therapeutics, a company focused on the development of a novel formulation of low-dose naltrexone (“LDN”) for the treatment of chronic regional pain syndrome (“CRPS”) in 2022. CRPS is a rare pain disorder, characterized by a complex set of symptoms, affecting approximately 200,000 patients annually in the US. There are currently no approved treatments for patients with CRPS. Prior to the acquisition, Soin Therapeutics received Orphan Drug Designation for the product, which provides a variety of incentives for developing the product in this indication.
JAN123
Generally
JAN123 is a novel formulation of 2.0 mg of LDN that results in a biphasic release of the product. The release properties of JAN123 provide for an immediate release of less than half the product with a slow, sustained release of the remaining product. Importantly, the rapid release of LDN has been reported to lead to vivid and lucid unpleasant dreams, which should be eliminated with the formulation of JAN123. Initially, a single tablet of JAN123 will be administered orally, once a day before sleep, with eventual titration up to two tablets (4 mg) before sleep.
Naltrexone
Naltrexone was first synthesized in 1965 and approved by the FDA for the oral treatment of opioid dependence in 1984, with the brand name Trexan. Later it was approved for the oral treatment of alcohol dependence in 1995, when the brand name was changed by DuPont to ReVia. A depot formulation for intramuscular injection was approved by the FDA under the brand name Vivitrol for alcohol dependence in 2006 and opioid dependence in 2010. Typical oral doses are 50 to 100 mg daily, with a once-monthly intramuscular formulation also available. At these doses, Naltrexone has been shown to function as a nonselective opioid antagonist with a high affinity for µ opioid receptors, which decreases addiction cravings (Schumacher, Basbaum et al. 2017, Opioid Agonists & Antagonists. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 14e. B. G. Katzung. New York, NY, McGraw-Hill Education). However, there is a risk that patients who are non-compliant with oral naltrexone may experience opioid intoxication simply by skipping doses of naltrexone. Oral bioavailability is also variable from patient to patient, largely due to first-pass metabolism. Thus, naltrexone is pharmacologically effective, but may be ineffective in a real world setting without counseling and strong patient support (Minozzi, 2011, Oral naltrexone maintenance treatment for opioid dependence. Chchrane Database Syst Rev(4), CD001333). There are also multiple generic Naltrexone tablets available on the market for oral administration.
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN)
Compared to the standard dose, LDN is defined as a daily dose of Naltrexone of 1 to 5 mg, which is 10- to 100-fold lower than the dose used to manage substance use disorders (LDN Research Trust , Toljan and Vrooman 2018, Low-Dose Naltrexone (LDN)-Review of Therapeutic Utilization. Med Sci (Basel) 6(4)). Off-label uses of Naltrexone at lower doses have been explored based on a different mechanism of action for the treatment of inflammatory, rheumatologic, and neurologic conditions. These include multiple sclerosis, fibromyalgia, Crohn disease, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), and more recently, CRPS. At the low doses used for these conditions, Naltrexone is thought to act as an immune modulator. Some speculate that this effect is related to reduced neuroinflammation in the case of disorders like CFS (Cant, Dalgleish et al. 2017, Naltrexone Inhibits IL-6 and TNFalpha Production in Human Immune Cell Subsets following Stimulation with Ligands for Intracellular Toll-Like Receptors. Front Immunol 8: 809).
19
Evidence suggests that, at low doses, Naltrexone antagonizes TLR4 on activated glial cells without the previously mentioned function as a mu-opioid receptor antagonist (Chopra and Cooper 2013, Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) using low dose naltrexone LDN). J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8(3): 470-476.). TLR4 has been shown to be a key mediator of microglial activation, which has been identified as a causal mechanism of neuropathic pain in CRPS. Microglial activation is associated with the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and prostaglandins, which amplify the inflammatory response (Carniglia, Ramírez et al. 2017, Neuropeptides and Microglial Activation in Inflammation, Pain, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mediators of Inflammation 2017: 5048616). Thus, LDN presents a promising therapeutic avenue for the treatment of CRPS, a condition in which TLR4 upregulation is a primary pathway, through attenuation of glial activation and direct targeting of TLR4 activity (Del Valle, Schwartzman et al. 2009, Spinal cord histopathological alterations in a patient with longstanding complex regional pain syndrome. Brain Behav Immun 23(1): 85-91.). By downregulating the inflammatory cytokine release, LDN should be beneficial for CRPS patients.
CRPS patients suffer from severe debilitating pain, and even light touch or benign stimulation elicits extreme amounts of pain. Microglial cells and glial cells oftentimes are involved in this pain-signaling pathway. By reducing glial cell activation, Low-dose Naltrexone can treat this pain syndrome. Another potential mechanism of action of LDN treatment on pain is a paradoxical upregulation of opioid signaling. It is noted that when taken at bedtime, the short-acting low-dose Naltrexone binds to receptors, which leads to a brief blockade of opioid receptors between 2 and 4 a.m. This blockade is believed to upregulate vital life elements of the body and cause an increase in endorphin and enkephalin production. This increase in endorphins and enkephalins will likely cause a decrease in pain that the patient experiences overall. Therefore, LDN leads to transient opioid receptor blockade, which triggers a positive feedback mechanism that increases the production of endogenous opioids (endogenous endorphins and enkephalins) and opioid signaling (Ludwig, Zagon et al. 2017, Serum [Met(5)]-enkephalin levels are reduced in multiple sclerosis and restored by low-dose naltrexone. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 242(15): 1524-1533; Toljan and Vrooman 2018, Low-Dose Naltrexone (LDN)-Review of Therapeutic Utilization. Med Sci (Basel) 6(4)). Together, these mechanisms may work to alleviate pain associated with CRPS.
Interestingly, low-dose Naltrexone also has effects on the peripheral nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system, it was found that low-dose Naltrexone can modulate T and B lymphocyte production. And it was noticed that low-dose Naltrexone could reduce interleukin 6, interleukin 12, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the periphery regarding peripheral nervous systems. CRPS patients often have an increase in inflammatory cytokines and may often note an increase in interleukin 6, 12, and tumor necrosis factor alpha. By reducing these inflammatory cytokines back to a normal state, it is predicted that low-dose Naltrexone could treat the actual disease state of CRPS.
In summary, low-dose Naltrexone has a very specific mechanism of action that will distinctly treat CRPS through inhibition of inflammatory cytokines, glial cell activation, neuroinflammation, and increase of endogenous enkephalins and endorphins. In other words, low-dose Naltrexone is not just treating the symptoms with this medication but also treating the underlying disease state and process specific to CRPS.
Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
CRPS, also termed reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD), is a chronic, orphan neurologic condition that typically affects the extremities after trauma or nerve injury, and can cause severe pain. As the most common and prominent symptom of CRPS, the pain is often deep inside the limbs with a burning, stinging, or tearing sensation. Sensory changes are also common and may include increased sensitivity to painful stimuli, feeling pain from stimuli that are usually non-painful, and in some instances, sensory loss (e.g., numbness). In addition to pain, patients commonly experience an affected extremity that is warm, red, and swollen, at least initially. As CRPS progresses, it becomes refractory to sympathetic nerve blocks, conventional analgesics, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants.
CRPS is a rare neurologic disease. It is a painful progressive condition and is listed in the rare disease database of the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). CRPS is subdivided into two categories: type I and type II CRPS. In CRPS type I, there are no nerve injuries or lesions identified. CRPS type I is also known as "reflex sympathetic dystrophy," and it comprises about 90 percent of all cases of CRPS. CRPS type II (causalgia), on the other hand, is diagnosed when there is evidence of nerve damage. As described in the NORD, it was found that CRPS type I developed in 5.46 persons out of every 100,000 per year and the incidence rate of CRPS type 2 was 0.82 persons out of every 100,000 per year, giving rise to a combined incidence rate for both CRPS types I and II of 6.28 per 100000
20
person-years (Sandroni, Benrud-Larson et al. 2003, Complex regional pain syndrome type I: incidence and prevalence in Olmsted county, a population-based study. Pain 103(1-2): 199-207; Goh, Chidambaram et al. 2017, Complex regional pain syndrome: a recent update. Burns Trauma 5: 2.).
The underlying cause of CRPS is not well understood. In most cases, it occurs after an illness or injury that did not directly damage the nerves in the affected area (Type I). In some cases, it occurs after a specific nerve injury (Type II). The exact trigger of CRPS after an injury is not known, but it may be due to abnormal interactions between the central and peripheral nervous systems and/or inappropriate inflammatory responses. There are multiple factors that may contribute to CRPS development, including immobilization, alterations to the nervous system of the body, and inflammation. Genetic factors and psychological factors, such as anxiety, depression, and anger, may also contribute to the symptoms of CRPS. However, there is no evidence that CRPS is a disease that can be caused by genetic factors alone, and the role of psychological factors in CRPS development remains unproven.
CRPS is treated by approaching it from different areas: physical therapy (PT), occupational therapy (OT), medications for pain management, neuromodulation through implantable devices, and/or nerve blocks targeting the sympathetic chain. Neridronate and zoledronate D,L-lysine monohydrate (ZLM) has been designated as an orphan drugs for the treatment of CRPS in 2013 and 2015, respectively. However, neither of them has been approved. Thus, there is no current FDA-approved drug for CRPS.
Clinical Studies of LDN on CRPS
LDN has been widely used for chronic pain and inflammatory condition and has been shown to alleviate symptoms of pain in patients with chronic pain. A number of case studies have also reported positive effects for LDN in the treatment of CRPS. Chopra et al. reported 2 patient case studies with CRPS who experienced significantly less pain with 4.5 mg daily LDN treatment (Chopra and Cooper 2013, Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) using low dose naltrexone (LDN). J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8(3): 470-476). The remission of pain and dystonic spasms in Case 1, as well a remission of all CRPS symptoms (including fixed dystonia) in Case 2, provide evidence that a multi-modal interventional approach, which includes low-dose Naltrexone (a known glial attenuator), should be considered as a treatment option for the treatment of CRPS patients, particularly those patients with dystonic movement disorders. In another CRPS case study, Sturn and Collin found alleviation of pain symptoms as early as 2 days after beginning LDN therapy, with significantly less pain at 4 weeks (Sturn and Collin 2016, Low-Dose Naltrexone: A New Therapy Option for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I Patients. Int J Pharm Compd 20(3): 197-201). Weinstock et al reported alleviation of pain symptoms within one month of LDN treatment, with complete remission of CRPS leg symptoms by 16 months (Weinstock, Myers et al. 2016, Identification and Treatment of New Inflammatory Triggers for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. A A Case Rep 6(9): 272-276). In a recent case study, an CRPS patient was able to discontinue gabapentin and amitriptyline via the use of LDN, while simultaneously achieving superior pain relied (Soin, 2021, Management of pediatric complex regional pain syndrome with low-dose naltrexone. Pain Medicine Case Reports, 5(3), 109-113). LDN has been reported to have benefits related to other symptoms of chronic pain syndromes as well, including dystonic spasms, CRPS flares, energy, sleep disturbances, and mood.
Systematic literature review of LDN use showed that he most commonly reported AEs with LDN use were dizziness, vomiting, nausea, and vivid dreams (Soin et al. 2021, Low-Dose Naltrexone Use for Patients with Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Literature Review. Pain Physician 24(4): E393-E406.). Other reported AEs included headaches, abdominal pain, gastrointestinal issues, peripheral edema, restlessness, falls, somnolence, irritability, hematological abnormalities, urinary infection, difficulty concentrating, anxiety, sleepiness, hot flashes/sweating, tachycardia, depression, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, tinnitus, heartburn, dry mouth, and joint pain. Another systematic review also evaluated occurrence of adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs) with LDN use and found that only mild AEs reported among the included studies (89 studies), including nausea, vomiting, and dizziness (Bolton, Hodkinson et al. 2019, Serious adverse events reported in placebo randomized controlled trials of oral naltrexone: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 17(1): 10). Although 119 patients reported at least one SAE in the naltrexone study arm, meta-analysis found no difference between occurrence of SAEs in naltrexone and placebo groups. Furthermore, secondary analysis found only 6 AEs that were statistically significant: decreased appetite, dizziness, nausea, sleepiness, sweating, and vomiting.
Efficacy of low-dose naltrexone treatment on CRPS
21
Author (year) |
Symptoms |
Symptoms alleviated |
Time to alleviation of symptoms |
Dose |
AEs and SAEs |
Chopra et al (2013) |
swelling, allodynia, color change, temperature change, some weakness, blisters, skin ulceration, dystonic spasms, dysesthesia |
Dystonic spasms, CRPS flares, energy, pain tolerance, sleep disturbances, pain, mood |
< 2 months |
4.5 mg/day |
None |
Sturn et al (2016) |
Pain |
Pain |
2 days |
1.5 mg |
None |
Weinstock et al (2016) |
Severe leg pain, episodic pain in arms and nose, asymmetric and shiny skin with fluctuating temperature changes, color change, edema, IBS, atypical chest pain and fatigue, edema, blue discoloration, tenderness, joint hypermobility with EDS diagnosis |
Leg and bowel symptoms; all CRPS pain, bowel symptoms, and fatigue |
< 1 month |
4.5 mg/day |
None |
Orphan Drug Designation
An orphan disease is a rare disease affecting less than 200,000 people in the US. It is often a serious or fatal condition for which there are no effective therapies. In 1983, the Orphan Drug Act was passed to incentivize companies to develop drugs for patients with rare diseases. Orphan drug designation provide incentives to companies, including:
In addition, given the small number of patients with a disease and the severity of the disease, approvals are often granted with fewer and smaller trials, saving costs and time. JAN123 was granted Orphan Status for the treatment of CRPS.
Clinical Development Plan
LDN can be rapidly developed in the US via the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway. This pathway is used for candidates which contain drugs that are already approved but come in a dosage form or delivery system which is different than the original, approved product. In this case, JAN123 fits these criteria perfectly. LDN has the added benefit of being developed at a much lower dose (< 5 milligrams) compared to approved naltrexone products, which are 50 milligrams per tablet. Therefore, it is likely that product development will consist of the following general steps:
A protocol synopsis of the development plan is presented below:
Title of study |
Phase I: The Pharmacokinetincs of LDN in the fed and fasted state of a Single Oral Dose of LDN, 4 mg Phase III: Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial of Low Dose Naltrexone to Treat Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) |
22
Clinical Phase |
Phase I: The Pharmacokinetincs of LDN in the fed and fasted state Phase III: Registration/Efficacy Study to hopefully facilitate an NDA application for the use of low dose naltrexone to treat CRPS |
Objectives: |
Phase I: To determine pharmacokinetics of single oral low dose naltrexone in healthy participants in fasting and fed state Phase3: The primary objective is to assess the efficacy of low-dose naltrexone in treating complex regional pain syndrome symptoms (CRPS). We plan to conduct a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to treat CRPS using low-dose naltrexone. For Efficacy: 1- Assess daily NRS (numerical pain scale 0 – 10) scores through the 3-month study 2- Study the possible changes or improvement in the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) over the three-month study For Safety: We will also monitor safety labs on enrollment and termination of the study. However, we would like to point out that this drug has been available and FDA approved at much higher doses (50 – 150mg or higher) orally with a long standing proven safety track record. The drug has been available with multiple different embodiments, route of administration and at much higher doses for quite a long time and the safety of the drug has already been extensively established and published. |
Investigational product |
JAN123 |
Study Design |
Phase 1: Single-center, dual arm, cross-over, open-label study Phase 3: Study Description We plan to conduct a randomized, double blind placebo controlled trial to treat Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. The study duration will be three months long. Patients in the treatment group will receive a single tablet for the first month of a 2mg dose of Naltrexone. Then after 1 month, the patient will take 2 tablets for a total of 4mg for months 2 and 3. Study conclusion will be after 3 months. Patients in the placebo group will take a single tablet for 1 month followed by 2 tablets for month 2 and 3. A total number of 200 patients with a 1:1 randomization will used. Since CRPS is an orphan disease we will likely have to use a total of 25 clinical sites or more to be able to adequately recruit the study. Safety labs will be completed prior to first dose and upon study completion. For clinical efficacy, we will be assessing daily NRS (1-10) pain scores, a brief pain inventory (BPI) at enrollment and at months 1, 2, and 3 (study completion) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) at enrollment and at months 1, 2, and 3 (study completion). Statistically significant improvement in pain scores or any scales in the BPI or ODI are desired outcomes. |
Treatment Regimen and Route of Administration |
Study Drugs are as follows: Phase I: Single Oral dose of JAN123, 4 mg given on separate days with and without food separated by a washout period of no less than 7 days Phase III: Patients will then be doses with either the low dose naltrexone or placebo for three months. Initially for the first month patients will take 1 tablet at bedtime (typically in the evenings) for the first month and then increase to 2 tablets for month 2 and 3. Specifically the Naltrexone will be 2mg tablets, such that for the first month with the 1 tablet per day the patient will be on 2mg doses and subsequently increase to 2 tablets in the evening for a total of 4mg. |
Duration of treatment: |
Phase I: One day for each dose. Two doses of 2 mg each, in total, separated by a washout period of no less than 7 days. Phase III: This will be a 3 month trial or approximately 90 days. Upon enrollment, patients will be on either low dose naltrexone or placebo for 90 days. |
23
|
Participant duration is expected to be 90 days, and at the conclusion of the study (approximately day 90) patients will come in for a final site visit to complete remaining surveys and within 7 days of completion the patients will obtain final safety labs which are anticipated to be a complete blood count and a comprehensive metabolic panel. Since Naltrexone is non opioid based and does not have withdrawal issues, patients can immediately discontinue the therapy without concerns. As referenced earlier, the safety of Naltrexone orally is already well established and our tested doses are low. |
Number of Centers |
Phase 1: Single Center Clinical Trial Phase 3: Multicenter Clinical Trial Likely 25 total sites. Keeping in mind this is an Orphan Disease state and recruitment may be quite difficult- we feel the need to have 25 clinical sites to enroll 200 patients Clinical sites will be likely Pain Management Centers, both academic and private practice facilities that have access to patients who suffer from CRPS and also include local PIs who have the skill set and ability to properly diagnose CRPS. Local or regional clinical trial coordinators will be assigned to each site as well. Enrolling participants are those who meet the diagnosis criteria of CRPS. Typically CRPS is diagnosed using the Budapest Criteria. Age range of 18 - 65 for enrollment, negative pregnancy test, and stable therapy for 3 months. |
Subjects: |
Phase I: Adult male and female healthy subjects, 18-65 years of age, satisfying all inclusion and exclusion criteria. Phase III: Patients diagnosed with CRPS (Complex Regional Pain Syndrome), Adult male and female patients, 18-65 years of age |
Number of Subjects |
Phase I: 10 patients Phase III: 200 patients |
Endpoints |
Phase1: Primary Outcome Measure: PK profile for low dose naltrexone (Time Frame: Day 1: predose and at multiple time points after low dose naltrexone administration) • Cmax (Maximum observed plasma concentration) • Tmax (Time to reach maximum plasma concentration) • AUC0-t (Area under the plasma concentration-time curve from 0 hour to the time of the last quantifiable concentration) • AUC0-inf (Area under the plasma concentration-time curve from 0 hour extrapolated to infinity) • CL/F (Oral clearance)
Phase 3: Primary Outcome Measure: Improvement in NRS pain scores over a 3 month time period. Secondary Outcome Measure: Improvement in Brief Pain Inventory and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) or other verified pain scales. End of Study will occur upon completion of the 90 day trial of the low dose naltrexone or placebo. It is expected that patients will complete all required surveys and testing requirements of the study. Early termination is also a possible way to end the study due to issues such as side effects, adverse events or patient desire to withdraw from the study, among other reasons. |
Safety Assessments |
Standard clinical evaluation and objective measures will be employed to monitor and assess safety during the conduct of the trial. Furthermore, the results of safety assessments will be used during the trial to monitor and protect the safety of enrolled subjects. |
24
|
Strict subject and study stopping criteria will be implemented to protect the subject's well-being. |
Intellectual Property
The composition of Naltrexone is off-patent and generic versions of the drug are available at 50 mg doses. LDN has been routinely compounded in compounding pharmacies and used clinically off-label. However, the 4.5 mg compounded tablets are associated with sleep disturbances, manifested in vivid and lucid unpleasant dreams. For these reasons, JAN 123 was developed as a biphasic release, orally available tablet to reduce the likelihood of unpleasant dreams. A provisional patent was filed in December 2020 and converted to a PCT application in November 2021 (Pub. No. US 2022/0202807 A1). The claims in this application cover the use of the biphasic LDN formulation for treatment of patients with chronic pain. In addition, claims are made to the titration of the LDN for treating chronic pain. While there is no guarantee that these or future pending claims will issue, the Orphan Drug Designation does provide 7 years of market exclusivity after drug approval.
Trade Secrets and Other Proprietary Information
In addition to patents, we rely on trade secrets and know-how to develop and maintain our competitive position. For example, we have developed methods for more efficient manufacture of the biphasic LDN. We seek to protect our proprietary information, in part, by confidentiality agreements and invention assignment agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors, contractors, and commercial partners.
Purchase Agreement
On December 28, 2022, we entered into a Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with Soin Therapeutics, LLC. Under the Purchase Agreement, JanOne acquired Soin Therapeutics and its LDN product, now known as JAN123. This all stock transaction has a value of $13M, with up to an additional $17M depending on revenues generated by the product, for a total value of up to $30M. The transaction includes restrictions on the maximum number of shares of preferred stock and common stock that can be issued to or transferred by Soin Therapeutics at any given time.
Our Team
Tony Giordano, Ph.D., our Chief Scientific Officer, joined the Company in December 2019 from the Cleveland Clinic, the No.2 rated hospital in the country, where he served as Senior Director of Special Projects in the Business Development group. Dr. Giordano has extensive experience in commercialization and drug development, having served as Vice President or President of seven different biotechnology companies he co-founded, including companies developing platform technologies, a cancer vaccine, and Alzheimer’s Disease and cardiovascular therapies. He has managed numerous clinical trials and the launch of a medical food product. Dr. Giordano has also served as an Associate Professor and Assistant Dean of Research and Business Development at LSU Health Sciences Center in Shreveport, Louisiana (“LSU Health Shreveport”), at which he led the licensing efforts at the campus and at Abbott Labs, where, in addition to serving as a Senior Research Scientist, he was involved in technology assessment activities. Dr. Giordano has a Ph.D. focused in Molecular Genetics from The Ohio State University and completed Fellowships at the NIH NCI-Designated Cancer Centers and the NIH National Institute of Aging.
25
Dr. Amol Soin, our Chief Medical Officer, joined the Company in January 2020. Dr. Soin is considered one of the nation’s top pain experts and is the Founder and Chairman of the Ohio Pain Clinic. Dr. Soin brings significant expertise for treating neuropathic and chronic pain and extensive research experience for non-opioid, nonaddictive pain solutions to the JanOne management team. In his role as Chief Medical Officer, Dr. Soin will guide JanOne’s drug development activities, manage clinical research, set patient safety standards, and ensure regulatory compliance. In addition, Dr. Soin will play an integral role in establishing partnerships and drug candidate selection as we expand our pipeline. Dr. Soin received his undergraduate degree from University of Akron, his MBA from University of Tennessee, his MD from Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine, and his master’s in science from Brown University and he has also studied at Dartmouth College. He is board certified in anesthesiology and pain medicine and a fellow of interventional pain management at the World Institute of Pain, and served as a pain management fellow at the Cleveland Clinic, the oldest and largest academic pain management department in the United States. The founder and chairman of the Ohio Pain Clinic, Dr. Soin has also held several prestigious positions, including President of the Ohio Society of Interventional Pain Physicians, President of the American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians Foundation, President of the Society of Interventional Pain Management Surgery Centers, and President – elect of TriState Pain Society. He was appointed by Governor Kasich to the Ohio Medical Board in 2012 to two 5-year terms and has served as the Ohio Medical Board’s president, where he was instrumental in passing statewide rules and guidelines to help the opioid crisis.
In November 2019, we formed a Scientific Board of Advisors (the “SBA”) and the following doctors and scientists currently are members of our SBA:
Chris Kevil, Ph.D., Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board – Dr. Kevil, an internationally known expert in vascular pathophysiology, PAD, and nitric oxide biology, discovered the role of sodium nitrite in promoting angiogenesis that led to the development of TV1001, now known as JAN101. Dr. Kevil earned his Ph.D. degree from LSU Health Shreveport in Molecular and Cellular Physiology, followed by a fellowship at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) with an emphasis on redox pathophysiology. Returning to LSU Health Shreveport in the Department of Pathology, he established cutting edge research programs regarding redox biology regulation of peripheral vascular diseases. This led to ground-breaking insights on how glutathione, nitrite/nitric oxide, and hydrogen sulfide regulate vascular health during ischemia.
Edgar Ross, MD, Dr. Ross is the current Director of the Pain Management Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of anesthesia at Harvard Medical School. Dr. Ross is recognized as Castle Connolly’s America’s top doctors for the fifth year in a row. In addition to serving as chairman of Pfizer’s partnership on pain, Dr. Ross also has served as a member of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Opioid Prescribing Policy Committee.
John Cooke, MD, Ph.D. – Dr. Cooke is the Chair of the Department of Cardiovascular Sciences at the Houston Methodist Research Institute, Director of the Center for Cardiovascular Regeneration, and Medical Director of the RNA Therapeutics Program in the Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart & Vascular Center in Houston, Texas. He trained in cardiovascular medicine and obtained a Ph.D. in physiology at the Mayo Clinic. He was recruited to Harvard Medical School as an assistant professor of medicine. In 1990, he was recruited to Stanford University to spearhead its program in vascular biology and medicine, and was appointed professor in the Division of Cardiovascular Medicine at Stanford University School of Medicine, and associate director of the Stanford Cardiovascular Institute until his recruitment to Houston Methodist in 2013. Dr. Cooke has published over 500 research papers, position papers, reviews, book chapters, and patents in the arena of vascular medicine and biology with over 30,000 citations. He has served on national and international committees that deal with cardiovascular diseases, including the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, Society for Vascular Medicine, and the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. He has served as president of the Society for Vascular Medicine, as a director of the American Board of Vascular Medicine, and as an associate editor of Vascular Medicine.
Joshua Beckman, MD – Dr. Beckman founded and is director of the Section of Vascular Medicine in the Division of Cardiovascular and is Professor of Medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center. The overriding theme linking all of his career activities is vascular function in health and disease. Dr. Beckman’s primary research focuses on the mechanisms by which diabetes mellitus impairs vascular function. Secondary investigations involve studying the effect on endothelial function of non-diabetes-related insulin resistance, androgen deprivation, and vascular function in venous bypass grafts. Dr. Beckman has been involved in numerous clinical studies and has published over 300 research papers with over 30,000 citations. In addition to a number of other journals, Dr. Beckman serves in editorial roles at Vascular Medicine and Circulation, two of the premier journals in the cardiovascular space.
26
Nicolas Goeders, Ph.D. – Dr. Goeders is a Professor and Head of the Department of Pharmacology, Toxicology and Neuroscience at LSU Health Shreveport. He has conducted addiction research for the past 30 years and is regarded as one of the world’s leaders on the role for stress in substance abuse disorder. His work has helped to determine the mechanisms responsible for how stress contributes to relapse to drug use. He has published over 100 manuscripts, has written 15 book chapters, and was issued five patents, one of which is a drug currently in clinical development. Dr. Goeders also serves as the Executive Director of the Louisiana Addiction Research Center.
Commercial Operations
We currently do not have any marketing and sales organization. We have retained global rights to JAN 101, and, if it or one of our potential subsequent product candidates is approved by the FDA to market in the United States, we expect that our sales force will be supported by sales management, internal sales support, an outside marketing group, and distribution support. We intend to invest in our commercial capabilities prudently by focusing our marketing efforts on the physician subspecialties that treat patients with PAD. These physicians include, but are not limited to, pain management specialists, rheumatologist, surgeons, and sports medicine physicians. We will also evaluate licensing and partnering with third parties to help us reach other sales channels and geographic markets inside and outside of the United States.
Government Regulation
The FDA and comparable regulatory authorities in state and local jurisdictions and in other countries impose substantial and burdensome requirements upon companies involved in the clinical development, manufacture, marketing, and distribution of drugs, such as those we are developing. These agencies, and other federal, state, and local entities regulate, among other things, the research and development, testing, manufacture, quality control, safety, effectiveness, labeling, storage, record keeping, approval, advertising and promotion, distribution, post-approval monitoring and reporting, sampling, and export and import of product candidates.
U.S. Government Regulation of Drug Products
In the United States, the FDA regulates drugs under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the “FDCA”) and its implementing regulations. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals and the subsequent compliance with applicable federal, state, local, and foreign statutes and regulations requires the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources. Failure to comply with the applicable United States requirements at any time during the product development process, the approval process, or thereafter, may subject an applicant to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as the FDA’s refusal to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, imposition of a clinical hold, issuance of warning letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, refusals of government contracts, restitution, disgorgement, or civil or criminal penalties.
The process required by the FDA before a drug may be marketed in the United States generally involves the following:
27
Pre-clinical Studies
Pre-clinical studies include laboratory evaluation of product chemistry, toxicity, and formulation, as well as animal studies to assess potential safety and efficacy. An IND sponsor must submit the results of the pre-clinical tests, together with manufacturing information, analytical data, and any available clinical data or literature, among other things, to the FDA as part of an IND. Some pre-clinical testing may continue even after the IND is submitted. An IND automatically becomes effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless before that time the FDA raises concerns or questions related to one or more proposed clinical trials and places the clinical trial on a clinical hold. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before the clinical trial can begin. As a result, submission of an IND may not result in the FDA allowing clinical trials to commence. Clinical holds also may be imposed by the FDA at any time before or during clinical trials, due to safety concerns about on-going or proposed clinical trials, or non-compliance with specific FDA requirements, and the trials may not begin or continue until the FDA notifies the sponsor that the hold has been lifted. Through the 505(b)2 regulatory path, the FDA allows a sponsor to rely on well documented, published studies to support the clinical development of the product. The FDA has indicated that it will accept published data in support of the Company’s development program for JAN101 but prior to filing an NDA would require the Company to complete developmental and reproductive toxicology studies.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational new drug to human subjects under the supervision of qualified investigators in accordance with GCP requirements, which include the requirement that all research subjects provide their informed consent in writing for their participation in any clinical trial. Clinical trials are conducted under protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the trial, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety, and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. A protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. In addition, an IRB at each institution participating in the clinical trial must review and approve the plan for any clinical trial before it commences at that institution. Information about certain clinical trials must be submitted within specific timeframes to the NIH for public dissemination on their www.clinicaltrials.gov website. The information contained in, or accessible through, this website does not constitute a part of this Annual Report. We have included this website address solely as an inactive, textual reference.
Human clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases, which may overlap or be combined:
28
Post-approval trials, sometimes referred to as Phase IV clinical trials, may be conducted after initial marketing approval. These trials are used to gain additional experience from the treatment of patients in the intended therapeutic indication. In certain instances, the FDA may mandate the performance of Phase IV clinical trials as a condition of approval of an NDA.
The FDA or the sponsor may suspend a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution if the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the drug has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients. In addition, some clinical trials are overseen by an independent group of qualified experts organized by the sponsor, known as a data safety monitoring board or committee. Depending on its charter, this group may determine whether a trial may move forward at designated check points based on access to certain data from the trial.
During the development of a new drug, sponsors are given opportunities to meet with the FDA at certain points. These points may be prior to submission of an IND, at the end of Phase II, and before an NDA is submitted. Meetings at other times may be requested. These meetings can provide an opportunity for the sponsor to share information about the data gathered to date, for the FDA to provide advice, and for the sponsor and the FDA to reach agreement on the next phase of development. Sponsors typically use the meetings at the end of the Phase II clinical trial to discuss Phase II clinical results and present plans for the pivotal Phase III clinical trials that they believe will support approval of the new drug. JanOne submitted briefing materials in 2021 describing the previous research and development activities and planned clinical trials. The Company is now working to implement suggestions by the FDA to be ready to submit a protocol amendment in late 2022.
Concurrently with clinical trials, companies usually complete additional animal studies and must also develop additional information about the chemistry and physical characteristics of the drug and finalize a process for manufacturing the product in commercial quantities in accordance with cGMP requirements. The manufacturing process must be capable of consistently producing quality batches of product candidates and, among other things, the manufacturer must develop methods for testing the identity, strength, quality, and purity of the final drug. In addition, appropriate packaging must be selected and tested and stability studies must be conducted to demonstrate that the product candidate does not undergo unacceptable deterioration over its shelf life.
While the IND is active and before approval, progress reports summarizing the results of the clinical trials and non-clinical studies performed since the last progress report must be submitted at least annually to the FDA, and written IND safety reports must be submitted to the FDA and investigators for serious and unexpected suspected adverse events, findings from other studies suggesting a significant risk to humans exposed to the same or similar drugs, findings from animal or in vitro testing suggesting a significant risk to humans, and any clinically important increased incidence of a serious suspected adverse reaction compared to that listed in the protocol or investigator brochure.
United States Review and Approval Process
The results of product development, pre-clinical, and other non-clinical studies and clinical trials, along with descriptions of the manufacturing process, analytical tests conducted on the chemistry of the drug, proposed labeling, and other relevant information are submitted to the FDA as part of an NDA requesting approval to market the product. The submission of an NDA is subject to the payment of substantial user fees; a waiver of such fees may be obtained under certain limited circumstances. The FDA reviews an NDA to determine, among other things, whether a product is safe and effective for its intended use and whether its manufacturing is cGMP-compliant to assure and preserve the product’s identity, strength, quality and purity. Under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (the “PDUFA”), guidelines that are currently in effect, the FDA has a goal of 10 months from the date of “filing” of a standard NDA for a new molecular entity to review and act on the submission. This review typically takes 12 months from the date the NDA is submitted to FDA because the FDA has approximately two months to make a “filing” decision after the application is submitted. The FDA conducts a preliminary review of all NDAs within the first 60 days after submission, before accepting them for filing, to determine whether they are sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. The FDA may request additional information rather than accept an NDA for filing. In this event, the NDA must be resubmitted with the additional information. The resubmitted application also is subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing.
29
The FDA may refer an application for a novel drug to an advisory committee. An advisory committee is a panel of independent experts, including clinicians and other scientific experts, that reviews, evaluates, and provides a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions. The FDA is not bound by the recommendations of an advisory committee; but, it considers such recommendations carefully when making decisions.
Before approving an NDA, the FDA will inspect the facility or facilities where the product is manufactured. The FDA will not approve an application unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications. Additionally, before approving an NDA, the FDA may inspect one or more clinical trial sites to assure compliance with GCP requirements.
After the FDA evaluates an NDA, it will issue an approval letter or a Complete Response Letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the drug with prescribing information for specific indications. A Complete Response Letter indicates that the review cycle of the application is complete and the application will not be approved in its present form. A Complete Response Letter usually describes the specific deficiencies in the NDA identified by the FDA and may require additional clinical data, such as an additional Phase III trial or other significant and time-consuming requirements related to clinical trials, non-clinical studies, or manufacturing. If a Complete Response Letter is issued, the sponsor must resubmit the NDA that addresses all of the deficiencies identified in the letter, or withdraw the application. Even if such additional data and information are submitted, the FDA may decide that the NDA does not satisfy the criteria for approval.
If a product receives regulatory approval, the approval may be significantly limited to specific diseases and dosages or the indications for use may otherwise be limited, which could restrict the commercial value of the product. In addition, the FDA may require a sponsor to conduct Phase IV clinical testing, which involves clinical trials designed to assess a drug’s safety and effectiveness further after NDA approval, and may require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the safety of approved products that already have been commercialized. The FDA may also place other conditions on approval, including the requirement for REMS, to assure the safe use of the drug. If the FDA concludes a REMS is needed, the sponsor of the NDA must submit a proposed REMS. The FDA will not approve the NDA without an approved REMS, if required. A REMS could include medication guides, physician communication plans, or elements to assure safe use, such as restricted distribution methods, patient registries, and other risk minimization tools. Any of these limitations on approval or marketing could restrict the commercial promotion, distribution, prescription, or dispensing of products. Marketing approval may be withdrawn for non-compliance with regulatory requirements or if problems occur following initial marketing.
The Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act (the “FDASIA”) made permanent the Pediatric Research Equity Act (the “PREA”), which requires a sponsor to conduct pediatric clinical trials for most drugs, for a new active ingredient, new indication, new dosage form, new dosing regimen, or new route of administration. Under PREA, original NDAs and supplements must contain a pediatric assessment unless the sponsor has received a deferral or waiver. The required assessment must evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the product for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations and support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. The sponsor or the FDA may request a deferral of pediatric clinical trials for some or all of the pediatric subpopulations. A deferral may be granted for several reasons, including a finding that the drug is ready for approval for use in adults before pediatric clinical trials are complete or that additional safety or effectiveness data needs to be collected before the pediatric clinical trials begin. The FDA must send a non-compliance letter to any sponsor that fails to submit the required assessment, keep a deferral current or fails to submit a request for approval of a pediatric formulation.
Special FDA Expedited Review and Approval Programs
The FDA has various programs, including Fast Track Designation, accelerated approval, priority review, and breakthrough therapy designation, which are intended to expedite or simplify the process for the development and FDA review of drugs that are intended for the treatment of serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions and demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs. The purpose of these programs is to provide important new drugs to patients earlier than under standard FDA review procedures.
30
To be eligible for a Fast Track Designation, the FDA must determine, based on the request of a sponsor, that a product is intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and demonstrates the potential to address an unmet medical need. The FDA will determine that a product will fill an unmet medical need if it will provide a therapy where none exists or provide a therapy that may be potentially superior to existing therapy based on efficacy or safety factors. The FDA may review sections of the NDA for a fast track product on a rolling basis before the complete application is submitted, if the sponsor provides a schedule for the submission of the sections of the NDA, the FDA agrees to accept sections of the NDA and determines that the schedule is acceptable, and the sponsor pays any required user fees upon submission of the first section of the NDA.
The FDA may give a priority review designation to drugs that offer major advances in treatment, or provide a treatment where no adequate therapy exists. A priority review means that the goal for the FDA to review an application is six months, rather than the standard review of 10 months under current PDUFA guidelines. Under the new PDUFA agreement, these six- and 10-month review periods are measured from the “filing” date, rather than the receipt date for NDAs for new molecular entities, which typically adds approximately two months to the timeline for review and decision from the date of submission. Most products that are eligible for Fast Track Designation are also likely to be considered appropriate to receive a priority review.
In addition, products studied for their safety and effectiveness in treating serious or life-threatening illnesses and that provide meaningful therapeutic benefit over existing treatments may be eligible for accelerated approval and may be approved on the basis of adequate and well-controlled clinical trials that establish that the drug product has an effect (i) on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit or (ii) on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, including taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. As a condition of approval, the FDA may require a sponsor of a drug receiving accelerated approval to perform post-marketing studies to verify and describe the predicted effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical endpoint, and the drug may be subject to accelerated withdrawal procedures.
Moreover, under the provisions of the FDASIA, a sponsor can request designation of a product candidate as a “breakthrough therapy.” A breakthrough therapy is defined as a drug that is intended, alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. Drugs designated as breakthrough therapies are also eligible for accelerated approval. The FDA must take certain actions, such as holding timely meetings and providing advice, intended to expedite the development and review of an application for approval of a breakthrough therapy.
Even if a product qualifies for one or more of these programs, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or decide that the time period for FDA review or approval will not be shortened. We may explore some of these opportunities for our initial (or subsequent) product candidates, as appropriate.
Post-Approval Requirements
Drugs manufactured or distributed pursuant to FDA approvals are subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA, including, among other things, requirements relating to recordkeeping, periodic reporting, product sampling and distribution, advertising and promotion and reporting of adverse experiences with the product. After approval, most changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications or other labeling claims are subject to prior FDA review and approval. There also are continuing, annual user program fee requirements for any marketed products.
The FDA may impose a number of post-approval requirements as a condition of approval of an NDA. For example, the FDA may require post-marketing testing, including Phase IV clinical trials, and surveillance to assess further and monitor the product’s safety and effectiveness after commercialization.
31
In addition, drug manufacturers and other entities involved in the manufacture and distribution of approved drugs are required to register their establishments with the FDA and state agencies, and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and these state agencies for compliance with cGMP requirements. Changes to the manufacturing process are strictly regulated and often require prior FDA approval before being implemented. FDA regulations also require investigation and correction of any deviations from cGMP requirements and impose reporting and documentation requirements upon the sponsor and any third-party manufacturers that the sponsor may decide to use. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money, and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain cGMP compliance.
Once an approval of a drug or medical device is granted, the FDA may withdraw the approval if compliance with regulatory requirements and standards is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in mandatory revisions to the approved labeling to add new safety information; imposition of post-market studies or clinical trials to assess new safety risks; or imposition of distribution or other restrictions under a REMS program. Other potential consequences include, among other things:
The FDA strictly regulates marketing, labeling, advertising and promotion of products that are placed on the market. Drugs or devices may be promoted only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved label. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses, and a company that is found to have promoted off-label uses improperly may be subject to significant liability.
The Hatch-Waxman Amendments
The Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, known as the Hatch-Waxman Act, added two pathways for FDA drug approval. First, the Hatch-Waxman amendments to the FDCA authorized the FDA to approve an alternative type of NDA under Section 505(b)(2) of the FDCA. Section 505(b)(2) permits the filing of an NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from trials not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference from the data owner. The applicant may rely upon the FDA’s findings of safety and efficacy for an approved product that acts as the “listed drug.” The FDA may also require 505(b)(2) applicants to perform additional studies or measurements to support the change from the listed drug. The FDA may then approve a new product candidate for all, or some, of the label indications for which the branded reference drug has been approved, as well as for any new indication sought by the 505(b)(2) applicant.
32
Second, the Hatch-Waxman amendments to the FDCA also established a statutory procedure for submission and FDA review and approval of abbreviated new drug applications (“ANDAs”) for generic versions of branded drugs previously approved by the FDA (such previously approved drugs are referred to as “listed drugs”). An ANDA is a comprehensive submission that contains, among other things, data and information pertaining to the active pharmaceutical ingredient, drug product formulation, specifications, and stability of the generic drug, as well as analytical methods, manufacturing process validation data and quality control procedures. Premarket applications for generic drugs are termed abbreviated because they generally do not include pre-clinical and clinical data to demonstrate safety and effectiveness. However, a generic manufacturer is typically required to conduct bioequivalence studies of its test product against the listed drug. The bioequivalence studies for orally administered, systemically available drug products assess the rate and extent to which active pharmaceutical ingredient (the “API”) is absorbed into the bloodstream from the drug product and becomes available at the site of action. Bioequivalence is established when there is an absence of a significant difference in the rate and extent for absorption of the generic product and the listed drug. For some drugs, other means of demonstrating bioequivalence may be required by the FDA, especially where rate and/or extent of absorption are difficult or impossible to measure. The FDA will approve the generic product as suitable for an ANDA application if it finds that the generic product does not raise new questions of safety and effectiveness as compared to the innovator product. A product is not eligible for ANDA approval if the FDA determines that it is not bioequivalent to the referenced innovator drug, if it is intended for a different use, or if it is not subject to an approved Suitability Petition.
In seeking approval for a drug through an NDA, including a 505(b)(2) NDA, applicants are required to list with the FDA certain patents whose claims cover the applicant’s product. Upon approval of an NDA, each of the patents listed in the application for the drug is then published in the Orange Book. Any applicant who files an ANDA seeking approval of a generic equivalent version of a drug listed in the Orange Book or a 505(b)(2) NDA that references a drug listed in the Orange Book must certify to the FDA that (1) no patent information on the drug product that is the subject of the application has been submitted to the FDA; (2) such patent has expired; (3) the date on which such patent expires; or (4) such patent is invalid or will not be infringed upon by the manufacture, use, or sale of the drug product for which the application is submitted. This last certification is known as a paragraph IV certification. A notice of the paragraph IV certification must be provided to each owner of the patent that is the subject of the certification and to the holder of the approved NDA to which the ANDA or 505(b)(2) application refers. The applicant may also elect to submit a “section viii” statement certifying that its proposed label does not contain (or carves out) any language regarding the patented method-of-use rather than certify to a listed method-of-use patent.
If the referenced NDA holder and patent owners assert a patent challenge directed to one of the Orange Book-listed patents within 45 days of the receipt of the paragraph IV certification notice, the FDA is prohibited from approving the application until the earlier of 30 months from the receipt of the paragraph IV certification expiration of the patent, settlement of the lawsuit, or a decision in the infringement case that is favorable to the applicant. The ANDA or 505(b)(2) application also will not be approved until any applicable non-patent exclusivity listed in the Orange Book for the branded reference drug has expired.
33
Marketing Exclusivity
Market exclusivity provisions under the FDCA can delay the submission or the approval of certain marketing applications. The FDCA provides a five-year period of non-patent marketing exclusivity within the United States to the first applicant to obtain approval of an NDA for a new chemical entity. A drug is a new chemical entity if the FDA has not previously approved any other new drug containing the same active moiety, which is the molecule or ion responsible for the action of the drug substance. During the exclusivity period, the FDA may not approve or even accept for review an abbreviated new drug application, or ANDA, or a NDA submitted under Section 505(b)(2), or 505(b)(2) NDA, submitted by another company for another drug based on the same active moiety, regardless of whether the drug is intended for the same indication as the original innovative drug or for another indication, where the applicant does not own or have a legal right of reference to all the data required for approval. However, an application may be submitted after four years if it contains a certification of patent invalidity or non-infringement to one of the patents listed with the FDA by the innovator NDA holder. The FDCA alternatively provides three years of marketing exclusivity for an NDA, or supplement to an existing NDA if new clinical investigations, other than bioavailability studies, that were conducted or sponsored by the applicant are deemed by the FDA to be essential to the approval of the application, for example new indications, dosages or strengths of an existing drug. This three-year exclusivity covers only the modification for which the drug received approval on the basis of the new clinical investigations and does not prohibit the FDA from approving ANDAs or 505(b)(2) NDAs for drugs containing the active agent for the original indication or condition of use. Five-year and three-year exclusivity will not delay the submission or approval of a full NDA. However, an applicant submitting a full NDA would be required to conduct or obtain a right of reference to all of the pre-clinical studies and adequate and well-controlled clinical trials necessary to demonstrate safety and effectiveness. Pediatric exclusivity is another type of marketing exclusivity available in the United States. Pediatric exclusivity provides for an additional six months of marketing exclusivity attached to another period of exclusivity if a sponsor conducts clinical trials in children in response to a written request from the FDA. The issuance of a written request does not require the sponsor to undertake the described clinical trials. In addition, orphan drug exclusivity, as described above, may offer a seven-year period of marketing exclusivity, except in certain circumstances.
United States Coverage and Reimbursement
Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of any therapeutic product candidate for which we may seek regulatory approval. Sales in the United States will depend in part on the availability of adequate financial coverage and reimbursement from third-party payors, which include government health programs such as Medicare, Medicaid, TRICARE, and the Veterans Administration, as well as managed care organizations and private health insurers. Prices at which we or our customers seek reimbursement for our initial or subsequent therapeutic product candidates can be subject to challenge, reduction, or denial by payors.
The process for determining whether a payor will provide coverage for a product is typically separate from the process for setting the reimbursement rate that the payor will pay for the product. A payor’s decision to provide coverage for a product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be available. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the price and examining the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of medical products and services, in addition to their safety and efficacy. In order to obtain coverage and reimbursement for any product that might be approved for marketing, we may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of any products, which would be in addition to the costs expended to obtain regulatory approvals. Third-party payors may not consider our initial or subsequent product candidates to be medically necessary or cost-effective compared to other available therapies, or the rebate percentages required to secure favorable coverage may not yield an adequate margin over cost or may not enable us to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on our investment in drug development.
Healthcare Reform
In the United States and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been, and continue to be, several legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could prevent or delay marketing approval of drug product candidates, restrict or regulate post-approval activities, and affect the profitable sale of drug product candidates.
34
Among policy makers and payors in the United States and elsewhere, there is significant interest in promoting changes in healthcare systems with the stated goals of containing healthcare costs, improving quality, and/or expanding access. In the United States, the pharmaceutical industry has been a particular focus of these efforts and has been significantly affected by major legislative initiatives. In March 2010, the Affordable Care Act, formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (the “ACA”), was enacted by Congress and signed into law by the President. It substantially changed the methods by which healthcare is financed by both the government and private insurers, and significantly impacted the United States pharmaceutical industry. The ACA, among other things: (i) increased the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extended the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid-managed care organizations; (ii) established an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports certain specified branded prescription drugs and biologic agents apportioned among these entities according to their market share in some government healthcare programs; (iii) expanded the availability of lower pricing under the 340B drug pricing program by adding new entities to the program; (iv) increased the statutory minimum rebates a manufacturer must pay under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program; (v) expanded the eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs; (vi) created a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research; and (vii) established a Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation to test innovative payment and service delivery models to lower Medicare and Medicaid spending, potentially including prescription drugs.
Some of the provisions of the ACA have yet to be implemented, and there have been judicial and Congressional challenges to certain aspects of the ACA. While Congress has not passed comprehensive repeal legislation, bills affecting the implementation of certain taxes under the ACA have been signed into law. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 includes a provision repealing, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the ACA on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year that is commonly referred to as the “individual mandate.” Additionally, on January 22, 2018, former President Trump signed a continuing resolution on appropriations for fiscal year 2018 that delayed the implementation of certain ACA-mandated fees, including the so-called “Cadillac” tax on certain high-cost employer-sponsored insurance plans, the annual fee imposed on certain health insurance providers based on market share, and the medical device excise tax on non-exempt medical devices.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the ACA was enacted, including aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of two percent per fiscal year and reduced payments to several types of Medicare providers. Moreover, there has recently been heightened governmental scrutiny over the manner in which manufacturers set prices for their marketed products, which has resulted in several Congressional inquiries and proposed and enacted federal and state legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to product pricing, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drug products. At the state level, legislatures have increasingly passed legislation and implemented regulations designed to control pharmaceutical product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing.
United States Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Laws and Compliance Requirements
Federal and state healthcare laws and regulations restrict business practices in the pharmaceutical industry. The United States laws that may affect our ability to operate include:
35
Regulation Outside of the United States
To the extent that our initial or subsequent product candidates, if and when approved, are sold in a foreign country, we may be subject to similar foreign laws and regulations, which may include, for instance, applicable post-marketing requirements, including safety surveillance, anti-fraud and abuse laws and implementation of corporate compliance programs and reporting of payments or other transfers of value to healthcare professionals.
In order to market our future products in the European Economic Area (the “EEA”) and many other foreign jurisdictions, we must obtain separate regulatory approvals. More concretely, in the EEA, medicinal products can only be commercialized after obtaining a Marketing Authorization (an “MA”). There are two types of marketing authorizations:
36
Under the above described procedures, before granting the MA, the EMA or the competent authorities of the Member States of the EEA make an assessment of the risk-benefit balance of the product on the basis of scientific criteria concerning its quality, safety and efficacy.
Data and Marketing Exclusivity
In the EEA, new products authorized for marketing, or reference products, qualify for eight years of data exclusivity and an additional two years of market exclusivity upon marketing authorization. The data exclusivity period prevents generic or biosimilar applicants from relying on the pre-clinical and clinical trial data contained in the dossier of the reference product when applying for a generic or biosimilar marketing authorization in the EU during a period of eight years from the date on which the reference product was first authorized in the EU. The market exclusivity period prevents a successful generic or biosimilar applicant from commercializing its product in the EU until 10 years have elapsed from the initial authorization of the reference product in the EU. The 10-year market exclusivity period can be extended to a maximum of 11 years if, during the first eight years of those 10 years, the marketing authorization holder obtains an authorization for one or more new therapeutic indications that, during the scientific evaluation prior to their authorization, are held to bring a significant clinical benefit in comparison with existing therapies. In Japan, medicinal products approved for administration to a patient via a new route of administration qualify for six years of market exclusivity.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials of medicinal products in the European Union must be conducted in accordance with European Union and national regulations and the International Conference on Harmonization (the “ICH”) guidelines on GCPs. Additional GCP guidelines from the European Commission, focusing in particular on traceability, apply to clinical trials of advanced therapy medicinal products. If the sponsor of the clinical trial is not established within the European Union, it must appoint an entity within the European Union to act as its legal representative. The sponsor must purchase a clinical trial insurance policy and, in most EU countries, the sponsor is liable to provide “no fault” compensation to any study subject injured in the clinical trial.
Prior to commencing a clinical trial, the sponsor must obtain a clinical trial authorization from the competent authority, and a positive opinion from an IEC. The application for a clinical trial authorization must include, among other things, a copy of the trial protocol and an investigational medicinal product dossier that contains information about the manufacture and quality of the medicinal product under investigation. Currently, clinical trial authorization applications must be submitted to the competent authority in each EU Member State in which the trial will be conducted. Under the new Clinical Trials Regulation (Regulation (EU) No 536/2014), which took effect on January 31, 2022, there will be a centralized application procedure where one national authority takes the lead in reviewing the application and the other national authorities have only a limited involvement. Any substantial changes to the trial protocol or other information submitted with the clinical trial applications must be notified to or approved by the relevant competent authorities and ethics committees. Medicines used in clinical trials must be manufactured in accordance with cGMP. Other national and European Union-wide regulatory requirements also apply.
Recycling
We started our business in 1976 as a used appliance retailer that reconditioned old appliances to sell in our stores. Under contracts with national and regional retailers of new appliances, we collected the replaced appliance from the retailer’s customer’s residence when one of their stores delivered a new appliance. Any old appliances that we could not sell in our stores were sold to scrap metal processors. In the late 1980s, stricter environmental regulations began to affect the disposal of unwanted appliances and we were no longer able to take appliances that contained hazardous components to scrap metal processors. At that time, we began to develop systems and equipment to remove the harmful materials so that metal processors would accept the appliance shells for processing. We then offered our services for disposing of appliances in an environmentally sound manner to appliance manufacturers and retailers, waste hauling companies, rental property managers, local governments, and the public. In 1989, we began contracting with electric utility companies to provide turnkey appliance recycling services to support their energy conservation efforts. Since that time, we have provided our services to approximately 400 utilities and other providers of energy efficiency programs throughout North America.
37
Through March 8, 2023, when we disposed of our recycling business, we had contracts to recycle, or to replace and recycle, major household appliances for approximately 100 utilities and other providers of energy efficiency services across North America. We operate 17 recycling centers in the United States and Canada to process and recycle old appliances according to all federal, state, provincial, and local rules and regulations. We used United States Environmental Protection Agency (the “EPA”) Responsible Appliance Disposal (“RAD”) Program-compliant methods to remove and manage hazardous components and materials properly, including CFC refrigerants, mercury, polyurethane foam insulation, and recyclable materials, such as ferrous and nonferrous metals, plastics, and glass. During our operations of the recycling business, all of our facilities complied with licensing and permitting requirements, and employees who process appliances receive extensive safety and hazardous materials training.
Our wholly-owned subsidiaries in our Recycling segment included, ARCA Canada, a Canadian corporation formed in September 2006 (“ARCA Canada”), ARCA Recycling, a California corporation formed in November 1991, and Connexx, a Nevada limited liability company formed in October 2016 that provides call center services for recycling business.
Disposition of our Recycling Business
On March 19, 2023, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with VM7 Corporation, a Delaware corporation (the “Buyer”), under which the Buyer agreed to acquire all of the outstanding equity interests of (a) ARCA Recycling, (b) Connexx, and (c) ARCA Canada (collectively, the “Subsidiaries”). The principal of the Buyer is Virland A. Johnson, our Chief Financial Officer. The sale of all of the outstanding equity interests of the Subsidiaries to the Buyer under the Purchase Agreement (the “Disposition Transaction”) was consummated simultaneously with the execution of the Purchase Agreement. Our Board of Directors unanimously approved the Purchase Agreement and the Disposition Transaction.
The economic aspects of the Disposition Transaction are: (i) we reduced the liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets by approximately $17.6 million (excluding those related to the California Business Fee and Tax Division, as discussed below); (ii) we will receive not less than $24.0 million in aggregate monthly payments from the Buyer, which payments are subject to potential increase due to the Subsidiaries’ future performance; and (iii) during the next five years, we may request that the Buyer prepay aggregate monthly payments in the aggregate amount of $1 million. We also received one thousand dollars for the equity of each of the Subsidiaries at the closing. Each monthly payment is to be the greater of (a) $140,000 (or $100,000 for each January and February during the 15-year payment period) or (b) a monthly percentage-based payment, which is an amount calculated as follows: (i) 5% of the Subsidiaries’ aggregate gross revenues up to $2,000,000 for the relevant month, plus (ii) 4% of the Subsidiaries’ aggregate gross revenues between $2,000,000 and $3,000,000 for the relevant month, plus (iii) 3% of the Subsidiaries aggregate gross revenues over $3,000,000 for the relevant month. The Buyer will receive credit toward the payment of the first monthly payment (March of 2023) for any payments, distributions, or cash dividends paid by any of the Subsidiaries to the Seller on or after March 19, 2023.
38
The Buyer may prepay, at any time and in total, the estimated aggregate of the future monthly payments. That amount will be an amount equal to the then-present value of the estimated future monthly payments, discounted at the rate of 5% per annum (the “Prepayment Price”). Furthermore, the Buyer will be required to pay the Prepayment Price upon the earliest of (i) Mr. Johnson holding less than 75% of the capital stock of the Buyer, (ii) the Buyer selling substantially all of its assets, (iii) the Buyer holding less than 50% of the capital stock of the Subsidiaries, or (iv) the Subsidiaries selling substantially all of their respective assets. Upon payment of the Prepayment Price, Buyer will have no further purchase price payment obligations to the Seller.
Additional terms of the Disposition Transaction are: (i) we have the right to appoint one member of the Buyer’s board of directors until the sooner of the Buyer having paid the Prepayment Price or having tendered all of the monthly payments; (ii) Mr. Johnson’s annual salary as Chief Executive Officer of the Buyer shall be $400,000, prorated, for the remainder of the 2023 calendar year, and then adjusted annually to an amount equal to 1% of the Subsidiaries’ aggregate gross revenues, until the sooner of the Buyer having paid the Prepayment Price or having tendered all of the monthly payments; and (iii) we will receive additional payments from the Buyer (that are not related to the on-going monthly payments) that relate to certain taxing agency issues. Upon settlement of the continuing dispute between ARCA and the California Business Fee and Tax Division (as to which settlement, there can be no assurance), the ARCA will pay to us 50% of the amount of the reduction between the current assessment and any such settlement. The payment will be memorialized by a three-year promissory note with interest at five percent per annum. The first payment under the note will be on the last day of the Buyer’s fiscal year in which the settlement occurs and the remaining payments each year thereafter. If ARCA receives a refund from the agency for payments previously made, it shall pay to us an amount equivalent to 25% of such refund after reduction for the legal fees payable to counsel for this proceeding. ARCA and Connexx are due to receive from the Internal Revenue Service two payments in the aggregate amount of approximately $931,000 in connection with the Employee Retention Credit provisions of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act and the Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Tax Relief Act of 2020. Those payments are to be tendered to us within 10 days of receipt by ARCA or Connexx.
To secure the Buyer’s obligations under the Purchase Agreement and pursuant to a Stock and Membership Interests Pledge Agreement dated March 19, 2023 (the “Pledge Agreement”), Mr. Johnson pledged to us all of the capital stock in the Buyer (the “Buyer’s Capital Stock”) and the Buyer pledged to us all of the equity interests of the Subsidiaries (the “Subject Securities”). Under the terms of the Pledge Agreement, upon an Event of Default (as defined in the Pledge Agreement), among other remedies in our favor, we may foreclose on any or all of the Buyer’s Capital Stock and the Subject Securities. We may also cause the ownership of the Buyer’s Capital Stock and of the Subject Securities to be transferred to us automatically, pursuant to an irrevocable transfer entered in our favor, as referenced in the Pledge Agreement. In the event of an automatic transfer, all of the monthly payments previously made by the Buyer pursuant to the terms of the Purchase Agreement will then be characterized as contributions to the capital of the Company without dilution of the Company’s capital stock.
The parties have made customary representations, warranties, covenants, and indemnities in connection with the Disposition Transaction.
The Purchase Agreement contains certain representations and warranties that the parties made to each other as of the date of the Purchase Agreement or such other date as explicitly referenced therein. The representations and warranties were made solely for purposes of the Purchase Agreement and (i) are subject to limitations agreed by the parties in negotiating the terms and conditions thereof, (ii) may not be accurate or complete as of any specified date, (iii) will be qualified by the underlying disclosure schedules, (iv) may be subject to a contractual standard of materiality different from those generally applicable to investors, and (v) may have been used for the purpose of allocating risk among the parties thereto, rather than for establishing any matters as facts. Information concerning the subject matter of the representations and warranties may change after March 19, 2023, and subsequent information may or may not be fully reflected in JanOne’s public disclosures. For the foregoing reasons, the representations and warranties contained in the Purchase Agreement should not be relied upon as statements of factual information.
39
Technology
During the year ended January 1, 2022, the Company took a full write-down of the unamortized portion of the GeoTraq intangible asset of approximately $9.8 million, and on May 24, 2022, the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with SPYR Technologies Inc., pursuant to which the Company sold to SPYR substantially all the assets and none of the liabilities of its wholly-owned subsidiary GeoTraq Inc. The aggregate purchase price for the GeoTraq Assets was $13.5 million, payable in cash and shares of SPYR’s capital stock. As of the closing of the transaction on May 24, 2022, SPYR issued to the Company 30,000,000 shares of its common stock at $0.03 per share, and delivered a five-year Promissory Note in the principal amount of $12.6 million. The Promissory Note bears simple interest at the rate of 8% per annum, provides quarterly interest payments due the first day of each calendar quarter, and may be prepaid at any time without penalty. Quarterly interest payments may be made in cash or in shares of SPYR's restricted common stock or preferred stock. The Promissory Note matures on May 23, 2027.
Employees
As of December 31, 2022, the Company had 207 employees, of which 199 were full-time employees.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
You should carefully consider the risks described below with respect to an investment in our shares. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business, financial condition, operating results or cash provided by operations could be materially harmed. As a result, the trading price of our common stock could decline, and you might lose all or part of your investment. When evaluating an investment in our common stock, you should also refer to the other information in this Form 10-K, including our consolidated financial statements and related notes.
Risks Relating to Our Business Generally
If we fail to implement our biopharmaceutical business strategy or if our biopharmaceutical business strategy is ineffective, our financial performance could be materially and adversely affected.
Our future financial performance and success are dependent in large part upon the effectiveness of our new biopharmaceutical business strategy and our ability to implement our biopharmaceutical business strategy successfully. Implementation of our strategy will require effective management of our operational, financial, and human resources and will place significant demands on those resources. There are risks involved in pursuing our strategy, including those under the caption “Risks Relating to Our Biotechnology Segment”. In addition to the risks set forth elsewhere in this Form 10-K, effectiveness of and the successful implementation of our business strategy could also be affected by a number of factors beyond our control, such as increased competition, legal developments, government regulation, general economic conditions, increased operating costs or expenses, and changes in industry trends. We may decide to alter or discontinue certain aspects of our business strategy at any time. If we are not able to implement our business strategy successfully, our long-term growth and profitability may be adversely affected. Even if we are able to implement some or all of the initiatives of our business strategy successfully, our operating results may not improve and could decline substantially.
We have identified and disclosed in this Form 10-K material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. If we are not able to remediate these material weaknesses and maintain an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately or timely report our financial results, which could cause our stock price to fall or result in our stock being delisted.
We need to devote significant resources and time to comply with the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Sarbanes-Oxley”) with respect to internal control over financial reporting. In addition, Section 404 under Sarbanes-Oxley requires that we assess the design and operating effectiveness of our controls over financial reporting, which are necessary for us to provide reliable and accurate financial reports.
40
As reported in Part II – Item 9A, Controls and Procedures, there were material weaknesses in our internal controls over financial reporting at January 1, 2022. Specifically, management noted the following material weaknesses in internal control when conducting their evaluation of internal control as of January 1, 2022: (1) insufficient information technology general controls and segregation of duties. It was noted that people who were negotiating a contract were also involved in approving invoices without proper oversight. Additional controls and procedures are necessary and are being implemented to have checks and balances on significant transactions and governance with those charged with governance authority; (2) inadequate control design or lack of sufficient controls over significant accounting processes; the cutoff and reconciliation procedures were not effective with certain accrued and deferred expenses; (3) insufficient assessment of the impact of potentially significant transactions; and (4) insufficient processes and procedures related to proper recordkeeping of agreements and contracts. In addition, contract-to-invoice reconciliation was not effective with certain transportation service providers. As part of its remediation plan, processes and procedures have been implemented to help ensure accruals and invoices are reviewed for accuracy and properly recorded in the appropriate period.
We expect our systems and controls to become increasingly complex to the extent that we integrate acquisitions and as our business grows. To effectively manage our Company today and this anticipated complexity, we need to remediate these material weaknesses and continue to improve our operational, financial, and management controls and our reporting systems and procedures. Any failure to remediate these material weaknesses and implement required new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in the implementation or operation of these controls, could harm our operating results or cause us to fail to meet our financial reporting obligations, which could adversely affect our business and jeopardize our listing on the Nasdaq Capital Market, either of which would harm our stock price.
Risks Relating to Our Biotechnology Segment
Our biotechnology business has a limited operating history
Our biotechnology business was started in September 2019 and has a limited operating history. We have not commenced revenue-producing operations. To date, our biotechnology-related operations have consisted of preliminary research and development, and characterization and testing of SR TV1001 (now known as JAN101) and our December 2022 acquisition of Soin Therapeutics and its LDN product (now known as JAN123). Our limited operating history makes it difficult for potential investors to evaluate our technology or the prospective operations of our biotechnology business. You should consider the prospects of our biotechnology business in light of the costs, uncertainties, delays, and difficulties frequently encountered by companies in the early stages of development, especially clinical-stage biopharmaceutical businesses such as ours. Potential investors should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties that a biotechnology business with a limited operating history faces. In particular, potential investors should consider that we may be unable to (i) successfully implement or execute the business plan of our biotechnology business or currently validate that our biotechnology business plan is sound; (ii) successfully complete clinical trials and obtain regulatory approval for the marketing of JAN 101; (iii) successfully demonstrate a favorable differentiation between JAN 101 and the current products on the market; (iv) successfully manufacture our clinical drug product and establish a commercial drug supply; (v) secure market exclusivity and/or adequate intellectual property protection for JAN 101; and (vi) raise sufficient funds in the capital markets to effectuate our biotechnology business plan, including product and clinical development, regulatory approval, and commercialization for JAN 101.
Our business model is partially dependent on certain patent rights licensed to us from the Licensors (as defined below), and the loss of those license rights would, in all likelihood, cause our business, as presently contemplated, to fail.
In November 2019, UABRF, TheraVasc, and the Board of Supervisors of Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, acting on behalf of LSU Health Shreveport, together with UABRF and TheraVasc, the “Licensors”), granted us an exclusive worldwide, royalty-bearing license to the patent rights for SR TV1001 (now known as JAN101) in the negotiated fields of use. The patent license agreement requires us to pay royalties and milestone payments and conform to a variety of covenants and agreements, and in the event of our breach of the agreement, the Licensors may elect to terminate the agreement. As of the date of this Form 10-K, we believe we are in compliance with the patent license agreement and consider our relationship with the Licensors to be excellent.
41
We will be completely dependent on third parties to manufacture JAN 101, and its commercialization could be halted, delayed, or made less profitable if those third parties fail to obtain manufacturing approval from the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, fail to provide us with sufficient quantities of JAN 101, or fail to do so at acceptable quality levels or prices.
We do not currently have, nor do we plan to acquire, the capability or infrastructure to manufacture our drug candidate for use in our clinical trials or for commercial sales, if any. As a result, we will be obligated to rely on contract manufacturers when we conduct clinical trials and if and when our initial or subsequent product candidates are approved for commercialization. In January 2020, we entered into a Master Agreement for Development, Manufacturing and Supply with CoreRx Inc. (“CoreRx”), pursuant to which CoreRx has agreed to provide to us certain product testing, development, and clinical manufacturing services for JAN 101. We have not entered into agreements with any contract manufacturers for commercial supply and may not be able to engage contract manufacturers for commercial supply of our initial or subsequent product candidates on favorable terms to us, or at all, should the need arise.
In a previous clinical trial, the manufacture of JAN101 by a different manufacturing company resulted in a product that demonstrated initial instability that led to the product being out-of-specification. While the FDA allowed the trial to continue, there is no guarantee that, if the product manufactured by CoreRx is similarly unstable, the FDA will allow us to continue to develop that product. Even if the product manufactured by CoreRx is stable, the FDA may require additional studies to confirm the stability of the product, increasing development cost and times.
The facilities used by CoreRx to manufacture JAN 101 must be approved by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Such approvals are subject to inspections that will be conducted after we submit an NDA to the FDA or their equivalents to other relevant regulatory authorities. We will not control the manufacturing process of JAN 101 or subsequent product candidates and will be completely dependent on our contract manufacturing partners for compliance with cGMPs, for manufacture of both active drug substances and finished drug products. These cGMP regulations cover all aspects of the manufacturing, testing, quality control, storage, distribution, and record keeping relating to our initial or subsequent product candidates. If our contract manufacturers do not successfully manufacture material that conforms to our specifications and the strict regulatory requirements of the FDA or others, we will not be able to secure or maintain regulatory approval for products made at their manufacturing facilities. If the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority does not approve these facilities for the manufacture of our initial or subsequent product candidates or if it withdraws any such approval in the future, we may need to find alternative manufacturing facilities, which would significantly impact our ability to develop, manufacture, obtain regulatory approval for, or market our initial or subsequent product candidates, if approved. Likewise, we could be negatively impacted if any of our contract manufacturers elect to discontinue their business relationship with us.
Our contract manufacturer will be subject to ongoing periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and corresponding state and foreign agencies for compliance with cGMPs and similar regulatory requirements. We will not have control over our contract manufacturer’s compliance with these regulations and standards. Failure by our contract manufacturer to comply with applicable regulations could result in sanctions being imposed on us, including fines, injunctions, civil penalties, failure to grant approval to market JAN 101, delays, suspensions or withdrawals of approvals, inability to supply product, operating restrictions, and criminal prosecutions, any of which could significantly and adversely affect our biotechnology business. In addition, we will not have control over the ability of our contract manufacturer to maintain adequate quality control, quality assurance, and qualified personnel. Failure by our contract manufacturer to comply with or maintain any of these standards could adversely affect our ability to develop, manufacture, obtain regulatory approval for or market JAN 101, if approved.
42
Our manufacturer must obtain the API from a third party. A number of groups manufacture our API; however, some of these are manufactured as a food product, and others, while manufactured under GMP, do not have the required Drug Master File on file with the FDA. CoreRx identified an API from Merck KGaA for use in the current production of clinical grade JAN101. At the time of the manufacture of the API, the product met the specifications outlined in both the drug substance monographs for Europe and the US. However, subsequent to the manufacture of the API, the US monograph was changed in the US Pharmacopeia (“USP”) and, while most of the tests conform, Merck KGaA was unable to complete two of the new testing requirements. Although the two tests are not considered safety issues and do not impact the quality of the product, there is no guarantee the FDA will approve the product for clinical trials if the two tests are not completed, which could delay our ability to start the Phase IIb clinical trial, as planned. Identifying an analytical laboratory to perform the two tasks may be difficult and could require development and validation of the tests, adding both time and costs to us. In addition, there is no guarantee that, once developed, the product will meet the specifications as outlined in the USP. Even if the FDA allows the current product to be used in the Phase IIb clinical trial, there is no guarantee that the FDA will allow further clinical work with the product or commercialization of the product until it is shown to conform to USP standards. We may be required to work with the API manufacturer to file the appropriate documents and there is no guarantee that the FDA will approve the filing. This could necessitate additional funding to hire an API manufacturer and produce the product under GMP with all necessary filings.
If, for any reason, these third parties are unable or unwilling to perform, we may not be able to locate alternative manufacturers or formulators or enter into favorable agreements with them and we cannot be certain that any such third parties will have the manufacturing capacity to meet future requirements. If these manufacturers or any alternate manufacturer of finished drug product experiences any significant difficulties in its respective manufacturing processes for APIs or finished products or should cease doing business with us for any reason, we could experience significant interruptions in the supply of our initial or subsequent product candidates or may not be able to create a supply of any of our ls at all. Were we to encounter manufacturing difficulties, our ability to produce a sufficient supply of any of our product candidates might be negatively affected. Our inability to coordinate the efforts of our third-party manufacturing partners, or the lack of capacity available at our third-party manufacturing partners, could impair our ability to supply any of our product candidates at required levels. Because of the significant regulatory requirements that we would need to satisfy in order to qualify a new bulk drug substance or finished product manufacturer, if we face these or other difficulties with our then-current manufacturing partners, we could experience significant interruptions in the supply of any of our product candidates if we decided to transfer the manufacture of any of our product candidates to one or more alternative manufacturers in an effort to deal with such difficulties.
CoreRx currently serves as our sole manufacturer of JAN101. As CoreRx also manufactures other products, there can be no guarantee that CoreRx will have the capacity to manufacture additional clinical product for us in a timely manner, when required, which could lead to significant delays in initiating other clinical studies. CoreRx will unlikely have the capacity to manufacture the amount of product needed, if and when JAN101 is approved for marketing. This would necessitate identifying additional manufacturer(s) who may or may not be able to replicate the manufacturing process developed at CoreRx. In addition, the increase in quantities required for commercialization of the product, if commercialization occurs, could require modifying the manufacturing process to produce larger quantities of tablets more efficiently. Such modifications of the manufacturing process, if even possible, could result in significant delays in the delivery of the product.
We will be validating the manufacturing process, with appropriate process parameters and critical process, at CoreRx in 2023. Based on current batch sizes, these validated processes will support the manufacture of approximately 6.5 million tablets a month. This would allow us to enter the marketplace, but would support sales of only 1-2% of the addressable market. There is no guarantee that CoreRx will increase its manufacturing capacity when needed by us; thus, we will likely need to identify another approved manufacturer with increased capacity. In addition, we will need to revalidate the manufacturing process to demonstrate to the FDA the ability to reproducibly manufacture larger batch sizes, which will increase time and costs. If these activities are not carried out in a timely manner, a shortage of product could result following commercial launch, which could significantly affect sales and overall valuation of the Company.
43
Any manufacturing problem or the loss of our contract manufacturer could be disruptive to our operations and result in development delays and lost sales. Additionally, we will rely on third parties to supply the raw materials needed to manufacture our initial or subsequent product candidates. Any such reliance on suppliers may involve several risks, including a potential inability to obtain critical materials and reduced control over production costs, delivery schedules, reliability, and quality. Any unanticipated disruption to the operation of one of our contract manufacturers caused by problems with suppliers could delay shipment of any of our product candidates, increase our cost of goods sold and result in lost sales.
If product liability lawsuits are brought against us, we may incur substantial liabilities and may be required to limit commercialization of our initial or subsequent product candidates.
We will face a potential risk of product liability as a result of the clinical testing of our initial or subsequent product candidates. For example, we may be sued if any product we develop, including JAN 101, or any materials that we use in it, allegedly causes injury or is found to be otherwise unsuitable during product testing and manufacturing. Any such product liability claims may include allegations of defects in manufacturing, defects in design, a failure to warn of dangers inherent in the product, negligence, strict liability, and a breach of warranties. In the United States, claims could also be asserted against us under state consumer protection acts. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against product liability claims, we may incur substantial liabilities or be required to limit commercialization of our initial or subsequent product candidates. Even successful defense of these claims would require us to employ significant financial and management resources. Regardless of the merits or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in, among other things (i) decreased demand for JAN 101 or any future products that we may develop; (ii) failure to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates; (iii) withdrawal of participants in our clinical trials; (iv) substantial monetary awards to trial participants or patients; (v) product recalls or withdrawals or labeling, marketing, or promotional restrictions; and (vi) the inability to commercialize our initial or subsequent product candidates. As of the date of this Form 10-K, we do not carry product liability insurance.
The success of our biotechnology business is entirely dependent on our ability to obtain the marketing approval for our product candidates by the FDA and the regulatory authorities in foreign jurisdictions in which we intend to market them, of which there can be no assurance.
We are not permitted to market JAN 101 or JAN 123 as prescription pharmaceutical products in the United States until we receive approval of an NDA from the FDA, or in any foreign countries until we receive the requisite approval from such countries. In the United States, the FDA generally requires the completion of clinical trials of each drug to establish its safety and efficacy and extensive pharmaceutical development to ensure its quality before an NDA is approved. Of the large number of drugs in development, only a small percentage result in the submission of an NDA to the FDA and even fewer are eventually approved for commercialization. As of the date of this Form 10-K, we have not submitted an NDA to the FDA or comparable applications to other regulatory authorities for any subsequent product candidates.
Because of the clinical trial history of JAN101, we believe that JAN 101 will qualify for FDA approval through the FDA’s 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway and in corresponding regulatory paths in other foreign jurisdictions. Notwithstanding the use of the FDA’s 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway, we will be required to conduct Phase IIb and Phase III studies prior to filing for marketing approval of JAN 101.
44
Our success depends on our receipt of the regulatory approvals described above, and the issuance of such regulatory approvals is uncertain and subject to a number of risks, including the following: (i) the results of toxicology studies may not support the filing of an NDA for JAN 101; (ii) the FDA may require additional pharmacokinetic studies with JAN101, including studies with food, prior to allowing the Company to conduct Phase IIb and Phase III clinical trials; (iii) the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities or Institutional Review Boards (“IRBs”) may disagree with the design or implementation of our clinical trials; (iv) we may not be able to provide acceptable evidence of JAN 101’s safety and efficacy; (v) the results of our clinical trials may not be satisfactory or may not meet the level of statistical or clinical significance required by the FDA, the EMA, or other regulatory agencies for us to receive marketing approval for JAN 101; (vi) the dosing of JAN 101 in a particular clinical trial may not be at an optimal level; (vii) patients in our clinical trials may suffer adverse effects for reasons that may or may not be related to JAN 101; (viii) the data collected from clinical trials may not be sufficient to support the submission of an NDA or other submission or to obtain regulatory approval in the United States or elsewhere; (ix) the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may fail to approve the manufacturing processes or facilities of third-party manufacturers with which we contract for clinical and commercial supplies; and (x) the approval policies or regulations of the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may significantly change in a manner rendering our clinical data insufficient for approval of JAN 101.
The process of obtaining regulatory approvals is expensive, often takes many years, if approval is obtained at all, and can vary substantially based upon, among other things, the type, complexity, and novelty of the product candidates involved, the jurisdiction in which regulatory approval is sought, and the substantial discretion of the regulatory authorities. Changes in regulatory approval policies during the development period, changes in or the enactment of additional statutes or regulations, or changes in regulatory review for a submitted product application may cause delays in the approval or rejection of an application. Regulatory approval obtained in one jurisdiction does not necessarily mean that a product candidate will receive regulatory approval in any or all other jurisdictions in which we may seek approval; but, the failure to obtain approval in one jurisdiction may negatively impact our ability to seek approval in a different jurisdiction. Failure to obtain regulatory approval for JAN 101 for the foregoing, or any other reasons, will prevent us from commercializing JAN 101, and our ability to generate revenue will be materially impaired.
Clinical testing is expensive, is difficult to design and implement, can take many years to complete and is uncertain as to outcome.
Our business model depends in part on the successful development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of JAN 101, which may never occur. JAN 101 is in the early stages of development and, as of the date of this Form 10-K, we have not progressed JAN 101 beyond early clinical studies designed only to show safety. Three INDs have previously been submitted by previous licensees/assignees of JAN101 and were accepted by the FDA. These INDs were transferred to JanOne in 2020. Even though the INDs were transferred to us, the FDA may still require additional work prior to re-initiation of clinical trials. If we do not obtain such approvals to re-initiate trials as presently planned, the time in which we expect to commence clinical programs for any product candidate will be extended and such extension will increase our expenses, delay our potential receipt of any revenues, and increase our need for additional capital. Moreover, there is no guarantee that we will receive approval to commence human clinical trials or, if we do receive approval, that our clinical trials will be successful or that we will continue clinical development in support of an approval from the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities for any indication. We note that most product candidates never reach the clinical development stage and even those that do commence clinical development have only a small chance of successfully completing clinical development and gaining regulatory approval. Success in early phases of pre-clinical and clinical trials does not ensure that later clinical trials will be successful, and interim results of a clinical trial do not necessarily predict final results. A failure of one or more of our clinical trials can occur at any stage of testing. We may experience numerous unforeseen events during, or as a result of, the clinical trial process that could delay or prevent our ability to receive regulatory approval or commercialize our initial or any subsequent product candidates. Therefore, our business currently depends entirely on the successful development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of our product candidates, which may never occur.
Even if we receive regulatory approval for JAN 101, we may not be able to commercialize it successfully and the revenue that we generate from its sales, if any, may be limited.
If approved for marketing, the commercial success of JAN 101 will depend upon the product’s acceptance by the medical community, including physicians, patients, and health care payors. The degree of market acceptance for JAN 101 will depend on a number of factors, including (i) demonstration of clinical safety and efficacy; (ii) relative
45
convenience, dosing burden, and ease of administration; (iii) the prevalence and severity of any adverse effects; (iv) the willingness of physicians to prescribe JAN 101 and the target patient population to try new therapies; (v) efficacy of JAN 101 compared to competing products; (vi) the introduction of any new products that may in the future become available, targeting indications for which JAN 101 may be approved; (vii) new procedures or therapies that may reduce the incidences of any of the indications in which JAN 101 may show utility; (viii) pricing and cost-effectiveness; (ix) the inclusion or omission of JAN 101 in applicable guidelines; (x) the effectiveness of our own or any future collaborators’ sales and marketing strategies; (xi) limitations or warnings contained in approved labeling from regulatory authorities; (xii) our ability to obtain and maintain sufficient third-party coverage or reimbursement from government health care programs, including Medicare and Medicaid, private health insurers, and other third-party payors or to receive the necessary pricing approvals from government bodies regulating the pricing and usage of therapeutics; and (xiii) the willingness of patients to pay out-of-pocket in the absence of third-party coverage or reimbursement or government pricing approvals.
If JAN 101 is approved but does not achieve an adequate level of acceptance by physicians, health care payors, and patients, our biotechnology business may not generate sufficient revenue to cover costs. Our efforts to educate the medical community and third-party payors on the benefits of JAN 101 may require significant resources and may never be successful.
In addition, even if we obtain regulatory approvals, the timing or scope of any approvals may prohibit or reduce our ability to commercialize JAN 101 successfully. For example, if the approval process takes too long, we may miss market opportunities and give other companies the ability to develop competing products or establish market dominance. Any regulatory approval we ultimately obtain may be limited or subject to restrictions or post-approval commitments that renders our product candidate not commercially viable. For example, regulatory authorities may approve our product candidate for fewer or more limited indications than we request, may not approve the price we intend to charge for our product candidate, may grant approval contingent on the performance of costly post-marketing clinical trials, or may approve any of our product candidates with a label that does not include the labeling claims necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of that indication. Further, the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may place conditions on approvals or require risk management plans or a REMS to assure the safe use of the drug. Moreover, product approvals may be withdrawn for non-compliance with regulatory standards or if problems occur following the initial marketing of the product. Any of the foregoing scenarios could materially harm the commercial success of our product candidate.
Even if we obtain marketing approval for our product candidate, we will be subject to ongoing obligations and continued regulatory review, which may result in significant additional expense. Additionally, our product candidate could be subject to labeling and other restrictions and withdrawal from the market and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems with our product candidate.
Even if we obtain regulatory approval for our product candidate for an indication, the FDA or foreign equivalent may still impose significant restrictions on its indicated uses or marketing or the conditions of approval, or impose ongoing requirements for potentially costly and time-consuming post-approval studies, including Phase IV clinical trials, and post-market surveillance to monitor safety and efficacy. Our product candidate will also be subject to ongoing regulatory requirements governing the manufacturing, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, safety surveillance, advertising, promotion, recordkeeping and reporting of adverse events, and other post-market information. These requirements include registration with the FDA, as well as continued compliance with current good clinical practices regulations for any clinical trials that we conduct post-approval. In addition, manufacturers of drug products and their facilities are subject to continual review and periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with current cGMPs, requirements relating to quality control, quality assurance and corresponding maintenance of records and documents.
The FDA has the authority to require a REMS as part of an NDA or after approval, which may impose further requirements or restrictions on the distribution or use of an approved drug, such as limiting prescribing to certain physicians or medical centers that have undergone specialized training, limiting treatment to patients who meet certain safe-use criteria or requiring patient testing, monitoring and/or enrollment in a registry.
46
With respect to sales and marketing activities related to our product candidate, advertising and promotional materials must comply with FDA rules in addition to other applicable federal, state and local laws in the United States and similar legal requirements in other countries. In the United States, the distribution of product samples to physicians must comply with the requirements of the United States Prescription Drug Marketing Act. Application holders must obtain FDA approval for product and manufacturing changes, depending on the nature of the change. We may also be subject, directly or indirectly through our customers and partners, to various fraud and abuse laws, including, without limitation, the United States Anti-Kickback Statute, United States False Claims Act, and similar state laws, which impact, among other things, our proposed sales, marketing, and scientific/educational grant programs. If we participate in the United States Medicaid Drug Rebate Program, the Federal Supply Schedule of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, or other government drug programs, we will be subject to complex laws and regulations regarding reporting and payment obligations. All of these activities are also potentially subject to United States federal and state consumer protection and unfair competition laws. Similar requirements exist in many of these areas in other countries.
In addition, if JAN 101 is approved for a particular indication, our product labeling, advertising, and promotion would be subject to regulatory requirements and continuing regulatory review. The FDA strictly regulates the promotional claims that may be made about prescription products. In particular, a product may not be promoted for uses that are not approved by the FDA as reflected in the product’s approved labeling. If we receive marketing approval for JAN 101, physicians may nevertheless legally prescribe our product to their patients in a manner that is inconsistent with the approved label. If we are found to have promoted such off-label uses, we may become subject to significant liability and government fines. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses, and a company that is found to have improperly promoted off-label uses may be subject to significant sanctions. The federal government has levied large civil and criminal fines against companies for alleged improper promotion and has enjoined several companies from engaging in off-label promotion. The FDA has also requested that companies enter into consent decrees of permanent injunctions under which specified promotional conduct is changed or curtailed.
If we or a regulatory agency discover previously unknown problems with one of our product candidates, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, problems with the facility where the product is manufactured, or we or our manufacturers fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, we may be subject to the following administrative or judicial sanctions: (i) restrictions on the marketing or manufacturing of the product, withdrawal of the product from the market, or voluntary or mandatory product recalls; (ii) issuance of warning letters or untitled letters; (iii) clinical holds; (iv) injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties or monetary fines; (v) suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approval; (vi) suspension of any ongoing clinical trials; (vii) refusal to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications filed by us, or suspension or revocation of product license approvals; (viii) suspension or imposition of restrictions on operations, including costly new manufacturing requirements; or (ix) product seizure or detention or refusal to permit the import or export of product. The occurrence of any event or penalty described above may inhibit our ability to commercialize our product candidates and generate revenue. Adverse regulatory action, whether pre- or post-approval, can also potentially lead to product liability claims and increase our product liability exposure.
Obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of JAN 101 in one jurisdiction does not mean that we will be successful in obtaining regulatory approval of JAN 101 in other jurisdictions.
Obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of our initial or subsequent product candidates in one jurisdiction does not guarantee that we will be able to obtain or maintain regulatory approval in any other jurisdiction; but, a failure or delay in obtaining regulatory approval in one jurisdiction may have a negative effect on the regulatory approval process in others. For example, even if the FDA grants marketing approval of a product candidate, comparable regulatory authorities in foreign jurisdictions must also approve the manufacturing, marketing, and promotion of that product candidate in those countries. Approval procedures vary among jurisdictions and can involve requirements and administrative review periods different from those in the United States, including additional preclinical studies or clinical trials, as clinical studies conducted in one jurisdiction may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other jurisdictions. In many jurisdictions outside the United States, a product candidate must be approved for reimbursement before it can be approved for sale in that jurisdiction. In some cases, the price that we intend to charge for our products is also subject to approval.
47
Current and future legislation may increase the difficulty and cost for us to obtain marketing approval of and commercialize our initial or subsequent product candidates and affect the prices we may obtain.
In the United States and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could prevent or delay marketing approval for JAN 101, restrict, or regulate post-approval activities and affect our ability to profitably sell JAN 101. Legislative and regulatory proposals have been made to expand post-approval requirements and restrict sales and promotional activities for pharmaceutical products. We do not know whether additional legislative changes will be enacted, or whether the FDA regulations, guidance, or interpretations will be changed, or what the impact of such changes on the marketing approvals of JAN 101, if any, may be. In addition, increased scrutiny by Congress of the FDA’s approval process may significantly delay or prevent marketing approval, as well as subject us to more stringent product labeling and post-marketing testing and other requirements.
Any termination or suspension of, or delays in the commencement or completion of, any necessary studies of any of our product candidate for any indications could result in increased costs to us, delay or limit our ability to generate revenue and adversely affect our commercial prospects.
The commencement and completion of clinical studies can be delayed for a number of reasons, including delays related to: (i) the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority failing to grant permission to proceed and placing the clinical study on hold; (ii) subjects for clinical testing failing to enroll or remain enrolled in our trials at the rate we expect; (iii) a facility manufacturing our initial or subsequent product candidates being ordered by the FDA or other government or regulatory authorities to shut down, temporarily or permanently, due to violations of cGMP requirements or other applicable requirements, or cross-contaminations of the product candidates in the manufacturing process; (iv) any changes to our manufacturing process that may be necessary or desired; (v) subjects choosing an alternative treatment for the indications for which we are developing our initial or subsequent product candidates, or participating in competing clinical studies; (vi) subjects experiencing severe or unexpected drug-related adverse effects; (vii) reports from clinical testing on similar technologies and products raising safety and/or efficacy concerns; (viii) third-party clinical investigators losing their licenses or permits necessary to perform our clinical trials, not performing our clinical trials on our anticipated schedule, or employing methods consistent with the clinical trial protocol, cGMP requirements, or other third parties not performing data collection and analysis in a timely or accurate manner; (ix) inspections of clinical study sites by the FDA, comparable foreign regulatory authorities, or IRBs finding regulatory violations that require us to undertake corrective action, result in suspension or termination of one or more sites or the imposition of a clinical hold on the entire study, or that prohibit us from using some or all of the data in support of our marketing applications; (x) third-party contractors becoming debarred or suspended or otherwise penalized by the FDA or other government or regulatory authorities for violations of regulatory requirements, in which case we may need to find a substitute contractor, and we may not be able to use some or any of the data produced by such contractors in support of our marketing applications; (xi) one or more IRBs refusing to approve, suspending, or terminating the study at an investigational site, precluding enrollment of additional subjects, or withdrawing its approval of the trial; (xii) reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective contract research organizations, or CROs, and clinical trial sites, the terms of which can be subject to extensive negotiation and may vary significantly among different CROs and trial sites; (xiii) deviations of the clinical sites from trial protocols or dropping out of a trial; (xiv) adding new clinical trial sites; (xv) the inability of the CRO to execute any clinical trials for any reason; and (xvi) government or regulatory delays or “clinical holds” requiring suspension or termination of a trial.
Product development costs for our initial and any subsequent product candidates will increase if we have delays in testing or approval or if we need to perform more or larger clinical studies than planned. Additionally, changes in regulatory requirements and policies may occur and we may need to amend study protocols to reflect these changes. Amendments may require us to resubmit our study protocols to the FDA, comparable foreign regulatory authorities, and IRBs for reexamination, which may impact the costs, timing, or successful completion of that study. If we experience delays in completion of, or if we, the FDA or other regulatory authorities, the IRB, or other reviewing entities, or any of our clinical study sites suspend or terminate any of our clinical studies of any of our product candidates, their commercial prospects may be materially harmed and our ability to generate product revenues will be delayed. Any delays in completing our clinical trials will increase our costs, slow our development and approval process, and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenues. Any of these occurrences may harm our business, financial condition, and prospects significantly. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or lead to, termination or suspension of, or a delay in the commencement or completion of, clinical studies may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of one of more of our product candidates. In addition, if one or more clinical studies are delayed, our competitors may be able to bring competing products to market before we do, and the commercial viability of our affected product candidates could be significantly reduced.
48
Third-party coverage and reimbursement and health care cost containment initiatives and treatment guidelines may constrain our future revenues.
Our ability to market JAN 101 successfully will depend in part on the level of reimbursement that government health administration authorities, private health coverage insurers, and other organizations provide for the cost of JAN 101 and related treatments. Countries in which JAN 101 is sold through reimbursement schemes under national health insurance programs frequently require that manufacturers and sellers of pharmaceutical products obtain governmental approval of initial prices and any subsequent price increases. In certain countries, including the United States, government-funded and private medical care plans can exert significant indirect pressure on prices. We may not be able to sell JAN 101 profitably if adequate prices are not approved or coverage and reimbursement is unavailable or limited in scope. Increasingly, third-party payors attempt to contain health care costs in ways that are likely to impact the development of our product including: (i) failing to approve or challenging the prices charged for health care products; (ii) introducing reimportation schemes from lower priced jurisdictions; (iii) limiting both coverage and the amount of reimbursement for new therapeutic products; (iv) denying or limiting coverage for products that are approved by the regulatory agencies but are considered to be experimental or investigational by third-party payors; and (v) refusing to provide coverage when an approved product is used in a way that has not received regulatory marketing approval.
It is difficult and costly to protect our intellectual property rights, and we cannot ensure the protection of these rights.
Our success depends on successfully blocking others from developing and commercializing similar products. As a repurposed drug, our API has previously been approved for other indications, none of which currently represent a threat to our product, and therefore cannot be protected. We will rely on our method of use and oral formulation patents to protect our product, which may also put our product at risk from companies developing oral formulations using the same API for other indications. Even though our patents provide protection for specific uses, we will not be able to prevent other companies from developing the same API for other uses. If a similar dose, formulation and route of administration is developed for another indication by a different company, we cannot guarantee that the product they market for the other indication will not be prescribed off-label by doctors or filled by pharmacists for use in indications our patents cover and that if less expensive, would not negatively affect our sales, if our product is ultimately approved by the FDA
The degree of future protection afforded by the patent rights licensed to us is uncertain, because legal means afford only limited protection and may not adequately protect our rights, permit us to gain or keep our competitive advantage, or provide us with any competitive advantage at all. We cannot be certain that any patent application owned by a third party will not have priority over patent applications in which we hold license rights or that we will not be involved in interference, opposition or invalidity proceedings before United States or foreign patent offices.
Additionally, if the Licensors were to initiate legal proceedings against a third party to enforce a patent covering JAN 101, the defendant could counterclaim that such patent is invalid and/or unenforceable. In patent litigation in the United States, defendant counterclaims alleging invalidity and/or unenforceability are commonplace. Grounds for a validity challenge include alleged failures to meet any of several statutory requirements, including lack of novelty, obviousness, or non-enablement. Grounds for unenforceability assertions include allegations that someone connected with prosecution of the patent withheld relevant information from the United States Patent and Trademark Office (the “PTO”) or made a misleading statement during prosecution. Third parties may also raise similar claims before administrative bodies in the United States or abroad, even outside the context of litigation. Such mechanisms include regarding-examination, post-grant review, and equivalent proceedings in foreign jurisdictions, e.g., opposition proceedings. Such proceedings could result in revocation or amendment of the Licensors’ patents in such a way that they no longer cover JAN 101 or competitive products. The outcome following legal assertions of invalidity and unenforceability is unpredictable. With respect to validity, for example, we cannot be certain that there is no invalidating prior art, of which the Licensors and the patent examiner were unaware during prosecution. If a defendant were to prevail on a legal assertion of invalidity and/or unenforceability, we would lose at least part, and perhaps all, of the patent protection on any of our product candidates. Such a loss of patent protection would have a material adverse impact on our business.
49
In the future, we may rely on know-how and trade secrets to protect technology, especially in cases in which we believe patent protection is not appropriate or obtainable. However, know-how and trade secrets are difficult to protect. While we intend to require employees, academic collaborators, consultants, and other contractors to enter into confidentiality agreements, we may not be able adequately to protect our trade secrets or other proprietary or licensed information. Typically, research collaborators and scientific advisors have rights to publish data and information in which we may have rights. Enforcing a claim that a third party illegally obtained and is using any of our trade secrets is expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts are sometimes less willing to protect trade secrets than patents. Moreover, our competitors may independently develop equivalent or better knowledge, methods, and know-how.
If we fail to obtain or maintain patent protection or trade secret protection for our product candidates or our technologies, third parties could use our proprietary information, which could impair our ability to compete in the market and adversely affect our ability to generate revenues and attain profitability.
It is difficult and costly to block others from developing similar products for other indications, and we cannot ensure that these products will not be less expensive and thus be prescribed off-label by physicians for use in our indications.
Our success depends on successfully blocking others from developing and commercializing similar products. As a repurposed drug, our API has previously been approved for other indications, none of which currently represents a threat to JAN 101, and therefore cannot be protected. We will rely on our method of use and oral formulation patents to protect JAN 101, which may also put JAN 101 at risk from companies developing oral formulations using the same API for other indications. Even though our patents provide protection for specific uses, we will not be able to prevent other companies from developing the same API for other uses. If a similar dose, formulation, and route of administration is developed for another indication by a different company, we cannot guarantee that the product they market for the other indication will not be prescribed off-label by doctors or filled by pharmacists for use in indications our patents cover and that if less expensive, would not negatively affect our sales, if JAN 101 is ultimately approved by the FDA.
JAN 101 may infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which could increase our costs and delay or prevent our development and commercialization efforts.
Our success depends in part on avoiding infringement of the proprietary technologies of others. The pharmaceutical industry has been characterized by frequent litigation regarding patent and other intellectual property rights. Identification of third-party patent rights that may be relevant to our proprietary technology is difficult because patent searching is imperfect due to differences in terminology among patents, incomplete databases, and the difficulty in assessing the meaning of patent claims. Additionally, because patent applications are maintained in secrecy until the application is published, we may be unaware of third-party patents that may be infringed by commercialization of JAN 101 or any subsequent product candidate. There may be certain issued patents and patent applications claiming subject matter that we may be required to license in order to research, develop, or commercialize any of our product candidates, and we do not know if such patents and patent applications would be available to license on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. Any claims of patent infringement asserted by third parties would be time-consuming and may: (i) result in costly litigation; (ii) divert the time and attention of our technical personnel and management; (iii) prevent us from commercializing a product candidate until the asserted patent expires or is held finally invalid or not infringed in a court of law; (iv) require us to cease or modify our use of the technology and/or develop non-infringing technology; or (v) require us to enter into royalty or licensing agreements.
Third parties may hold proprietary rights that could prevent JAN 101 from being marketed. Any patent-related legal action against us claiming damages and seeking to enjoin commercial activities relating to any of our product candidates or our processes could subject us to potential liability for damages and require us to obtain a license to continue to manufacture or market JAN 101 or any subsequent product candidates. We cannot predict whether we would prevail in any such actions or that any license required under any of these patents would be made available on commercially acceptable terms, if at all. In addition, we cannot be sure that we could redesign JAN 101 or any subsequent product candidates or processes to avoid infringement, if necessary. Accordingly, an adverse determination in a judicial or administrative proceeding, or the failure to obtain necessary licenses, could prevent us from developing and commercializing JAN 101 or a subsequent product candidate, which could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
50
We expect that there are other companies, including major pharmaceutical companies, working in the areas competitive to JAN 101 that either have resulted, or may result, in the filing of patent applications that may be deemed related to our activities. If we were to challenge the validity of these or any issued United States patent in court, we would need to overcome a statutory presumption of validity that attaches to every issued United States patent. This means that, in order to prevail, we would have to present clear and convincing evidence as to the invalidity of the patent’s claims. If we were to challenge the validity of these or any issued United States patent in an administrative trial before the Patent Trial and Appeal Board in the PTO, we would have to prove that the claims are unpatentable by a preponderance of the evidence. There is no assurance that a jury and/or court would find in our favor on questions of infringement, validity, or enforceability. Even if we are successful, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management.
GENERAL RISK FACTORS
Isaac Capital Group, LLC (“ICG”) owns a large percentage of our voting stock, which may allow it to control substantially all matters requiring stockholder approval.
Currently, ICG owns approximately 18.7% of our outstanding shares of common stock. ICG’s sole member is Jon Isaac, the President and Chief Executive Officer of Live Ventures. Jon Isaac is the son of our Chief Executive Officer Tony Isaac. Because of such ownership and the relationship, ICG may be able significantly, and possibly adversely, to affect our corporate decisions, including the election of the board of directors.
The market price of our common stock has been, and may continue to be volatile and fluctuate significantly, which could result in substantial losses for investors and subject us to securities class action litigation.
The trading price for our common stock has been, and we expect it to continue to be, volatile. The price at which our common stock trades depends upon a number of factors, including our historical and anticipated operating results, our financial situation, announcements of technological innovations or new products by us, our ability or inability to raise the additional capital we may need and the terms on which we raise it, and general market and economic conditions. Some of these factors are beyond our control. Broad market fluctuations may lower the market price of our common stock and affect the volume of trading in our stock, regardless of our financial condition, results of operations, business or prospect. Among the factors that may cause the market price of our common stock to fluctuate are the risks described in this “Risk Factors” section. In addition, the stock markets, in general, The Nasdaq Capital Market and the market for biopharmaceutical companies in particular, may experience a loss of investor confidence. Such loss of investor confidence may result in extreme price and volume fluctuations in our common stock that are unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of our business, financial condition or results of operations. These broad market and industry factors may materially harm the market price of our common stock and expose us to securities class action litigation. Such litigation, even if unsuccessful, could be costly to defend and divert management’s attention and resources, which could further materially harm our financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be able to maintain compliance with the continued listing requirements of The Nasdaq Global Market.
Our common stock is listed on the Nasdaq Global Market. In order to maintain that listing, we must satisfy minimum financial and other requirements including, without limitation, a requirement that our closing bid price be at least $1.00 per share. If we fail to continue to meet all applicable continued listing requirements for The Nasdaq Global Market in the future and Nasdaq determines to delist our common stock, the delisting could adversely affect the market liquidity of our common stock, our ability to obtain financing to repay debt, and fund our operations.
51
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
Our executive offices are located in Las Vegas, Nevada in a leased facility consisting of 11,000 square feet of office space.
Recycling Centers
We lease the recycling center facilities described below.
Approximate Ft2 |
|
Location |
18,500 |
|
Santa Fe Springs, California |
9,200 |
|
Newark, California |
12,900 |
|
Sacramento, California |
14,800 |
|
Tulare, California |
7,500 |
|
Commerce City, Colorado |
12,600 |
|
North Haven, Connecticut |
14,700 |
|
Norcross, Georgia |
19,800 |
|
Franklin, Massachusetts |
3,000 |
|
Baltimore, Maryland |
6,500 |
|
Edina, Minnesota |
27,000 |
|
Hainesport, New Jersey |
5,900 |
|
Albuquerque, New Mexico |
5,100 |
|
Dartmouth, Nova Scotia |
7,900 |
|
Syracuse, New York |
23,200 |
|
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania |
9,600 |
|
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania |
8,100 |
|
Mechanicsburg, Pennsylvania |
14,500 |
|
Kent, Washington |
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
The information in response to this item is included in Note 17, Commitments and Contingencies, to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8, of this Form 10-K.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
None.
52
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR OUR COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information and Dividends
Our common stock trades under the symbol “JAN” on The Nasdaq Capital Market. As of April 12, 2023, there were 37 stockholders of record, which excludes stockholders whose shares were held in nominee or street name by brokers. We have no record of the number of holders of our common stock who hold their shares in “street name” with various brokers.
We have not paid dividends on our common stock and do not presently plan to pay dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future.
Information concerning securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans is included in Part III, Item 12 of this report.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
Not applicable.
53
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
For a description of our significant accounting policies and an understanding of the significant factors that influenced our performance during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, this “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” (hereafter referred to as “MD&A”) should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements, including the related notes, appearing in Part II, Item 8 of this 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022.
Note about Forward-Looking Statements
This Form 10-K includes statements that constitute “forward-looking statements.” These forward-looking statements are often characterized by the terms “may,” “believes,” “projects,” “intends,” “plans,” “expects,” or “anticipates,” and do not reflect historical facts. Specific forward-looking statements contained in this portion of the Form 10-K include, but are not limited to: (i) statements relating to JAN 101, JAN101, including statements relating to the commencement of Phase IIb clinical trials for the treatment of PAD in 2021 and the results of those trials, (ii) statements that are based on current projections and expectations about the markets in which we operate, (iii) statements relating to the prospective sale of our Recycling business, (iv) statements about current projections and expectations of general economic conditions, (v) statements about specific industry projections and expectations of economic activity, (vi) statements relating to our future operations and prospects, (vii) statements about future results and future performance, (viii) statements that the cash on hand and additional cash generated from operations, together with potential sources of cash through issuance of debt or equity, will provide the Company with sufficient liquidity for the next 12 months, and (ix) statements that the outcome of pending legal proceedings will not have a material adverse effect on business, financial position and results of operations, cash flow, or liquidity.
Forward-looking statements involve risks, uncertainties, and other factors, which may cause our actual results, performance, or achievements to be materially different from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Factors and risks that could affect our results, future performance, and capital requirements and cause them to differ materially from those contained in the forward-looking statements include those identified in this Form 10-K under Item 1A “Risk Factors”, as well as other factors that we are currently unable to identify or quantify, but that may exist in the future.
In addition, the foregoing factors may generally affect our business, results of operations and financial position. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date the statements were made. We do not undertake and specifically decline any obligation to update any forward-looking statements. Any information contained on our website www.janone.com or any other websites referenced in this Form 10-K are not part of this Form 10-K.
Our Company
We are focused on finding treatments for conditions that cause severe pain and bringing to market drugs with non-addictive pain-relieving properties. In addition, through our subsidiaries ARCA Recycling, Connexx, and ARCA Canada, we are engaged in the business of recycling major household appliances in North America by providing turnkey appliance recycling and replacement services for utilities and other sponsors of energy efficiency programs. Also, through our GeoTraq Inc. subsidiary, we have been engaged in the development and design of wireless transceiver modules with technology that provides LBS directly from global Mobile IoT networks. However, Our GeoTraq subsidiary has not generated any revenue to date, including in the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. Consequently, during the year ended January 1, 2022, the Company took a full write-down of the unamortized portion of the GeoTraq intangible asset of approximately $9.8 million, and, on May 24, 2022, we sold substantially all of the GeoTraq assets (see Note 26 to the Consolidated Financial Statements below).
We operate three reportable segments:
54
Reporting Period. We report on a 52-or 53-week fiscal year. Our 2022 fiscal year ended on December 31, 2022 (“fiscal 2022”). Our 2022 fiscal year ended on January 1, 2022 (“fiscal 2021”).
Application of Critical Accounting Policies
Our discussion of the financial condition and results of operations is based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of our consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of any contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements. Management regularly reviews its estimates and assumptions, which are based on historical factors and other factors believed to be relevant under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions, estimates or conditions.
Critical accounting policies are defined as those that are reflective of significant judgments and uncertainties and potentially result in materially different results under different assumptions and conditions. ARCA Recycling’s critical accounting policies include intangible impairment under ASC 350, revenue recognition under ASC 606, and going concern under ASC 205.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth certain statement of operations items from continuing and discontinued operations and as a percentage of revenue, for the periods indicated (in $000's):
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended |
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended |
|
||||||||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
Statement of Operations Data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Revenues |
|
$ |
39,611 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
$ |
40,022 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
% |
Cost of revenues |
|
|
31,992 |
|
|
|
80.8 |
% |
|
|
31,154 |
|
|
|
77.8 |
% |
Gross profit |
|
|
7,619 |
|
|
|
19.2 |
% |
|
|
8,868 |
|
|
|
22.2 |
% |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
11,790 |
|
|
|
29.8 |
% |
|
|
12,089 |
|
|
|
30.2 |
% |
Operating loss |
|
|
(4,171 |
) |
|
|
(10.5 |
)% |
|
|
(3,221 |
) |
|
|
(8.0 |
)% |
Gain on debt settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
0.0 |
% |
|
|
1,799 |
|
|
|
4.5 |
% |
Interest expense, net |
|
|
(489 |
) |
|
|
(1.2 |
)% |
|
|
(773 |
) |
|
|
(1.9 |
)% |
Gain (loss) on litigation settlement |
|
|
942 |
|
|
|
2.4 |
% |
|
|
(1,950 |
) |
|
|
(4.9 |
)% |
Gain on settlement of vendor advance payments |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
0.0 |
% |
|
|
952 |
|
|
|
2.4 |
% |
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
|
|
(631 |
) |
|
|
(1.6 |
)% |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Gain on reversal of contingency loss |
|
|
637 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Other income, net |
|
|
630 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
|
152 |
|
|
|
0.4 |
% |
Net loss before provision for income taxes |
|
|
(3,082 |
) |
|
|
(7.8 |
)% |
|
|
(3,041 |
) |
|
|
(7.6 |
)% |
Income tax provision |
|
|
(6,671 |
) |
|
|
(16.8 |
)% |
|
|
273 |
|
|
|
0.7 |
% |
Net loss from continuing operations |
|
|
3,589 |
|
|
|
9.1 |
% |
|
|
(3,314 |
) |
|
|
(8.3 |
)% |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations |
|
|
9,562 |
|
|
|
24.1 |
% |
|
|
(13,573 |
) |
|
|
(33.9 |
)% |
Income tax provision for discontinued operations |
|
|
2,159 |
|
|
|
5.5 |
% |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Net income (loss) from discontinued operations |
|
|
7,403 |
|
|
|
18.7 |
% |
|
|
(13,573 |
) |
|
|
(33.9 |
)% |
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
10,992 |
|
|
|
27.7 |
% |
|
$ |
(16,887 |
) |
|
|
(42.2 |
)% |
55
The following tables set forth revenues for key product and service categories, percentages of total revenue and gross profits earned by key product and service categories and gross profit percent as compared to revenues for each key product category indicated (in $000's):
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended |
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended |
|
||||||||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
Net |
|
|
Percent |
|
|
Net |
|
|
Percent |
|
||||
|
|
Revenue |
|
|
of Total |
|
|
Revenue |
|
|
of Total |
|
||||
Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Recycling and Byproducts |
|
$ |
23,264 |
|
|
|
58.7 |
% |
|
$ |
21,603 |
|
|
|
54.0 |
% |
Replacement Appliances |
|
|
16,347 |
|
|
|
41.3 |
% |
|
|
18,419 |
|
|
|
46.0 |
% |
Total Revenue |
|
$ |
39,611 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
$ |
40,022 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended |
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended |
|
||||||||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
Gross |
|
|
Gross |
|
|
Gross |
|
|
Gross |
|
||||
|
|
Profit |
|
|
Profit % |
|
|
Profit |
|
|
Profit % |
|
||||
Gross Profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Recycling and Byproducts |
|
$ |
1,548 |
|
|
|
6.7 |
% |
|
$ |
2,897 |
|
|
|
13.4 |
% |
Replacement Appliances |
|
|
6,071 |
|
|
|
37.1 |
% |
|
|
5,971 |
|
|
|
32.4 |
% |
Total Gross Profit |
|
$ |
7,619 |
|
|
|
19.2 |
% |
|
$ |
8,868 |
|
|
|
22.2 |
% |
Revenue
Revenue decreased by approximately $400,000, or 1.0%, for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 as compared to the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. Recycling and Byproduct revenue increased by approximately $1.7 million primarily due to stronger demand, partially offset by lower byproduct commodity pricing. Replacement Appliances revenue decreased by approximately $2.1 million or 11.2%, primarily due to decreased sales volume. We generated no revenue from discontinued operations for the years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenue increased by approximately $840,000, or 2.7% for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 as compared to the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. Recycling and Byproducts cost of revenue increased by approximately $3.0 million, or 16.1%, which generally aligns with increases in revenue. Replacement Appliances cost of revenue decreased by approximately $2.2 million primarily due to decreases in revenue. Both Replacement Appliances and Recycling and Byproducts cost of revenue were impacted by higher transportation, facilities and labor costs. As no revenue was generated for the years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, we did not incur any costs of revenue for these periods.
Selling, General and Administrative Expense
Selling, general and administrative expenses from decreased by approximately $300,000, or 2.5%, for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 as compared to the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022, primarily due to lower amortization costs, legal and professional fees and share based compensation, partially offset by an increase in labor costs. Selling, general and administrative expenses from discontinued operations was a gain of approximately $9.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, primarily due to the gain on sale of GeoTraq, and expense of approximately $13.6 million for the year ended January 1, 2022, primarily due to recording full impairment of the GeoTraq intangible.
Interest Expense, net
Interest expense, net, decreased by approximately $284,000 or 36.7%, for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 as compared to the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022 primarily due to interest income related to the accretion of discount relating to the SPYR note receivable, and lower interest rates on revolver debt due to the change of credit facility.
56
Impairment Charges
Impairment charges of approximately $9.8 million from discontinued operations were recorded for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022 due to the full impairment of our GeoTraq intangible. This amount is reflected as a component of Net income (loss) from discontinued operations in the table above. See Note 9 of the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of this matter. No impairment charges were recorded for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022.
Gain on Sale of GeoTraq
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, we recorded a gain on the sale of GeoTraq of approximately $9.4 million from discontinued operations. See Note 26 of the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Unrealized Loss on Marketable Securities
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, an unrealized loss on marketable securities of approximately $631,000 was recorded to mark to fair value securities received in connection to the sale of GeoTraq. See Note 10 of Consolidated Financial Statements. There were no similar transactions for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022.
Gain (Loss) on Litigation Settlement, net
For the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company recorded a gain on litigation settlement of approximately $942,000 due to the receipt of a $1.95 million payment from Sompo International Companies (“Sompo”) in exchange for a full release in favor of Sampo from liability for both the GeoTraq and SEC-related matters, partially offset by an accrual of approximately $894,000 for the Skybridge settlement (see Note 17 of the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of this matter), and an accrual of approximately $115,000 for adjudication of the Blackhawk matter. For the year ended January 1, 2022, the Company recorded a loss on litigation settlement of approximately $2.0 million due to payments made under the terms of a settlement agreement with Gregg Sullivan (see Note 17 of the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of this matter).
Gain on Reversal of Contingency Loss
Gain on reversal of continency liabilities of approximately $637,000 relating to guarantees of ApplianceSmart leases that no longer exist as a result of ApplianceSmart's emergence from bankruptcy (see Notes 17 and 24 to the Consolidated Financial Statements).
Other Income, net
Other income, net from continuing operations was approximately $630,000 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 as compared to income of approximately $152,000 the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. Other income from discontinued operations was approximately $144,000 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, as compared to expense of approximately $96,000 for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022.
Segment Reporting
We report our business in the following segments: Biotechnology, Recycling, and Technology. We identified these segments based on a combination of business type, customers serviced, and how we divide management responsibility. Our revenues and profits are driven through our recycling centers, e-commerce, individual sales representatives, and our internet services for our recycling and technology segment. We expect revenues and profits for our biotechnology segment to be driven by the development of pharmaceuticals that treat the root cause of pain but are non-opioid painkillers. We include Corporate expenses within the Recycling segment. As discussed above, we sold our Technology segment, GeoTraq, during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, and detail its results as discontinued operations below.
57
Operating income (loss) by operating segment, is defined as income (loss) before net interest expense, other income and expense, provision for income taxes.
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2022 |
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended January 1, 2022 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Biotechnology |
|
|
Recycling |
|
|
Continuing Operations |
|
|
Discontinued Operations |
|
|
Total |
|
|
Biotechnology |
|
|
Recycling |
|
|
Continuing Operations |
|
|
Discontinued Operations |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||||||
Revenue |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
39,611 |
|
|
$ |
39,611 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
39,611 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
40,022 |
|
|
$ |
40,022 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
40,022 |
|
Cost of revenue |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
31,992 |
|
|
|
31,992 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
31,992 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
31,154 |
|
|
|
31,154 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
31,154 |
|
Gross profit |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
7,619 |
|
|
|
7,619 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
7,619 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,868 |
|
|
|
8,868 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,868 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expense |
|
|
414 |
|
|
|
11,376 |
|
|
|
11,790 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
11,800 |
|
|
|
1,351 |
|
|
|
10,738 |
|
|
|
12,089 |
|
|
|
3,767 |
|
|
|
15,856 |
|
Impairment charges |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
9,783 |
|
|
|
9,783 |
|
Gain on sale of GeoTraq |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(9,428 |
) |
|
|
(9,428 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
||
Operating loss |
|
$ |
(414 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,757 |
) |
|
$ |
(4,171 |
) |
|
$ |
9,418 |
|
|
$ |
5,247 |
|
|
$ |
(1,351 |
) |
|
$ |
(1,870 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,221 |
) |
|
$ |
(13,550 |
) |
|
$ |
(16,771 |
) |
Biotechnology Segment
For the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, respectively, our biotechnology segment incurred expenses of approximately $414,000 and $1.4 million, related to employee costs and professional services related to research.
Recycling Segment
Our recycling segment consists of ARCA Recycling, Connexx, and ARCA Canada. Revenue decreased by approximately $400,000, or 1.0%, for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 as compared to the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. Recycling and Byproduct revenue increased by approximately $1.7 million primarily due to stronger demand, partially offset by lower byproduct commodity pricing. Replacement Appliances revenue decreased by approximately $2.1 million or 11.2%, primarily due to decreased sales volume.
Cost of revenue increased by approximately $840,000, or 2.7%, for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, as compared to the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. Recycling and Byproducts cost of revenue increased by approximately $3.0 million, or 16.1%, which generally aligns with increases in revenue. Replacement Appliances cost of revenue decreased by approximately $2.2 million primarily due to lower appliance costs. Both Replacement Appliances and Recycling and Byproducts cost of revenue were impacted by higher transportation, facilities and labor costs.
Operating loss for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, increased by approximately $1.9 million as compared to the prior year period. The increase in operating loss was due to a decrease in gross margin and an increase in labor costs, partially offset by decreases in legal and professional fees.
Discontinued Operations
Our discontinued operations consists of GeoTraq, which was sold during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022. Operating income for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 increased by approximately $23.0 million, as compared to the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. The increase in operating income is due to the gain on sale of the GeoTraq intangible, in the amount of approximately $9.4 million (see Note 27 to the Consolidated Financial Statements below), as well as the suspension of operations that occurred in connection to the sale.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared under the assumption that we will continue as a going concern. Such assumption contemplates the realization of assets and satisfaction of liabilities in the normal course of business.
As of December 31, 2022, our cash on hand was $115,000. We intend to fund operations by using cash on hand, monthly revenues from the sale of our Subsidiaries, and funds received from approved Employee Retention Credits (“ERC’s”). Debt recorded, as of December 31, 2022, belongs to the Subsidiaries, and will no longer impact us as of the date of sale. We intend to raise funds to support future development of JAN 123 either through capital raises or structured arrangements.
58
Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon the success of future capital raises or structured settlements to fund the required testing to obtain FDA approval of JAN 123, as well as to fund our day-to-day operations. The accompanying financial statements do not include any adjustments that might be necessary should we be unable to continue as a going concern. While we will actively pursue these additional sources of financing, management cannot make any assurances that such financing will be secured.
Cash Flows
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, cash used in operations was approximately $3.1 million, compared to cash used in operations of approximately $5.3 million during the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022. The decrease in cash used in operations was primarily due to changes in deferred tax assets, and changes in assets and liabilities. Cash used in operating activities from discontinued operations during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 was approximately $10,000, as compared to approximately $23,000 for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022.
Cash used in investing activities was approximately $1.5 million for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, and was primarily due to purchases of property and equipment and intangibles. Cash used in investing activities of approximately $1.7 million for fiscal year ended January 1, 2022 was primarily due to purchases of property and equipment and intangibles.
Cash provided by financing activities was approximately $4.0 million for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 was primarily due to proceeds net of repayments of approximately $4.1 million from notes payable, partially offset by payments of $162,000 on a related party note. Cash provided by financing activities was approximately $7.4 million for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022 was primarily due to net proceeds of approximately $5.5 million from an equity financing, and approximately $1.8 million in proceeds from notes payable, net of repayments.
Sources of Liquidity
We acknowledge that we continue to face a challenging competitive environment as we continue to focus on our overall profitability, including managing expenses. We reported net income of approximately $3.6 million from continuing operations in fiscal 2022, primarily due to a tax benefit of approximately $6.7 million, and a loss from continuing operations of approximately $3.3 million in fiscal 2021. Additionally, the Company has total current assets of approximately $9.2 million and total current liabilities approximately of $23.9 million resulting in a net negative working capital of approximately $14.8 million. Cash used in operations was approximately $3.1 million.
In Item 1A. Risk Factors, management has addressed and evaluated the risk factors that could materially and adversely affect the entity’s business, financial condition and results of operations, cash flows, and liquidity. The Company has determined that the risk factors do not materially affect the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern within one year after the date that the financial statements are issued.
Based on the above, management has concluded that the Company is not aware and did not identify any other conditions or events that would cause the Company to not be able to continue business as a going concern for the next 12 months.
Future Sources of Cash; New Acquisitions, Products and Services
We may require additional debt financing and/or capital to finance new acquisitions, refinance existing indebtedness or consummate other strategic investments in our business. Any financing obtained may further dilute or otherwise impair the ownership interest of our existing stockholders.
On March 22, 2023, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with certain institutional investors (the “Purchasers”) for the sale by the Company in a registered direct offering (the “Offering”) of 361,000 shares of the Company’s Common Stock at a purchase price per share of Common Stock of $1.17. The Offering closed on March 24, 2023.
The aggregate gross proceeds for the sale of the shares of Common Stock were approximately $422,000, before deducting the placement agent fees and related expenses. The Company intends to use the net proceeds for working capital and general corporate purposes.
59
The Purchase Agreement contains customary representations, warranties and agreements by the Company and the Purchasers and customary indemnification rights and obligations of the parties. Pursuant to the terms of the Purchase Agreement, the Company has agreed to certain restrictions on the issuance and sale of its shares of Common Stock or Common Stock Equivalents (as defined in the Purchase Agreement) during the 15-day period following the closing of the Offering and certain restrictions on issuing any shares of Common Stock or Common Stock Equivalents in a Variable Rate Transaction (as defined in the Purchase Agreement) for twelve (12) months following the closing of the Offering.
H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC acted as the sole placement agent (the “Placement Agent”) for the Company on a “reasonable best efforts” basis in connection with the Offering. In connection with the closing of the Offering, the Placement Agent received an aggregate cash fee of 7.0% of the gross proceeds paid to the Company for the securities, a management fee of 1.0% of the gross proceeds raised in the Offering and reimbursement for accountable expenses incurred by it in connection with the Offering of $20,000. In addition, the Company granted warrants (the “Placement Agent Warrants”) to the Placement Agent, or its designees, to purchase up to an aggregate of 25,270 shares of the Company’s common stock. The Placement Agent Warrants have a per-share exercise price of $1.4625 and are exercisable through and including March 24, 2028.
The shares of Common Stock sold in the Offering were offered and sold by the Company pursuant to an effective shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-251645), which was initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 23, 2020, and was declared effective on December 29, 2020. The Company will file a prospectus supplement with the SEC in connection with the sale of the Common Stock.
The representations, warranties and covenants contained in the Purchase Agreement were made solely for the benefit of the parties to the Purchase Agreement. In addition, such representations, warranties, and covenants (i) are intended as a way of allocating the risk between the parties to the Purchase Agreement and not as statements of fact, and (ii) may apply standards of materiality in a way that is different from what may be viewed as material by stockholders of, or other investors in, the Company. Accordingly, the Purchase Agreement is included with this filing only to provide investors with information regarding the terms of the transaction, and not to provide investors with any other factual information regarding the Company. Stockholders should not rely on the representations, warranties, and covenants or any descriptions thereof as characterizations of the actual state of facts or condition of the Company or any of its subsidiaries or affiliates. Moreover, information concerning the subject matter of the representations and warranties may change after the date of the Purchase Agreement, which subsequent information may or may not be fully reflected in public disclosures.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
At December 31, 2022, we had no off-balance sheet arrangements, commitments or guarantees that require additional disclosure or measurement.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Market Risk and Impact of Inflation
Interest Rate Risk. We do not believe there is any significant risk related to interest rate fluctuations on our short and long-term fixed rate debt.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk. We currently generate revenues in Canada. The reporting currency for our consolidated financial statements is United States dollars. It is not possible to determine the exact impact of foreign currency exchange rate changes; however, the effect on reported revenue and net earnings can be estimated. We estimate that the overall strength of the United States dollar against the Canadian dollar had an immaterial impact on the revenues and net income for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022. We do not currently hedge foreign currency fluctuations and do not intend to do so for the foreseeable future.
We do not hold any derivative financial instruments, nor do we hold any securities for trading or speculative purposes.
60
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Description |
|
Page |
|
|
|
Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-1 |
|
|
F-4 |
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Financial Statements |
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022 |
|
F-5 |
|
F-6 |
|
|
F-7 |
|
|
F-8 |
|
|
F-9 |
61
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and Board of Directors of
JanOne Inc.
Las Vegas, Nevada
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of JanOne Inc. (the "Company") as of December 31, 2022, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss), changes in stockholders' equity (deficit) and cash flows for the year then ended, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2022, and the results of their operations and cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”).
Substantial Doubt About the Company’s Ability to Continue as a Going Concern
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has negative working capital, an accumulated deficit, a history of significant operating losses from continuing operations, and a history of negative operating cash flow. These factors raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management's plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
F-1
Valuation of Note Receivable
As described in Note 27 to the consolidated financial statements, on May 24, 2022, the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with SPYR Technologies Inc. (SPYR), pursuant to which the Company sold SPYR substantially all the assets of its wholly-owned subsidiary GeoTraq Inc. SPYR issued shares of its common stock and delivered a five-year promissory note for the acquisition consideration.
We identified the Company's valuation of the promissory note at the transaction date as a critical audit matter because of the significant estimates and assumptions management used in the estimate of the fair value, mainly as it relates to the selection of the discount rate. Auditing management's selection of the discount rate involved a high degree of auditor judgment and increased audit effort, including the use of our valuation specialists, as changes in this assumption could have a significant impact on the preliminary fair value of the promissory note received.
Our audit procedures related to the Company's fair value estimate of the promissory note received included the following, among others:
Valuation of purchase price consideration
As described in Note 3 to the consolidated financial statements, on December 28, 2022, the Company acquired Soin Therapeutics LLC (Soin) through an all-stock transaction. As part of the consideration of the transaction, the Company issued Soin shares of its Series S preferred convertible stock.
We identified the Company's valuation of the preferred shares issued as a critical audit matter because of the significant estimates and assumptions management used in its fair value estimate, including forecasted product revenues, the expected FDA approval date and the selection of discount rates. Auditing management's estimates of the forecasted product revenues, the expected FDA approval date and the selection of discount rates involves a high degree of auditor judgment and increased audit effort, including the use of our valuation specialists, as changes in these assumptions could have a significant impact on the acquisition date fair value of the purchase price consideration.
Our audit procedures related to the Company's estimate of the fair value of the preferred Series S shares included the following, among others:
F-2
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2023.
/s/
April 17, 2023
F-3
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and
Stockholders of JanOne Inc.
Las Vegas, Nevada
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of JanOne Inc. (the “Company”) as of January 1, 2022, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the year then ended, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of January 1, 2022, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the year then ended,in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ WSRP, LLC
We served as the Company's auditor from 2019 to 2022.
Salt Lake City, Utah
April 1, 2022, except for Note 27 to the consolidated financial statements, as to which the date is April 17, 2023.
F-4
JANONE INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Trade and other receivables, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current assets from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Right of use asset - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Intangible assets-Soin, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Intangible assets, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Note receivable, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deposits and other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other assets from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Liabilities, Mezzanine Equity, and Stockholders' Equity (Deficit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accrued liabilities - other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued liability - California sales taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Lease obligation short term - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Short term debt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current portion of note payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Related party note |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current liabilities from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Lease obligation long term - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred income taxes, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Notes payable - long term portion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Long-term portion related party note payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other noncurrent liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Mezzanine equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Convertible preferred stock, series S - par value $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Stockholders' equity (deficit): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Convertible preferred stock, series A-1 - par value $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Common stock, par value $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional paid in capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total stockholders' equity (deficit) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total liabilities, mezzanine equity, and stockholders' equity (deficit) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
JANONE INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Revenues |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Cost of revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Operating loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Other income (expense): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on debt settlement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Interest expense, net |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Gain (loss) on litigation settlement |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Gain on settlement of vendor advance payments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on reversal of contingent liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Other income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total other income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Loss before benefit from income taxes |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Income tax (benefit) provision |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Income (loss) from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Income tax provision for discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Income (loss) per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) per share from continuing operations, basic and diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Net income (loss) per share from discontinued operations, basic and diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Net income (loss) per share, basic and diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Effect of foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total other comprehensive loss, net of tax |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
JANONE INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(Dollars in thousands)
|
|
Series A Preferred |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||||
Balance, January 2, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|||||
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Share based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Series A-1 preferred converted |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
Stock option exercise |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Shares issued |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Balance, January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||||
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Share based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Series A-1 preferred converted |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Balance, December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
JANONE INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in thousands)
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Amortization of debt issuance costs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on Payroll Protection Program loan forgiveness |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Accretion of note receivable discount |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Stock based compensation expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on reversal of contingent liabilities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Impairment charges |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on sale of GeoTraq |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on settlement of vendor advance payments |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Amortization of right-of-use assets |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Change in deferred income taxes |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Gain on sale of property |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Loss on litigation settlement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Changes in assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accounts receivable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Income taxes receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Proceeds from the sale of property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Purchase of intangible assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Proceeds from note payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Payment on related party note |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of short term notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Payments on short term notes payable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Proceeds from equity financing, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Payments on notes payable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Proceeds from stock option exercise |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Effect of changes in exchange rate on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
(DECREASE) INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Supplemental cash flow disclosures: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Noncash recognition of new leases |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Interest paid |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Income taxes paid, net |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-8
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1: Background and Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of JanOne Inc., a Nevada corporation, and its subsidiaries (collectively, the “Company” or “JanOne”).
The Company has
During September 2019, JanOne, through its biotechnology segment, broadened its business perspectives to become a pharmaceutical company focused on finding treatments for conditions that cause severe pain and bringing to market drugs with non-addictive pain-relieving properties.
ARCA Recycling, Inc. (“ARCA Recycling”) is the Company’s Recycling segment and provides turnkey recycling services for electric utility energy efficiency programs in the United States. ARCA Canada Inc. (“ARCA Canada”) provides turnkey recycling services for electric utility energy efficiency programs in Canada. Customer Connexx, LLC (“Connexx”) provides call center services for ARCA Recycling and ARCA Canada.
On March 9, 2023, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with VM7 Corporation, a Delaware corporation (the “Buyer”), under which the Buyer agreed to acquire all of the outstanding equity interests of (a) ARCA Recycling, (b) Connexx, and (c) ARCA Canada (collectively, the “Subsidiaries”). The principal of the Buyer is Virland A. Johnson, our Chief Financial Officer. The sale of all of the outstanding equity interests of the Subsidiaries to the Buyer under the Purchase Agreement (the “Disposition Transaction”) was consummated simultaneously with the execution of the Purchase Agreement. Our Board of Directors unanimously approved the Purchase Agreement and the Disposition Transaction.
The economic aspects of the Disposition Transaction are: (i) we reduced the liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets by approximately $
The Buyer may prepay, at any time and in total, the estimated aggregate of the future monthly payments. That amount will be an amount equal to the then-present value of the estimated future monthly payments, discounted at the rate of
F-9
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Additional terms of the Disposition Transaction are: (i) we have the right to appoint one member of the Buyer’s board of directors until the sooner of the Buyer having paid the Prepayment Price or having tendered all of the monthly payments; (ii) Mr. Johnson’s annual salary as Chief Executive Officer of the Buyer shall be $
To secure the Buyer’s obligations under the Purchase Agreement and pursuant to a Stock and Membership Interests Pledge Agreement dated March 19, 2023 (the “Pledge Agreement”), Mr. Johnson pledged to us all of the capital stock in the Buyer (the “Buyer’s Capital Stock”) and the Buyer pledged to us all of the equity interests of the Subsidiaries (the “Subject Securities”). Under the terms of the Pledge Agreement, upon an Event of Default (as defined in the Pledge Agreement), among other remedies in our favor, we may foreclose on any or all of the Buyer’s Capital Stock and the Subject Securities. We may also cause the ownership of the Buyer’s Capital Stock and of the Subject Securities to be transferred to us automatically, pursuant to an irrevocable transfer entered in our favor, as referenced in the Pledge Agreement. In the event of an automatic transfer, all of the monthly payments previously made by the Buyer pursuant to the terms of the Purchase Agreement will then be characterized as contributions to the capital of the Company without dilution of the Company’s capital stock.
The parties have made customary representations, warranties, covenants, and indemnities in connection with the Disposition Transaction.
The Purchase Agreement contains certain representations and warranties that the parties made to each other as of the date of the Purchase Agreement or such other date as explicitly referenced therein. Information concerning the subject matter of the representations and warranties may change after March 19, 2023, and subsequent information may or may not be fully reflected in JanOne’s public disclosures. For the foregoing reasons, the representations and warranties contained in the Purchase Agreement should not be relied upon as statements of factual information.
GeoTraq Inc. (“GeoTraq”) was the Company’s Technology segment. The Company suspended all operations for GeoTraq during the year ended January 1, 2022. On May 24, 2022, the Company sold substantially all of the GeoTraq assets . GeoTraq is being presented as a discontinued operation (see Note 27). As discussed previously, the accounts for the Technology segment have been presented as discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
The Company reports on a 52- or 53-week fiscal year. The Company's 2022 fiscal year (“2022”) ended on December 31, 2022, and our fiscal year (“2021”) ended on January 1, 2022.
F-10
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Going concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared under the assumption that the Company will continue as a going concern. Such assumption contemplates the realization of assets and satisfaction of liabilities in the normal course of business, however, the issues described below raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to do so.
The Company currently faces a challenging competitive environment and is focused on improving its overall profitability, which includes managing expenses. The Company reported a net income from continuing operations of approximately $
The Company intends to fund operations by using cash on hand, monthly receipts in connection with the sale of its Subsidiaries, and funds received from approved Employee Retention Credits (“ERC’s”). Debt recorded, as of December 31, 2022, belongs to the Subsidiaries, and will no longer be the responsibility of the Company as of the date of sale. The Company intends to raise funds to support future development of JAN 123 either through capital raises or structured arrangements. However, the success of such funding cannot be assured.
The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern is dependent upon the success of future capital raises or structured settlements to fund the required testing to obtain FDA approval of JAN 123, as well as to fund its day-to-day operations. Such approval is contingent on several factors and no assurance can be provided that approval will be obtained. The accompanying financial statements do not include any adjustments that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern. While the Company will actively pursue these additional sources of financing, management cannot make any assurances that such financing will be secured or FDA approvals will be obtained.
Note 2: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Financial Statement Reclassification
Certain account balances from prior periods have been reclassified in these consolidated financial statements to conform to current period classifications. The prior year amounts have also been modified in these financial statements to properly report amounts under current operations and discontinued operations (see Note 26).
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumption that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Significant estimates made in connection with the accompanying consolidated financial statements include the fair values in connection with the GeoTraq promissory note, analysis of other intangibles and long-lived assets for impairment, valuation allowance against deferred tax assets, lease terminations, and estimated useful lives for intangible assets and property and equipment.
F-11
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Financial Instruments
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents consist of highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less at the time of purchase. Fair value of cash equivalents approximates carrying value.
Trade Receivables and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
The Company carries unsecured trade receivables at the original invoice amount less an estimate made for doubtful accounts based on a monthly review of all outstanding amounts. Management determines the allowance for doubtful accounts by regularly evaluating individual customer receivables and considering a customer’s financial condition, credit history and current economic conditions. The Company writes off trade receivables when it deems them to be uncollectible. The Company records recoveries of trade receivables previously written off when we receive them. The Company considers a trade receivable to be past due if any portion of the receivable balance is outstanding for more than ninety days. The Company does not charge interest on past due receivables. The Company had
Inventories
Inventories, consisting primarily of appliances, are stated at the lower of cost, determined on a specific identification basis, or net realizable value. The Company provides estimated provisions for the obsolescence of our appliance inventories, including adjustment to market, based on various factors, including the age of such inventory and management’s assessment of the need for such provisions. The Company looks at historical inventory aging reports and margin analyses in determining its provision estimate. A revised cost basis is used once a provision for obsolescence is recorded. The Company does
Property and Equipment
Property and Equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Expenditures for repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred and additions and improvements that significantly extend the lives of assets are capitalized. Upon sale or other retirement of depreciable property, the cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the related accounts and any gain or loss is reflected in operations. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. The useful lives of building and improvements are
The Company periodically reviews its property and equipment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying amounts may not be recoverable, or their depreciation or amortization periods should be accelerated. The Company assesses recoverability based on several factors, including its intention with respect to maintaining its facilities, and projected discounted cash flows from operations. An impairment loss would be recognized for the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds their fair value, as approximated by the present value of their projected discounted cash flows.
F-12
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Intangible Assets
The Company accounts for intangible assets in accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other. Under ASC 350, intangible assets subject to amortization, shall be reviewed for impairment in accordance with the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets in ASC 360, Property, Plant, and Equipment.
Under ASC 360, long-lived assets are tested for recoverability whenever events or changes in circumstances (‘triggering event’) indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. In making this determination, triggering events that were considered included:
If a triggering event has occurred, for purposes of recognition and measurement of an impairment loss, a long-lived asset or assets shall be grouped with other assets and liabilities at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of other assets and liabilities. If after identifying a triggering event it is determined that the asset group’s carrying value may not be recoverable, a recoverability test is performed by forecasting the expected cash flows to be derived from the asset group for the remaining useful life of the asset group’s primary asset compared to its carrying value. The recoverability test relies upon the undiscounted cash flows (excluding interest and taxes) which are derived from the Company’s specific use of those assets (not how a market participant would use those assets); and, are based upon the existing service potential of the current assets (excluding any improvements that would materially enhance the assets). If the expected undiscounted cash flows exceed the carrying value, the assets are considered recoverable.
The Company’s intangible assets consist of trade names, licenses for the use of internet domain names, Universal Resource Locators, or URL’s, computer software, patent USPTO reference No. 10,182,402, and designs and related manufacturing procedures. In connection with the Soin merger (see Note 3), intangible assets consist of three patents pending, orphan drug status for Naltrexone, as granted by the FDA, and the formula for Naltrexone. Upon acquisition, critical estimates are made in valuing acquired intangible assets, which include but are not limited to: future expected cash flows from customer contracts, customer lists, and estimating cash flows from projects when completed; tradename and market position, as well as assumptions about the period of time that customer relationships will continue; and discount rates. Management's estimates of fair value are based upon assumptions believed to be reasonable, but which are inherently uncertain and unpredictable and, as a result, actual results may differ from the assumptions used in determining the fair values. All intangible assets are capitalized at their original cost and amortized over their estimated useful lives as follows: domain name and marketing –
For the year ended January 1, 2022, the Company took an impairment charge for the full unamortized balance, in the amount of approximately $
F-13
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Revenue Recognition
Biotechnology Revenue
The Company currently generates no revenue from its Biotechnology segment.
Recycling Revenue
The Company provides replacement appliances and provides appliance pickup and recycling services for consumers (“end users”) of public utilities, our customers. The Company receives, as part of our de-manufacturing and recycling process, revenue from scrap dealers for refrigerant, steel, plastic, glass, copper and other residual items.
The Company accounts for revenue in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification 606 Revenue from Contracts with Customers.
Under the revenue standard revenue is recognized as follows:
The Company determines revenue recognition utilizing the following steps:
As part of its assessment of each contract, the Company evaluates certain factors including the customer’s ability to pay, or credit risk. For each contract, the Company considers the promise to transfer products or services, each of which is distinct, to be the identified performance obligations. In determining the transaction price, the price stated on the contract is typically fixed and represents the net consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled per order, and therefore there is no variable consideration. As the Company’s standard payment terms are less than 90 days, the Company has elected, as a practical expedient, to not assess whether a contract has a significant financing component. The Company allocates the transaction price to each distinct product or service based on its relative standalone selling price. The product or service price as specified on the contract is considered the standalone selling price as it is an observable source that depicts the price as if sold to a similar customer in similar circumstances.
Recycling Services and Byproduct Revenue
The Company generates revenue by providing pickup and recycling services. The Company recognizes revenue at the point in time when we have picked up a to be recycled appliance and transfer of ownership has occurred, and therefore the Company's performance obligations are satisfied, which typically occur upon pickup from the Company's end user’s home.
The Company generates other recycling byproduct revenue (the sale of copper, steel, plastic and other recoverable non-refrigerant byproducts) as part of its de-manufacturing process. The Company recognizes byproduct revenue upon delivery and transfer of control of byproduct to a third-party recycling customer, having a mutually agreed upon price per pound and collection reasonably assured. Transfer of control occurs at the time the customer is in possession of the byproduct material. Revenue recognized is a function of byproduct weight, type and in some cases volume of the byproduct delivered multiplied by the market rate as quoted.
Recycling Services and Byproduct revenue was $
F-14
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Replacement Appliances Revenue
The Company generates revenue by providing replacement appliances. The Company recognizes revenue at the point in time when control over the replacement product is transferred to the end user, when its performance obligations are satisfied, which typically occur upon delivery from the Company's center facility and installation at the end user’s home.
Replacement Appliances revenue was $
Contract Liability
Receivables are recognized in the period the Company ships the product, or provides the service. Payment terms on invoiced amounts are based upon contractual terms with each customer. When the Company receives consideration, or such consideration is unconditionally due, prior to transferring goods or services to the customer under the terms of a sales contract, the Company records deferred revenue, which represents a contract liability. The Company recognizes a contract liability as net sales once control of goods and/or services have been transferred to the customer and all revenue recognition criteria have been met and any constraints have been resolved. The Company defers recording product costs until recognition of the related revenue occurs.
Assets Recognized from Costs to Obtain a Contract with a Customer
The Company recognizes an asset for the incremental costs of obtaining a contract with a customer if it expects the benefit of those costs to be longer than one year. The Company has concluded that no material costs have been incurred to obtain and fulfill our FASB Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC 606 contracts, meet the capitalization criteria, and, as such, there are
Other:
Revenue recognized for Company contracts - approximately $
Technology Revenue
The Company generates no revenue from its Technology segment. GeoTraq Inc. (“GeoTraq”) was the Company’s Technology segment. The Company suspended all operations for GeoTraq during the year ended January 1, 2022. On May 24, 2022, the Company sold substantially all of the GeoTraq assets . GeoTraq is being presented as a discontinued operation (see Note 27). As discussed previously, the accounts for the Technology segment have been presented as discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Shipping and Handling
The Company classifies shipping and handling charged to customers as revenues and classifies costs relating to shipping and handling as cost of revenues.
Advertising Expense
Advertising expense is charged to operations as incurred. Advertising expense was
F-15
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Fair Value Measurements
ASC Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” requires disclosure of the fair value of financial instruments held by the Company. ASC Topic 825, “Financial Instruments,” defines fair value, and establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for disclosures of fair value measurement that enhances disclosure requirements for fair value measures. The three levels of valuation hierarchy are defined as follows: Level 1 - inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. Level 2 – to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument. Level 3 – inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method. The asset and liability method requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for expected future tax consequences of temporary differences that currently exist between tax bases and financial reporting bases of the Company's assets and liabilities. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which these temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. A valuation allowance is provided on deferred taxes if it is determined that it is more likely than not that the asset will not be realized. The Company recognizes penalties and interest accrued related to income tax liabilities in the provision for income taxes in its Consolidated Statements of Income.
Significant management judgment is required to determine the amount of benefit to be recognized in relation to an uncertain tax position. The Company uses a two-step process to evaluate tax positions. The first step requires an entity to determine whether it is more likely than not (greater than 50% chance) that the tax position will be sustained. The second step requires an entity to recognize in the financial statements the benefit of a tax position that meets the more-likely-than-not recognition criterion. The amounts ultimately paid upon resolution of issues raised by taxing authorities may differ materially from the amounts accrued and may materially impact the financial statements of the Company in future periods.
Lease Accounting
The Company accounts for leases in accordance with ASC 842 - Leases This accounting standard requires all lessees to record the impact of leasing contracts on the balance sheet as a right to use asset and corresponding liability. This is measured by taking the present value of the remaining lease payments over the lease term and recording a right to use asset (“ROU”) and corresponding lease obligation for lease payments. Rent expense is realized on a straight-line basis and the lease obligation is amortized based on the effective interest method. The amounts recognized reflect the present value of remaining lease payments for all leases that have a lease term greater than 12 months. The discount rate used is an estimate of the Company’s incremental borrowing rate based on information available at lease commencement.
In considering the lease asset value, the Company considers fixed or variable payment terms, prepayments and options to extend, terminate or purchase. Renewal, termination or purchase options affect the lease term used for determining lease asset value only if the option is reasonably certain to be exercised. The Company uses an estimate of its incremental borrowing rate based on information available at lease commencement in determining the present value of lease payments.
F-16
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company leases warehouse facilities and office space. These assets and properties are generally leased under noncancelable agreements that expire at various dates through
The Company's operating leases do not contain residual value guarantees, and do not contain restrictive covenants. The Company currently has
Leases accounted for under ASC 842 were determined based on analysis of the lease contracts using lease payments and timing as documented in the contract. Non-lease contracts were also evaluated to understand if the contract terms provided for an asset that the Company controlled and provided us with substantially all the economic benefits. The Company did not observe any contracts with embedded leases. Lease contracts were reviewed, and distinctions made between non lease and lease payments. Only payments related to the lease of the asset were included in lease payment calculations.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company from time to time grants stock options to employees, non-employees and Company executives and directors. Such awards are valued based on the grant date fair-value of the instruments. The value of each award is amortized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period.
Foreign Currency
The financial statements of the Company’s non-U.S. subsidiary are translated into U.S. dollars in accordance with ASC 830, Foreign Currency Matters. Under ASC 830, if the assets and liabilities of the Company are recorded in certain non-U.S. functional currencies other than the U.S. dollar, they are translated at rates of exchange at year end. Revenue and expense items are translated at the average monthly exchange rates. The resulting translation adjustments are recorded directly into accumulated other comprehensive loss.
Earnings Per Share
Earnings per share is calculated in accordance with ASC 260, “Earnings Per Share”. Under ASC 260 basic earnings per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period except that it does not include unvested restricted stock subject to cancellation. Diluted earnings per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares and, if dilutive, potential common shares outstanding during the period. Potential common shares consist of the incremental common shares issuable upon the exercise of warrants, options, restricted shares and convertible preferred stock. The dilutive effect of outstanding restricted shares, options and warrants is reflected in diluted earnings per share by application of the treasury stock method. Convertible preferred stock is reflected on an if-converted basis.
Segment Reporting
ASC Topic 280, “Segment Reporting,” requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a Company’s management organizes segments within the Company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. The Company determined it has
F-17
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Concentration of Credit Risk
The Company maintains cash balances at several banks in several states including, California, Minnesota and Nevada. Accounts are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation up to $
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued ASU No. 2016-13, Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, which introduces a new approach to estimate credit losses on certain types of financial instruments based on expected losses instead of incurred losses. It also modifies the impairment model for available-for-sale debt securities and provides a simplified accounting model for purchased financial assets with credit deterioration since their origination. ASU No. 2016-13 is effective for smaller reporting companies for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022 and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact of adopting this new accounting standard on our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
Note 3: Mergers and Acquisitions
Soin Pharmaceuticals
Effective as of December 28, 2022, the Company acquired Soin Therapeutics LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“STLLC”), and its product, a patent-pending, novel formulation of low-dose naltrexone. The product is being developed for the treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), an indication that causes severe, chronic pain generally affecting the arms or legs. At present, there are no truly effective treatments for CRPS. Because of the relatively small number of patients afflicted with CRPS, the FDA has granted Orphan Drug Designation for any product approved for treatment of CRPS. This designation will provide the Company with tax credits for its clinical trials, exemption of user fees, and the potential of seven years of market exclusivity following approval. In addition, development of orphan drugs currently also involves smaller trials and quicker times to approval, given the limited number of patients available to study. However, there can be no assurance that the product will receive FDA approval or that it will result in material sales.
In anticipation of the closing of the merger, the Company formed a merger subsidiary known as STI Merger Sub, Inc., a Delaware corporation (our “Merger Sub”), and designated a series of
For not less than six months after the closing and potentially up to approximately one year from the closing, Dr. Soin will remain the Company's Chief Medical Officer.
At the closing of the merger, (i) our Merger Sub merged with and into STLLC with STLLC as the surviving entity and (ii) the Company issued
F-18
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
At the completion of the merger, the Company performed a screen test, as defined in ASC 805 (“Business Combinations”), to determine whether the Soin Pharmaceutical merger was considered a business combination or an asset acquisition. The results of the screen test revealed that substantially all of the fair value was concentrated in a group of similar assets, and that the assets did not possess the inputs, outputs, nor processes required to be considered a business, as defined in ASC 805. Consequently, no goodwill was recognized as part of this transaction.
The fair value of the Series S Stock issued in connection with the merger, as valued by a third-party, independent, valuation firm was approximately $
Note 4: Trade and other receivables
The Company's trade and other receivables are as follows (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Trade receivables, net |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Factored accounts receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Prestige Capital reserve receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Trade and other receivables, net |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Trade accounts receivable |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Un-billed trade receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total trade receivables, net |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Prestige Capital
On March 26, 2018, Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. (“ARCA”) entered into a purchase and sale agreement with Prestige Capital Corporation (“Prestige Capital”), whereby from time to time ARCA can factor certain accounts receivable to Prestige Capital up to a maximum advance and outstanding balance of $
F-19
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5: Note receivable
ApplianceSmart
On December 30, 2017, the Company sold its retail appliance segment, ApplianceSmart, Inc. (“ApplianceSmart”) to ApplianceSmart Holdings LLC (the “Purchaser”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Live Ventures Incorporated, a related party, pursuant to a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”). Pursuant to the Agreement, the Purchaser purchased from the Company all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of ApplianceSmart in exchange for $
On December 9, 2019, ApplianceSmart filed a voluntary petition in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York seeking relief under Chapter 11 of Title 11 of the United States Code. Consequently, the Company recorded an impairment charge of approximately $
On October 13, 2021, a hearing was held to consider approval of a disclosure statement filed by ApplianceSmart in conjunction with its bankruptcy proceedings. On December 14, 2021, a hearing was held to confirm ApplianceSmart’s plan for reorganization (the “Plan”). On January 10, 2022, ApplianceSmart paid $
GeoTraq
On May 24, 2022, the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with SPYR Technologies Inc. (“SPYR”), pursuant to which the Company sold to SPYR substantially all of the assets and none of the specified liabilities of GeoTraq, as discussed in Note 27 below. In connection with the Purchase Agreement, SPYR delivered to the Company a five-year Promissory Note in the initial principal amount of $
As of December 31, 2022, no interest payments had been received in connection with the Asset Purchase Agreement. SPYR is reviewing options to issue shares permitting it to remain in compliance with the Asset Purchase Agreement and not violate rules as set forth by the SEC. Any future shares of SPYR stock issued to the Company will be restricted. On March 15, 2023, the Company received
In connection with the asset sale, the Company engaged a third-party valuation firm to assess the fair value of the consideration received. Based on the valuation, the Promissory Note (“Note”) was valued at approximately $
The balance appearing on the Company's consolidated balance sheets represents the principal balance of the Promissory Note, net of the discount balance. During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022,
F-20
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
approximately $
Note 6: Inventory
Inventories, consisting principally of appliances, are stated at the lower of cost, determined on a specific identification basis, or net realizable value, and consist of the following (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Appliances held for resale |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Inventory from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Inventory from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total inventory |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The Company provides estimated provisions for the obsolescence of its appliance inventories, as necessary, including adjustments to net realizable value, based on various factors, including the age of such inventory and management’s assessment of the need for such provisions. The Company looks at historical inventory aging reports and margin analyses in determining its provision estimate. A revised cost basis is used once a provision for obsolescence is recorded.
Note 7: Prepaids and other current assets
Prepaids and other current assets consist of the following (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Prepaid insurance |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Prepaid rent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total prepaids and other current assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Note 8: Property and equipment
Property and equipment consist of the following (in $000's):
|
|
Useful Life |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Buildings and improvements |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Projects under construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less accumulated depreciation |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total property and equipment, net, from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Property and equipment, net, from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
F-21
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Depreciation expense was approximately $
Equipment Financing Agreement
On March 25, 2021, ARCA Recycling entered into a Master Equipment Finance Agreement (collectively, the “Equipment Finance Agreement”) with KLC Financial, Inc. (“KLC”). Under the terms of the Equipment Finance Agreement, KLC has agreed to make loans to ARCA Recycling secured by certain equipment purchased or to be purchased by ARCA Recycling on terms set forth or to be set forth in schedules to the Equipment Finance Agreement. Under the terms of Schedule No. 01 (the “Initial Loan”), KLC has agreed to loan ARCA Recycling approximately $
On May 4, 2022, ARCA Recycling entered into a second Equipment Finance Agreement with KLC. Under the terms of the Equipment Finance Agreement, KLC has agreed to make loans to ARCA Recycling secured by certain equipment purchased or to be purchased by ARCA Recycling on terms set forth or to be set forth in schedules to the Equipment Finance Agreement. Under the terms of Schedule No. 01 (“Second Loan”), KLC has agreed to loan ARCA Recycling an additional $
Note 9: Intangible assets
Intangible assets as of consist of the following (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Soin intangibles |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Patents and domains |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Computer software |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less accumulated amortization |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total intangible assets, net |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
F-22
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Intangible amortization expense for continuing operations was approximately $
Soin Intangible Assets
Effective as of December 28, 2022, the Company acquired Soin Therapeutics LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“STLLC”), and its product, a patent-pending, novel formulation of low-dose naltrexone. The assets acquired by the Company consist of 1) three pending patents related to the methods of using low-dose Naltrexone to treat chronic pain, 2) final formula for Naltrexone, and 3) orphan drug designation as approved by the FDA. The Company reviewed the assets acquired and determined that no in-process research and development costs were acquired as part of the transaction, and, thus, all assets acquired represent intellectual property and should be capitalized. The Company will amortize the intangible assets ratably over a
GeoTraq Intangible Asset
During the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022, the Company determined that long-term revenue projections for the Technology segment would be unattainable, and, as such, performed a qualitative assessment of the GeoTraq intangible asset, in accordance with ASC 350-30, General intangibles other than goodwill. The triggering events for this assessment were 1) its history of negative cash flows and operating losses since acquisition, 2) no foreseeable revenues during the final three years of its useful life such that would allow for full cost recovery, and, 3) no further investment in GeoTraq is imminent due to the Company's lack of resources (human and financial). The assessment further concluded that any opportunities for investment from outside the Company was minimal due to barriers to entry, and inflationary and supply-chain-related issues. Consequently, during the year ended January 1, 2022, the Company took a full write-down of the unamortized portion of the GeoTraq of approximately $
Note 10: Marketable Securities
Marketable securities consist of the following (in $000’s, except shares):
|
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
||
Beginning balance, January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
Securities received |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Mark-to-market |
|
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
Ending balance, December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
Marketable securities reflect shares of SPYR stock received by the Company in connection with the sale of GeoTraq (see Note 27 below). Shares held are marked to fair market value as of each balance sheet date, with the resulting change recorded as an unrealized gain or loss. Unrealized loss recorded for the year ended December 31, 2022 was approximately $
Note 11: Deposits and other assets
Deposits and other assets consist of the following (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Deposits |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total deposits and other assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
During the year ended December 31, 2022, the deposit for a refundable “deposit in lieu of bond”, in the amount of $
F-23
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 12: Leases
The Company accounts for leases in accordance with ASC 842. The amount recorded is the present value of all remaining lease payments for leases with terms greater than 12 months. The right of use asset is offset by a corresponding liability. The discount rate is based on an estimate of our incremental borrowing rate for terms similar to our lease terms at the time of lease commencement. The asset is amortized over remaining lease terms. See Lease Accounting in Note 2.
Total present value of future lease payments as of December 31, 2022 (in $000's):
2023 |
|
$ |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
|
2025 |
|
|
|
|
2026 |
|
|
|
|
2027 |
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
Less interest |
|
|
( |
) |
Present value of payments |
|
$ |
|
During the years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, approximately $
The Company obtained right-of-use assets in exchange for lease liabilities of approximately $
Note 13: Accrued liabilities
Accrued liabilities of continuing consist of the following (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Compensation and benefits |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Contract liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued incentive and rebate checks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued transportation costs* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued guarantees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued purchase orders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued litigation settlement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total accrued liabilities |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
F-24
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Contract liabilities rollforward
The following table summarizes the contract liability activity (in $000's):
Beginning balance, January 2, 2021 |
|
$ |
|
|
Accrued |
|
|
|
|
Settled |
|
|
( |
) |
Ending balance, January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
Accrued |
|
|
|
|
Settled |
|
|
( |
) |
Ending balance, December 31, 2022 |
|
$ |
|
Note 14: Accrued liability – California sales tax
The Company operates in fourteen states in the U.S. and in various provinces in Canada. From time to time, the Company is subject to sales and use tax audits that could result in additional taxes, penalties and interest owed to various taxing authorities.
The California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (formerly known as the California Board of Equalization) (“CDTFA”) conducted a sales and use tax examination covering ARCA Recycling’s California operations for the years 2011, 2012 and 2013. The Company believed it was exempt from collecting sales taxes under service agreements with utility customers that included appliance replacement programs. During the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company received communication from the CDTFA indicating they were not in agreement with the Company’s interpretation of the law. Consequently, the Company applied for and, as of February 9, 2015, received approval to participate in the CDTFA’s Managed Audit Program. The period covered under this program included years 2011, 2012, 2013 and extended through the nine-month period ended September 30, 2014.
On April 13, 2017 the Company received the formal CDTFA assessment for sales tax for tax years 2011, 2012 and 2013 in the amount of approximately $
As of December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, the Company's accrued liability for California sales tax was approximately $
Note 15: Income taxes
For fiscal years ended December 31, 2022, and January 1, 2022, the Company recorded an income tax benefit from continuing operation of approximately $
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Current tax expense: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
State |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Federal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current tax expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred tax benefit - domestic |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Total (benefit) provision of income taxes |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
F-25
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
A reconciliation of the Company's income tax benefit (provision) with the federal statutory tax rate for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022, and January 1, 2022, respectively, is shown below:
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
U.S statutory rate |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Federal income tax for installment sale |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
State tax rate |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Foreign rate differential |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
% |
|
Permanent differences |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Change in tax rates |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Benefit from CARES Act carryback claim |
|
|
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
Change in valuation allowance |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
- |
% |
Other |
|
|
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
- |
% |
Income (l
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
United States |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Canada |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
The components of net deferred tax assets (liabilities) as of December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, respectively, are as follows (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Deferred tax assets (liabilities): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Allowance for bad debts |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accrued expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Section 174 expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net operating loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Lease liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Tax credits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Share-based compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Intangibles |
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( |
) |
Property and equipment |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Installment sale |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Unrealized losses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Section 163(j) interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less: valuation allowance |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
F-26
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As of December 31, 2022, the Company has net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $
The Company annually conducts an analysis of its uncertain tax positions and has concluded that it has no uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2022. The Company’s policy is to record uncertain tax positions as a component of income tax expense.
The Company files U.S. and state income tax returns in jurisdictions with differing statutes of limitations. The tax years remain subject to selection for examination as of December 31, 2022. None of the Company’s income tax returns are currently under audit. During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2022, the Company released the valuation allowance of approximately $
Note 16: Long-term debt
Long-term debt and other financing obligations consist of the following (in $000's):
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
AFCO Finance |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
KLC Financial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gulf Coast Bank and Trust Company |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total debt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less unamortized debt issuance costs |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net amount |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less current portion |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total long-term debt |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Future maturities of long-term debt at December 31, 2022 are as follows and does not include related party debt (in $000's):
For the fiscal year ended |
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
$ |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
|
2025 |
|
|
|
|
2026 |
|
|
|
|
2027 |
|
|
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
— |
|
Total future maturities of long-term debt |
|
$ |
|
|
F-27
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
AFCO Finance
The Company has entered into a financing agreement with AFCO Credit Corporation (“AFCO”) purchased through Marsh Insurance on an annual basis to fund the annual premiums on insurance policies due July 1 of each year. These policies relate to workers’ compensation and various liability policies including, but not limited to, General, Auto, Umbrella, Property, and Directors’ and Officers’ insurance. The total amount of the premiums financed in July 2022 was approximately $
The outstanding principal due AFCO at December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022 was approximately $
Payroll Protection Program
On May 1, 2020, the Company entered into a promissory note (the “Promissory Note”) with Texas Capital Bank, N.A. that provides for a loan in the amount of approximately $
KLC Financial
On March 25, 2021, ARCA Recycling entered into a Master Equipment Finance Agreement (collectively, the “Equipment Finance Agreement”) with KLC Financial, Inc. (“KLC”). Under the terms of the Equipment Finance Agreement, KLC has agreed to make loans to ARCA Recycling secured by certain equipment purchased or to be purchased by ARCA Recycling on terms set forth or to be set forth in schedules to the Equipment Finance Agreement. Under the terms of Schedule No. 01 (the “Initial Loan”), KLC has agreed to loan ARCA Recycling approximately $
On May 4, 2022, ARCA Recycling entered into a second Equipment Finance Agreement with KLC. Under the terms of the Equipment Finance Agreement, KLC has agreed to make loans to ARCA Recycling secured by certain equipment purchased or to be purchased by ARCA Recycling on terms set forth or to be set forth in schedules to the Equipment Finance Agreement. Under the terms of Schedule No. 01 (“Second Loan”), KLC has agreed to loan ARCA Recycling an additional $
Gulf Coast Bank and Trust Company
F-28
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
On September 26, 2022, ARCA Recycling, Inc. entered into a series of agreements with Gulf Coast to refinance its existing credit facility with Prestige Capital (see Note 4). The principal limit of the refinanced facility is $
F-29
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Advances under the new credit facility will bear interest at the prime rate, as published daily in the Wall Street Journal, plus
The facility matures on
Note 17: Commitments and Contingencies
Litigation
SEC Complaint
On August 2, 2021, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) filed a civil complaint (the “SEC Complaint”) in the United States District Court for the District of Nevada naming the Company and one of its executive officers, Virland Johnson, the Company's Chief Financial Officer, as defendants (collectively, the “Defendants”).
The SEC Complaint alleges financial, disclosure and reporting violations against the Company and the executive officer under Section 10(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”) and Rule 10b-5. The SEC Complaint also alleges various claims against the executive officer under Sections 13(a), 13(b)(2)(A), 13(b)(2)(B) and 13(b)(5) of the Exchange Act and Rules 12b-20, 13a-1, 13a-13, 13a-14, 13b2-1, and 13b2-2. The SEC seeks permanent injunctions and civil penalties against the Defendants, and an officer-and-director bar against the executive officer. The foregoing is only a general summary of the SEC Complaint, which may be accessed on the SEC’s website at https://www.sec.gov/litigation/litreleases/2021/lr25155.htm.
The Company continues to assert that the SEC’s pursuit of this matter will not result in any benefit to investors and instead will only serve as a distraction from core business. On October 1, 2021, the Company, filed a motion with the court to dismiss the complaint. The SEC filed its response opposing the motions on November 1, 2021. On September 7, 2022, the motions to dismiss were denied by the court. Pursuant to the automatic stay of proceedings under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act, all discovery was stayed pending the motions to dismiss and continues to be stayed pending the June 23, 2023 mediation to which all of the parties have agreed.
The Defendants strongly dispute and deny the allegations and are vigorously defending themselves against the claims.
Skybridge
On December 29, 2016, the Company served a Minnesota state court complaint for breach of contract on Skybridge Americas, Inc. (“SA”), the Company’s primary call center vendor throughout 2015 and most of 2016. The Company seeks damages in the millions of dollars as a result of alleged overcharging by SA and lost client contracts. On January 25, 2017, SA served a counterclaim for unpaid invoices in the amount of approximately $
F-30
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
issue back to the District Court for further proceedings, (ii) reversed the District Court’s judgment in favor of Skybridge on the net payment issue and remanded the issue to the District Court for further proceedings, and (iii) affirmed the District Court’s judgment in Skybridge’s favor against the Company’s claim that Skybridge breached the contract when it failed to meet the service level agreements. As a result of the decision by the Court of Appeals, the District Court’s award of interest and attorneys’ fees, etc. was reversed. The Company and SA held a mediation session in July 2020. Trial was held in August 2020 and on February 1, 2021, the District Court assessed damages against the Company in the amount of approximately $
AMTIM Capital
AMTIM Capital, Inc. (“AMTIM”) acts as the Company’s representative to market our recycling services in Canada under an arrangement that pays AMTIM for revenues generated by recycling services in Canada as set forth in the agreement between the parties. A dispute has arisen between AMTIM and the Company with respect to the calculation of amounts due to AMTIM pursuant to the agreement. In a lawsuit filed by AMTIM in the province of Ontario, AMTIM claims a discrepancy in the calculation of fees due to AMTIM by the Company of approximately $
GeoTraq
On or about April 9, 2021, GeoTraq, Gregg Sullivan, Tony Isaac, and we, among others, resolved all of their claims that related to, among other items, the Company's acquisition of GeoTraq in August 2017, all post-acquisition activities, and Mr. Sullivan’s post-acquisition employment relationship with GeoTraq (all of such claims, the “GeoTraq Matters”). The resolution was effectuated through the parties’ execution and delivery of a Settlement Agreement and Mutual Agreement of Claims (the “GeoTraq Settlement Agreement”).
Under the terms of the Settlement Agreement, the Company, on its own behalf and on behalf of GeoTraq and Mr. Isaac, agreed to tender to Mr. Sullivan an aggregate of $
Pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement, Mr. Sullivan provided the Company with his proxy to vote his remaining shares of its Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock that the Company had issued to him in connection with its acquisition of GeoTraq in 2017, as well as his proxy for the shares of the Company's common stock into which those shares of preferred stock may be converted. The Company may utilize the proxy in the context of an annual meeting of its stockholders, a special meeting of its stockholders, and a written consent of its stockholders. Subject to the above-described contingent GeoTraq Prepayment tender
The parties to the Settlement Agreement released and forever discharged one another from any and all known and unknown claims that were asserted or could have been asserted arising out of the GeoTraq Litigation Matters. The accrued liability for payments due to Mr. Sullivan is $
F-31
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Alixpartners, LLC
On October 19, 2022, Alixpartners, LLC filed a complaint in the Supreme Court of the State of New York, County of New York, styled Alixpartners, LLC, plaintiff/petitioner, against JanOne Inc., Index No. 653877/2022. Plaintiff alleged the breach of an agreement and sought damages in the amount of approximately $
Sieggreen
On March 6, 2023, Sieggreen, Individually and On Behalf of All Others Similarly Situated, Plaintiff, v. Live Ventures Incorporated, Jon Isaac, and Virland A. Johnson, Defendants, the Company was added as a defendant on March 6, 2023, and was served on March 23, 2023. Plaintiff has alleged causes of action against the Company for (i) violation of Section 10(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and Rule 10b-5 promulgated thereunder and (ii) violation of Section 10(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and Rules 10b-5(a) and 10b-5(c) promulgated thereunder. The Company has not filed a responsive pleading as of the date of these financial statements and strongly disputes and denies all of the allegations contained therein and will vigorously defend itself against the claims.
Main/270
The Company is a defendant in an action filed on April 11, 2022, in the U.S. District Court Southern District of Ohio, Eastern Division, styled, Trustees Main/270, LLC, Plaintiff, vs ApplianceSmart, Inc. and JANONE, Inc., Defendant, Case no.: 2:22-cv-01938-ALM-EPD. The Company was a guarantor of the lease between the Plaintiff and ApplianceSmart, Inc. Plaintiff alleged a cause of action against the Company in respect of the guaranty and seeks approximately $
Westerville Square
In an attempt to recover payments due under a lease, in 2019, Westerville Square, Inc., as the landlord, initiated a civil action against the Company, styled Westerville Square, Inc. v. Appliance Recycling Centers Of America, Inc., et al., in the Court of Common Pleas of Franklin County, Ohio, Case No. 19 CV 8627. The case was stayed during the bankruptcy proceedings of ApplianceSmart, Inc., and was reinstated on June 7, 2021. The landlord is currently seeking $
Other Commitments
As previously disclosed and as discussed, on December 30, 2017, the Company disposed of its retail appliance segment and sold ApplianceSmart to the Purchaser (see Note 25). In connection with that sale, as of December 28, 2019, the Company accrued an aggregate amount of future real property lease payments of approximately $
The Company is party from time to time to other ordinary course disputes that we do not believe to be material to our financial condition as of December 31, 2022.
F-32
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 18: Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock.
History
On August 18, 2017, the Company acquired GeoTraq by way of merger. In connection with this transaction, the Company tendered to the owners of GeoTraq $
Conversion
The “
Dividends
The Company cannot declare, pay or set aside any dividends on shares of any other class or series of our capital stock unless (in addition to the obtaining of any consents required by our Articles of Incorporation) the holders of the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock then outstanding shall first receive, or simultaneously receive, a dividend in the aggregate amount of one dollar, regardless of the number of then-issued and outstanding shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock. Any remaining dividends allocated by the Board of Directors shall be distributed in an equal amount per share to the holders of outstanding common stock and Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock (on an as-if-converted to common stock basis pursuant to the Conversion Ratio as defined below).
Voting Rights
Redemption
Preemptive Rights
Holders of the Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock and holders of JanOne common stock are not entitled to any preemptive, subscription, or similar rights in respect of any securities of JanOne, except as set forth in the Amended and Restated Series A-1 Certificate of Designation or in any other document agreed to by JanOne.
Protective Provisions
Without first obtaining the affirmative approval of a majority of the holders of the shares of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock, the Company may not directly or indirectly (i) increase or decrease (other than by redemption or conversion) the total number of authorized shares of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock; (ii) effect an exchange, reclassification, or cancellation of all or a part of the Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock, but excluding a stock split or reverse stock split or combination of the common stock or preferred stock; (iii) effect an exchange, or create a right of exchange, of all or part of the shares of another class of shares into shares of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred
F-33
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Stock; or (iv) alter or change the rights, preferences or privileges of the shares of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock so as to affect adversely the shares of such series, including the rights set forth in this Designation; provided, however, that we may, without any vote of the holders of shares of the Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock, make technical, corrective, administrative or similar changes to the Amended and Restated Series A-1 Certificate of Designation that do not, individually or in the aggregate, materially adversely affect the rights or preferences of the holders of shares of the Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock.
Note 19: Series S Convertible Preferred Stock.
History
On December 28, 2022 the acquired Soin Therapeutics by way of merger. In connection with this transaction, with a potential value of up to $
Conversion
Dr. Soin may convert up to
Dr. Soin further agreed to certain restrictions on the maximum number of shares of Series S Stock that he may ultimately keep or that he may convert into shares of our common stock or sell into the public markets at any given time: (i) Dr. Soin may not convert shares of Series S Stock into shares of the Company's common stock in an amount such that, upon any such conversion, he beneficially own shares of the Company's common stock in excess of
|
|
Series S Preferred Stock |
|
|||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
||
Balance, January 2, 2021 |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Balance, January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Series S preferred issued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Balance, December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
Dividends
Shares of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock do not have dividend rights.
Voting Rights
The Holder of each share of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock shall have one vote for such share. With respect to any stockholder vote, the Holder shall have full voting rights and powers equal to the voting rights and powers of the Common Stock stockholders, and shall be entitled to notice of any stockholders' meeting in accordance with the Bylaws of the Company, and shall be entitled to vote, together with Common Stock stockholders, with respect to any question upon which the Common Stock stockholders have the right to vote. The Holders of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock shall vote together with all other classes and series of common and preferred stock of the Company as a single class on all actions to be taken by the Common Stock stockholders, except to the extent that voting as a separate class or series is required by law.
F-34
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Redemption
The Series S Convertible Preferred Stock has no redemption rights by JanOne, or any other entity.
Preemptive Rights
Holders of the Series S Convertible Preferred Stock and holders of JanOne common stock are not entitled to any preemptive, subscription, or similar rights in respect of any securities of JanOne, except as set forth in the Amended and Restated Series A-1 Certificate of Designation or in any other document agreed to by JanOne.
Protective Provisions
Without first obtaining the affirmative approval of a majority of the holders of the shares of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock, the Company may not directly or indirectly (i) increase or decrease (other than by redemption or conversion) the total number of authorized shares of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock; (ii) effect an exchange, reclassification, or cancellation of all or a part of the Series S Convertible Preferred Stock, but excluding a stock split or reverse stock split or combination of the common stock or preferred stock; (iii) effect an exchange, or create a right of exchange, of all or part of the shares of another class of shares into shares of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock; (iv) issue additional shares of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock other than in connection with the merger agreement, or (v) alter or change the rights, preferences or privileges of the shares of Series S Convertible Preferred Stock so as to affect adversely the shares of such series, including the rights set forth in this Designation; provided, however, that we may, without any vote of the holders of shares of the Series S Convertible Preferred Stock, make technical, corrective, administrative or similar changes to the Amended and Restated Series S Certificate of Designation that do not, individually or in the aggregate, materially adversely affect the rights or preferences of the holders of shares of the Series S Convertible Preferred Stock.
Note 20: Stockholders’ Equity
Common Stock: The Company's Articles of Incorporation authorize
Equity Offering: On January 29, 2021, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with certain institutional investors (the “Purchasers”) for the sale by the Company in a registered direct offering (the “Offering”) of
The Purchase Agreement contains customary representations, warranties and agreements by the Company and the Purchasers and customary indemnification rights and obligations of the parties.
A.G.P./Alliance Global Partners acted as the sole placement agent (the “Placement Agent”) for the Company on a “reasonable best efforts” basis in connection with the Offering. The Company entered into a Placement Agency Agreement, dated as of January 29, 2021, by and between the Company and the Placement Agent (the “Placement Agency Agreement”). Pursuant to the Placement Agency Agreement, the Placement Agent was paid a cash fee of
The shares of Common Stock sold in the Offering were offered and sold by the Company pursuant to an effective shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-251645) (the “Registration Statement”), which was initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 23, 2020 and was declared effective on December 29, 2020.
F-35
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The representations, warranties and covenants contained in the Purchase Agreement were made solely for the benefit of the parties to the Purchase Agreement. In addition, such representations, warranties, and covenants (i) are intended as a way of allocating the risk between the parties to the Purchase Agreement and not as statements of fact, and (ii) may apply standards of materiality in a way that is different from what may be viewed as material by stockholders of, or other investors in, the Company. Accordingly, the Purchase Agreement incorporated by reference in this filing only to provide investors with information regarding the terms of the transaction, and not to provide investors with any other factual information regarding the Company. Stockholders should not rely on the representations, warranties, and covenants or any descriptions thereof as characterizations of the actual state of facts or condition of the Company or any of its subsidiaries or affiliates. Moreover, information concerning the subject matter of the representations and warranties may change after the date of the Purchase Agreement, which subsequent information may or may not be fully reflected in public disclosures.
The foregoing descriptions of the Purchase Agreement and the Placement Agency Agreement are not complete and are qualified in their entireties by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement and the Placement Agency Agreement, a copy of each of which is filed as Exhibit 10.1 and Exhibit 1.1, respectively, to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K as field on January 29, 2021 and each is incorporated by reference herein.
Stock options: The 2016 Plan, which replaces the 2011 Plan, authorizes the granting of awards in any of the following forms: (i) incentive stock options, (ii) nonqualified stock options, (iii) restricted stock awards, and (iv) restricted stock units, and expires on the earlier of
The Company's 2011 Plan authorizes the granting of awards in any of the following forms: (i) stock options, (ii) stock appreciation rights, and (iii) other share-based awards, including but not limited to, restricted stock, restricted stock units or performance shares, and expired on the earlier of
The following table summarizes stock option activity for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022, and January 1, 2022 (Aggregate Intrinsic Value in $000's):
|
|
Options |
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
Aggregate |
|
|
Weighted |
|
||||
|
|
Outstanding |
|
|
Price |
|
|
Value |
|
|
Life |
|
||||
Outstanding at January 2, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
||||
Cancelled/expired |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercised |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Outstanding at January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Cancelled/expired |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Outstanding at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
||||
F-36
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The exercise price for stock options outstanding and exercisable outstanding at December 31, 2022 is as follows:
Outstanding |
|
Exercisable |
||||||||
Number of Options |
|
|
Exercise Price ($) |
|
Number of Options |
|
|
Exercise Price ($) |
||
|
|
|
$17.35 to $23.45 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
||
|
|
|
$11.10 to $15.00 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
||
|
|
|
$5.70 to $9.90 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
||
|
|
|
$3.54 to $5.25 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
The following table summarizes information about the Company’s non-vested shares outstanding as of December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022:
Non-vested Shares |
|
Number of |
|
|
Non-vested at January 2, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
( |
) |
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
Non-vested at January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
Non-vested at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
The Company recognized share-based compensation expense related to stock options of approximately $
Note 21: Earnings (Loss) per share
Net loss per share is calculated using the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the applicable period. Basic weighted average common shares outstanding do not include shares of restricted stock that have not yet vested, although such shares are included as outstanding shares in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet. Diluted net earnings per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding, and, if dilutive, potential common shares outstanding during the period. Potential common shares consist of the additional common shares issuable with respect to restricted share awards, stock options and convertible preferred stock.
The following table presents the computation of basic and diluted net loss per share (in $000's, except per share data):
F-37
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
For the Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Continuing Operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic and diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) from continuing operations |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic and diluted loss per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Discontinued Operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic and diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic and diluted loss per share from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic and diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic and diluted loss per share |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Potentially dilutive securities totaling approximately
Note 22: Major customers and suppliers
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, five customers represented approximately
The Company purchased appliances for resale from five suppliers. The Company is continuing to secure other vendors from which to purchase appliances. However, the curtailment or loss of one of these suppliers or any appliance supplier could adversely affect our operations.
Note 23: Defined contribution plan
The Company has a defined contribution salary deferral plan covering substantially all employees under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”). The Company contributes an amount equal to 10 cents for each dollar contributed by each employee up to a maximum of
F-38
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 24: Segment information
The Company operates within targeted markets through
The following tables present our segment information (in $000's):
|
|
For the Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Recycling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total Revenues |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Recycling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total Gross profit |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Operating income (loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Recycling |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Operating loss from continuing operations |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total Operating income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Recycling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Depreciation and amortization from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total Depreciation and amortization |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Interest expense, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Recycling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total Interest expense |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Net income (loss) after provision for income taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Recycling |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net loss from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total Net income (loss) after provision for income taxes |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
F-39
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
As of |
|
|
As of |
|
||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Recycling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Discontinue operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total Assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Intangible Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biotechnology |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Recycling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Discontinue operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total Intangible Assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Note 25: Related parties
Tony Isaac, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, is the father of Jon Isaac, President and Chief Executive Officer of Live Ventures Incorporated (“Live Ventures”) and managing member of ICG, a greater than
ApplianceSmart Note
As stated in Note 5, on December 30, 2017, the Company sold its retail appliance segment, ApplianceSmart, Inc. (“ApplianceSmart”) to ApplianceSmart Holdings LLC (the “Purchaser”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Live Ventures Incorporated, pursuant to a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”). Pursuant to the Agreement, the Purchaser purchased from the Company all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of ApplianceSmart in exchange for $
On December 9, 2019, ApplianceSmart filed a voluntary petition in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York seeking relief under Chapter 11 of Title 11 of the United States Code. Consequently, the Company recorded an impairment charge of approximately $
On October 13, 2021, a hearing was held to consider approval of a disclosure statement filed by ApplianceSmart in conjunction with its bankruptcy proceedings. On December 14, 2021, a hearing was held to confirm ApplianceSmart’s plan for reorganization (the “Plan”). On January 10, 2022, ApplianceSmart paid $
F-40
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Related Party Note
On August 28, 2019, ARCA Recycling entered into and delivered to ICG a secured revolving line of credit promissory note, whereby ICG agreed to provide ARCA Recycling with a $
Future maturities of the related party note at December 31, 2022 are as follows and does not include related party debt (in $000's):
For the fiscal year ended |
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
$ |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
|
2025 |
|
|
|
|
2026 |
|
|
|
|
Total future maturities of related party debt |
|
$ |
|
|
F-41
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
ARCA Purchasing Agreement
On April 5, 2022, ARCA entered into a Purchasing Agreement with Live Ventures. Pursuant to the agreement, Live agrees to purchase inventory from time to time for ARCA, as set forth in submitted purchase orders. The inventory is owned by Live until which time payment by ARCA is received. All purchases made by ARCA shall be paid back to Live in full plus an additional five percent surcharge or broker-type fee. The term of the Agreement is one year, and automatically renews if not terminated by either party, as provided for in the Agreement. As of the year ended December 31, 2022, the amount due to Live Ventures was approximately $
Note 26: Sale of ARCA and Connexx
On February 19, 2021, the Company, together with its subsidiaries (a) ARCA Recycling, Inc., a California corporation (“ARCA”), and (b) Customer Connexx LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“Connexx”), entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with (i) ARCA Affiliated Holdings Corporation, a Delaware corporation, (ii) ARCA Services Inc., a Delaware corporation, and (iii) Connexx Services Inc, a Delaware corporation (collectively, the “Buyers”), pursuant to which the Buyers agreed to acquire substantially all of the assets, and assume certain liabilities, of ARCA and Connexx (the “Disposition Transaction”). The principal of the Buyers is Virland A. Johnson, our Chief Financial Officer. The Disposition Transaction was previously expected to be consummated on or before August 18, 2021 (the "Outside Date"). On August 12, 2021, the parties entered into Amendment No. One to Asset Purchase Agreement (the “Recycling Sale Amendment”) to extend the Outside Date to September 30, 2021. In the event the Disposition Transaction is not closed by such date, the Purchase Agreement may be terminated and, in accordance with its terms, the Buyers may be required to pay to us a “break fee” of $
Note 27: GeoTraq
Sale of GeoTraq
On May 24, 2022, the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with SPYR Technologies Inc., pursuant to which the Company sold to SPYR substantially all the assets and none of the liabilities of its wholly-owned subsidiary GeoTraq Inc. The aggregate purchase price for the GeoTraq Assets was $
F-42
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
In connection with the Asset Purchase Agreement, the Company employed an independent third-party firm to assess the fair value of the
As of December 31, 2022, based on declining financial trends at SPYR, the Company reviewed the original valuation of the Promissory Note to determine whether a revision of the estimate of the original
The following table illustrates the calculation of the gain on sale of GeoTraq, including the charges to income referenced above, as shown on the income statement (in $000's):
Purchase price |
|
$ |
|
|
Discount on note receivable |
|
|
( |
) |
Premium on shares received |
|
|
|
|
Derecognition of GeoTraq inventory |
|
|
( |
) |
Gain on sale |
|
$ |
|
Discontinued Operation
For the year ended, December 31, 2022, the Company determined that the GeoTraq sale qualified for accounting treatment as a discontinued operation under ASC 205 ("Discontinued Operations"). In accordance with ASC 205, the Company has reported the assets and liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets.
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Assets from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Inventories |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Total current assets from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total assets from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Liabilities from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Total current liabilities from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Property and equipment, net, from discontinued operations consist of the following:
|
|
Useful Life |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Equipment |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less accumulated depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total property and equipment, net, from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
F-43
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Depreciation expense was approximately $
In accordance with the provisions of ASC 205, the Company has not included in the results of continuing operations the results of operations of the discontinued operations in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss).
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Operating expenses from discontinued operations: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Impairment charges |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on sale of GeoTraq |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses from discontinued operations |
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
|
|
Operating income (loss) from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Other income (expense) from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on debt settlement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total other income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Income (loss) before benefit from income taxes from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Income tax provision |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income (loss) from |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
In accordance with the provisions of ASC 205, the Company would typically separately reported the cash flow activity of the discontinued operations in the consolidated statements of cash flows. However, due to the immateriality of the impact on cash flows from discontinued operations, the Company has chosen not to breakout these amounts on the consolidated statement of cash flows. The cash flow activity from discontinued operations was $
F-44
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 28: Restatement
On April 17, 2023, the Company’s management and the Audit Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Audit Committee”) reached a determination that the Company’s previously issued unaudited consolidated financial statements and related disclosures for each of the quarterly periods ended July 2, 2022 and October 1, 2022, should no longer be relied upon because of a material misstatement contained in those two quarterly unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements. In connection with the Company’s preparation of its unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and related disclosures for each of the two referenced periods, the Company’s management and Audit Committee relied upon the report issued by a third-party valuation firm to determine the carrying value of the promissory note the Company had received from SPYR Technologies, Inc. (the “SPYR Note”), in connection with the Company’s sale of the assets of its GeoTraq, Inc. subsidiary to SPYR Technologies, Inc. in the first quarter of the Company’s 2022 fiscal year. At December 31, 2022, the Company reviewed the original valuation of the Promissory Note to determine if the original 10.5% used to discount the Note was appropriate. In connection with this review, the Company determined that the discount rate should be revised to 14.5%.
The Company’s management and the Audit Committee discussed the matters with Frazier & Deeter, LLC, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the 2022 fiscal year, and with WSRP, LLC, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm during the second and third quarters in the 2022 fiscal year and prior fiscal periods since 2019, and determined to restate the Company’s unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements for the second and third fiscal quarters ended July 2, 2022, and October 1, 2022.
F-45
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
July 2, |
|
|
January 1, |
|
||||||||
|
|
(Unaudited) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
||||
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Trade and other receivables, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Income taxes receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Right to use asset - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Intangible assets, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Note receivable, net |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Deposits and other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total assets |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity (Deficit) |
|
|
||||||||||||
Liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Accrued liabilities - other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accrued liability - California Sales Taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Lease obligation short–term - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Short–term debt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Current portion of notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Current portion of related party note payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Lease obligation long term - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Long–term portion of notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Long-term portion related party note payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Other noncurrent liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Stockholders' equity (deficit): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Preferred stock, series A - par value $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Common stock, par value $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total stockholders' equity (deficit) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity (deficit) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
F-46
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
For the Thirteen Weeks Ended |
|
|
For the Twenty Six Weeks Ended |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
July 2, |
|
|
July 3, |
|
|
July 2, |
|
|
July 3, |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Revenues |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||||||
Cost of revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gain on sale of GeoTraq |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Operating income (loss) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||
Other income (expense): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Interest expense, net |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Gain on Payroll Protection Program loan forgiveness |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gain (loss) on litigation settlement, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||||||
Gain on settlement of vendor advance payments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gain on reversal of contingency loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||||
Other income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Total other income (expense), net |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Income (loss) from operations before provision for income taxes |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||
Provision (benefit) for income taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Net income (loss) from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||
F-47
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Net income from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
||||
Net income (loss) per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Basic income per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
||
Diluted income per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
||
Basic income per share from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||||||
Diluted income per share from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||||||
Basic income per share |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
||||
Diluted income per share |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Basic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Effect of foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||||||
Total other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
||||
F-48
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
Series A Preferred |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Equity (Deficit) |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(As restated) |
|
||||||||
Balance, January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
||||
Share based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Balance, April 2, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||||
Series A-1 preferred converted |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other comprehensive income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income, as restated |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Balance, July 2, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|||||
F-49
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
For the Twenty Six Weeks Ended |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
July 2, 2022 |
|
|
July 3, 2021 |
|
||||||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
||||
OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Amortization of debt issuance costs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Stock based compensation expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accretion of note receivable discount |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Gain on legal settlement |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Gain on Payroll Protection Program loan forgiveness |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||
Gain on settlement of vendor advance payments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||
Gain on reversal of contingent liability |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Gain on sale of GeoTraq |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Changes in assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accounts receivable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Income taxes receivable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Right of use assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Lease liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Deposits and other Assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Purchases of intangibles |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Proceeds from equity financing, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Proceeds from stock option exercise |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Proceeds from notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Payments on related party notes payable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Payments on notes payable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Payments on short-term notes payable |
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( | ) |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Effect of changes in exchange rate on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||
INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||
Supplemental cash flow disclosures: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Interest paid |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Income taxes paid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Right to use asset - operating leases capitalized |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
F-50
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
October 1, |
|
|
January 1, |
|
||||||||
|
|
(Unaudited) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
||||
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Trade and other receivables, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Right to use asset - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Intangible assets, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Note receivable, net |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Deposits and other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total assets |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity (Deficit) |
|
|
||||||||||||
Liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Accrued liabilities - other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accrued liability - California Sales Taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Lease obligation short–term - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Short–term debt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Current portion of notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Current portion of related party note payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Lease obligation long term - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Notes payable - long term portion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Long-term portion related party note payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Other noncurrent liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Stockholders' equity (deficit): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Preferred stock, series A - par value $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Common stock, par value $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total stockholders' equity (deficit) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity (deficit) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
F-51
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
For the Thirteen Weeks Ended |
|
|
For the Thirty-Nine Weeks Ended |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
October 1, |
|
|
October 2, |
|
|
October 1, |
|
|
October 2, |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Revenues |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||||||
Cost of revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gain on sale of GeoTraq |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Operating income (loss) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||
Other income (expense): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Interest income (expense), net |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Gain on Payroll Protection Program loan forgiveness |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gain (loss) on litigation settlement, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||||||
Gain on settlement of vendor advance payments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Gain on reversal of contingency loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||||
Other income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Total other income (expense), net |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Income (loss) from operations before provision for income taxes |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Net income (loss) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net income from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|||
F-52
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Net income (loss) per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Basic income per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
|
Diluted income per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( | ) |
$ |
( | ) |
|
$ |
( | ) |
|
Basic income per share from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||||||
Diluted income per share from discontinued operations |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||||||
Basic income per share |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|||
Diluted income per share |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|||
Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Basic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Effect of foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||||||
Total other comprehensive income loss, net of tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|||
F-53
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
Series A Preferred |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Equity (Deficit) |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(As restated) |
|
||||||||
Balance, January 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
||||
Share based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Balance, April 2, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||||
Series A-1 preferred converted |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Other comprehensive income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net income, as restated |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Balance, July 2, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|||||
Net income, as restated |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Balance, October 1, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|||||
F-54
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
For the Thirty-Nine Weeks Ended |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
October 1, 2022 |
|
|
October 2, 2021 |
|
||||||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
Effect of Restatement |
|
As restated |
|
|
|
|
||||
OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash used in operating |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Amortization of debt issuance costs |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
||
Stock based compensation expense |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Accretion of note receivable discount |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Gain on legal settlement |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Gain on Payroll Protection Program loan forgiveness |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Gain on settlement of vendor advance payments |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Gain on reversal of contingent liability |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Gain on sale of GeoTraq |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
||
Changes in assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Accounts receivable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Income taxes receivable |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Right of use assets |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Lease liability |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Deposits and other Assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Purchases of intangibles |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Proceeds from equity financing, net |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of short-term notes payable |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Proceeds from stock option exercise |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from notes payable |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Payments on related party notes payable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
— |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Payments on notes payable |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Payments on short-term notes payable |
|
|
( | ) |
|
— |
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( | ) |
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Effect of changes in exchange rate on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
) |
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||
Supplemental cash flow disclosures: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Interest paid |
|
$ |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Income taxes paid |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Right to use asset - operating leases capitalized |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
F-55
JANONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 29: Subsequent events
The Company has evaluated subsequent events through the filing of this Form 10-K, and determined that there have been no events that have occurred that would require adjustments to disclosures in its consolidated financial statements other than as discussed below:
ARCA and Subsidiaries Disposition
On March 19, 2023, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement with VM7 Corporation, a Delaware corporation, under which the Buyer agreed to acquire all of the outstanding equity interests of (a) ARCA Recycling, Inc., a California corporation, (b) Customer Connexx LLC, a Nevada limited liability company, and (c) ARCA Canada Inc., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“ARCA Canada”; and, together with ARCA and Connexx, the “Subsidiaries”). The principal of the Buyer is Virland A. Johnson, our Chief Financial Officer. The sale of all of the outstanding equity interests of the Subsidiaries to the Buyer under the Purchase Agreement was consummated simultaneously with the execution of the Purchase Agreement. The Company's Board of Directors unanimously approved the Purchase Agreement and the Disposition Transaction.
The economic aspects of the Disposition Transaction are: (i) the Company reduced the liabilities on its consolidated balance sheets by approximately $
Securities Purchase Agreement
On March 22, 2023, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement with certain institutional investors for the sale by the Company in a registered direct offering of
F-56
ITEM 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosures
None.
ITEM 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure control and Procedures. We carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) to ensure that information required to be disclosed in reports filed under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the required time periods and is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Based upon that evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of December 31, 2022, the period covered in this report, our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective because of the material weaknesses discussed below.
In light of the conclusion that our internal disclosure controls are ineffective as of December 31, 2022, we have applied procedures and processes as necessary to ensure the reliability of our financial reporting in regard to this annual report. Accordingly, the Company believes, based on its knowledge, that: (i) this annual report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit a material fact; and (ii) the financial statements, and other financial information included in this annual report, fairly present in all material respects our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows as of and for the periods presented in this annual report.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)). Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Our management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2022. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”) in 2013 regarding Internal Control – Integrated Framework. Based on our assessment using those criteria, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2022.
Management noted material weaknesses in internal control when conducting their evaluation of internal control as of December 31, 2022. (1) Insufficient information technology general controls and segregation of duties. (2) inadequate control design or lack of sufficient controls over significant accounting processes; (3) insufficient assessment of the impact of potentially significant transactions; and (4) insufficient processes and procedures related to proper recordkeeping of agreements and contracts.
These material weaknesses remained outstanding as of the filing date of this Form 10-K and management is currently working to remedy these outstanding material weaknesses.
62
The Company’s management, including the Company’s CEO and CFO, do not expect that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures or the Company’s internal control over financial reporting will prevent or detect all error and all fraud. A control system, regardless of how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system will be met. These inherent limitations include the following: judgements in decision-making can be faulty, and control and process breakdowns can occur because of simple errors or mistakes, controls can be circumvented by individuals, acting alone or in collusion with each other, or by management override, the design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions, over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance with policies or procedures. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. There were no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. Other Information
None.
ITEM 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
None.
63
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The directors and executive officers of the Company and their ages as of December 31, 2022, are as follows:
Name |
|
Age |
|
|
Position |
|
Richard D. Butler, Jr. |
|
|
72 |
|
|
Director |
Nael Hajjar |
|
|
38 |
|
|
Director |
John Bitar |
|
|
60 |
|
|
Director |
Tony Isaac |
|
|
69 |
|
|
President and Chief Executive Officer |
Virland A. Johnson |
|
|
62 |
|
|
Chief Financial Officer |
Richard D. Butler, Jr. has been a director of the Company since May 2015. Mr. Butler is the owner of an advisory firm that provides real estate, corporate, and financial advisory services since 1999, and is the co-Founder, Managing Director, and, since 2005, a major stockholder of Ref-Razzer Company, a whistle manufacturing and vending company. Prior to this, Mr. Butler was the Co-Founder and Executive Vice President of Aspen Healthcare, Inc. from 1996 to 1999. From 1993 to 1996, Mr. Butler was a Managing Director at Landmark Financial and from 1989 to 1993 he was a Partner at Cal Ventures Real Estate Investment Group. Prior to this, Mr. Butler has also served as the President and Chief Executive Officer of Mt. Whitney Savings Bank, Chief Executive Officer of First Federal Mortgage Bank, Chief Executive Officer of Trafalgar Mortgage, and Executive Officer and Member of the President’s Advisory Committee at State Savings & Loan Association (peak assets $14 billion) and American Savings & Loan Association (NYSE: FCA; peak assets $34 billion). Mr. Butler has served on the board of directors of Live Ventures (Nasdaq: Live)”) since August 2006. On December 9, 2019, ApplianceSmart, a subsidiary of Live Ventures, filed a voluntary petition in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York seeking relief under Chapter 11 of Title 11 of the United States Code. Mr. Butler attended Bowling Green University in Ohio, San Joaquin Delta College in California, and Southern Oregon State College. We believe that Mr. Butler brings to the Board extensive experience in financial management and executive roles, which enable him to provide important expertise in financial, operating and strategic matters that impact our Company.
Nael Hajjar has been a director of the Company since August 2018. Mr. Hajjar is currently the Unit Head for the Annual Wholesale Trade Survey in Statistics Canada’s Manufacturing and Wholesale Trade Division. From March 2011 through May 2016, Mr. Hajjar was a Senior Analyst – Economist of Statistics Canada’s Producer Prices Division where he developed Canada’s first ever Investment Banking Services Price Index while leading the development of a variety of Financial Services Price Index development projects. We believe that Mr. Hajjar brings to the Board extensive experience in research and analysis of financial statistics, economics, and business practices in a variety of industries including manufacturing, logging, Wholesale Trade, and financial services. We believe that Mr. Hajjar also has extensive experience in project management, and he holds a Bachelor of Social Science, Honors in Economics, and Bachelor of Commerce, Option in Finance, from the University of Ottawa.
John Bitar has been a director of the Company since January 2020. Since 2012, Mr. Bitar has been providing consulting services to companies and clients on business and legal strategies, management, operations, and cost controls. From 2007 to 2012, Mr. Bitar co-founded and was Managing Partner of a worker’s compensation law firm. Mr. Bitar has been an attorney admitted to the California State Bar since 1999. Mr. Bitar graduated from the University of Southern California in 1996 and earned his Juris Doctorate Degree in 1999 from University of the Pacific, McGeorge School of Law. We believe that Mr. Bitar has significant business experience and brings operational expertise to the Board.
Tony Isaac has been a director of the Company since May 2015 and Chief Executive Officer of the Company since May 2016. He served as Interim Chief Executive Officer of the Company from February 2016 until May 2016. Mr. Isaac has served as Financial Planning and Strategist/Economist of Live Ventures since July 2012. He is the Chairman and Co-Founder of Isaac Organization, a privately held investment company. Mr. Isaac has invested in various companies, both private and public from 1980 to the present. Mr. Isaac’s specialty is negotiation and problem-solving of complex real estate and business transactions. Mr. Isaac has served as a director of Live Ventures since December 2011. Mr. Isaac graduated from Ottawa University in 1981, where he majored in Commerce and Business Administration and Economics. We believe that Mr. Isaac has significant investment and financial expertise and public board experience that he brings to the Board.
64
Virland A. Johnson was appointed Chief Financial Officer of the Company on August 21, 2017. Mr. Johnson had previously served the Company as a consultant beginning in February 2017. Mr. Johnson also served as Chief Financial Officer for Live Ventures from January 3, 2017 through October 1, 2021. Mr. Johnson is a director and Chief Financial Officer and Secretary of ApplianceSmart. Prior to joining Live Ventures Incorporated, Mr. Johnson was Sr. Director of Revenue for JDA Software from February 2010 to April 2016, where he was responsible for revenue recognition determination, sales and contract support while acting as a subject matter expert. Prior to joining JDA, Mr. Johnson provided leadership and strategic direction while serving in C-Level executive roles in public and privately held companies such as Cultural Experiences Abroad, Inc., Fender Musical Instruments Corp., Triumph Group, Inc., Unitech Industries, Inc. and Younger Brothers Group, Inc. Mr. Johnson’s more than 25 years of experience is primarily in the areas of process improvement, complex debt financings, SEC and financial reporting, turn-arounds, corporate restructuring, global finance, merger and acquisitions and returning companies to profitability and enhancing stockholder value. Mr. Johnson holds a Bachelor’s degree in Accountancy from Arizona State University, and holds an active CPA license in the State of Arizona.
Delinquent Section 16(a) Reports
Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, requires the Company’s officers and directors, and persons who own more than 10% of a registered class of the Company’s equity securities, to file reports of ownership on Form 3 and changes in ownership on Form 4 or Form 5 with the SEC. Such officers, directors and 10% stockholders are also required by SEC rules to furnish the Company with copies of all Section 16(a) forms they file.
Based solely on its review of copies of such forms received by it, or written representations from certain reporting persons, the Company believes that, during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, all of its officers, directors and 10% stockholders complied with all Section 16(a) timely filing requirements.
Code of Ethics
Our Audit Committee has adopted a code of ethics applicable to our directors and officers (including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer) and other of our senior executives and employees in accordance with applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and The Nasdaq Stock Market. A copy of the code of ethics may be obtained upon request, without charge, by addressing a request to Investor Relations, JanOne Inc., 325 E. Warm Springs Road, Suite 102, Las Vegas, Nevada 89119. The code of ethics is also posted on our website at www.janone.com under “Investor Relations — Corporate Governance.”
We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding the amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of the code of ethics by posting such information on our website at the address and location specified above and, to the extent required by the listing standards of the Nasdaq Capital Market, by filing a Current Report on Form 8-K with the SEC disclosing such information.
Audit Committee
The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors is comprised entirely of non-employee directors. In fiscal 2021, the members of the Audit Committee were Mr. Butler (Chair), Mr. Bitar, and Mr. Hajjar. Each of Messrs. Bitar, Butler, and Hajjar was an “independent” director as defined under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market. The Audit Committee is responsible for selecting and approving the Company’s independent auditors, for relations with the independent auditors, for review of internal auditing functions (whether formal or informal) and internal controls, and for review of financial reporting policies to assure full disclosure of financial condition. The Audit Committee operates under a written charter adopted by the Board of Directors, which is posted on the Company’s website at www.janone.com under the caption “Investor Relations - Governance.” The Board has determined that Mr. Butler is an “audit committee financial expert” as defined in SEC rules.
65
Compensation and Benefits Committee
The Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors is comprised entirely of non-employee directors. In fiscal 2021, the members of the Compensation Committee were Mr. Butler (Chair) and Mr. Hajjar, each of whom was also an “independent” director as defined under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market. The Compensation Committee is responsible for review and approval of officer salaries and other compensation and benefits programs and determination of officer bonuses. Annual compensation for the Company’s executive officers, other than the CEO, is recommended by the CEO and approved by the Compensation Committee. The annual compensation for the CEO is recommended by the Compensation Committee and formally approved by the full Board of Directors.
In the performance of its duties, the Compensation Committee may select independent compensation consultants to advise the committee when appropriate. In addition, the Compensation Committee may delegate authority to subcommittees where appropriate. The Compensation Committee may separately meet with management if deemed necessary and appropriate. The Compensation Committee operates under a written charter adopted by the Board of Directors in March 2011, which is posted on the Company’s website at www.janone.com under the caption “Investor Relations - Governance.”
Governance Committee
The Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee (the “Governance Committee”) is comprised entirely of non-employee directors. In fiscal 2021, the members of the Governance Committee were Mr. Butler (Chair) and Mr. Bitar, each of whom was also an “independent” director as defined under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market. The primary purpose of the Governance Committee is to ensure an appropriate and effective role for the Board of Directors in the governance of the Company. The principal recurring duties and responsibilities of the Governance Committee include (i) making recommendations to the Board regarding the size and composition of the Board, (ii) identifying and recommending to the Board of Directors candidates for election as directors, (iii) reviewing the Board’s committee structure, composition and membership and recommending to the Board candidates for appointment as members of the Board’s standing committees, (iv) reviewing and recommending to the Board corporate governance policies and procedures, (v) reviewing the Company’s Code of Business Ethics and Conduct and compliance therewith, and (vi) ensuring that emergency succession planning occurs for the positions of Chief Executive Officer, other key management positions, the Board chairperson and Board members. The Governance Committee operates under a written charter adopted by the Board of Directors in March 2011, which is posted on the Company’s website at www.janone.com under the caption “Investor Relations - Governance.”
The Governance Committee will consider director candidates recommended by stockholders. The criteria applied by the Governance Committee in the selection of director candidates is the same whether the candidate was recommended by a Board member, an executive officer, a stockholder or a third party, and, accordingly, the Governance Committee has not deemed it necessary to adopt a formal policy regarding consideration of candidates recommended by stockholders. Stockholders wishing to recommend candidates for Board membership should submit the recommendations in writing to the Secretary of the Company.
The Governance Committee identifies director candidates primarily by considering recommendations made by directors, management, and stockholders. The Governance Committee also has the authority to retain third parties to identify and evaluate director candidates and to approve any associated fees or expenses. Board candidates are evaluated on the basis of a number of factors, including the candidate’s background, skills, judgment, diversity, experience with companies of comparable complexity and size, the interplay of the candidate’s experience with the experience of other Board members, the candidate’s independence or lack of independence, and the candidate’s qualifications for committee membership. The Governance Committee does not assign any particular weighting or priority to any of these factors and considers each director candidate in the context of the current needs of the Board as a whole. Director candidates recommended by stockholders are evaluated in the same manner as candidates recommended by other persons.
66
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The following table sets forth the cash and non-cash compensation for fiscal years ended December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, earned by each person who served as Chief Executive Officer and our other two most highly compensated executive officers who held office as of December 31, 2022 (“named executive officers”):
Summary Compensation Table
Name and Principal Position (1) |
|
Year |
|
Salary ($) |
|
|
Bonus ($) |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
|
Option |
|
|
All Other |
|
|
Total ($) |
|
||||||
Tony Isaac |
|
2022 |
|
|
550,324 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
625,324 |
|
President, Chief Executive Officer, and Secretary |
|
2021 |
|
|
550,324 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
550,324 |
|
Virland A. Johnson |
|
2022 |
|
|
250,324 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
250,324 |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
2021 |
|
|
149,363 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
149,363 |
|
Outstanding Equity Awards at December 31, 2022
The following table provides a summary of equity awards outstanding for our Named Executive Officers at December 31, 2022:
Name |
Number of |
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Option |
|
|
Option |
|||
Tony Isaac |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
9.90 |
|
|
05/18/2025 |
Virland A. Johnson |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
Stock Option Plans
The Company uses stock options to attract and retain executives, directors, consultants and key employees. Stock options are currently outstanding under three stock option plans. The Company’s 2016 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2016 Plan”) was adopted by the Board of Directors in October 2016 and approved by the stockholders at the 2016 annual meeting of stockholders. Under the 2016 Plan, the Company has reserved an aggregate of 400,000 shares of its common stock for option grants. On November 4, 2020, at the Annual Meeting, the Company’s stockholders approved an amendment (the “Plan Amendment”) to the 2016 Plan to increase the total number of shares of the Company’s common stock reserved for issuance under the 2016 Plan from 400,000 shares to 800,000 shares. The Company’s 2011 Stock Compensation Plan (the “2011 Plan”) was adopted by the Board of Directors in March 2011 and approved by the stockholders at the 2011 annual meeting of stockholders. The 2011 Plan expired on December 29, 2016; but, options granted under the 2011 Plan before it expired will continue to be exercisable in accordance with their terms. As of December 31, 2022, options to purchase an aggregate of 117,500 shares were outstanding, including options for 90,000 shares under the 2016 Plan and options for 27,500 shares under the 2011 Plan. The Plans are administered by the Compensation Committee or the full Board of Directors acting as the Committee.
67
The 2016 Plan permits the grant of the following types of awards, in the amounts and upon the terms determined by the Administrator:
Compensation of Non-Employee Directors
The Company uses cash compensation to attract and retain qualified candidates to serve on the Board of Directors. In setting director compensation, the Company considers the significant amount of time that directors expend fulfilling their duties to the Company as well as the skill level required by the Company of members of the Board. All of the Company’s directors are reimbursed for reasonable travel expenses incurred in attending meetings.
The table below presents cash and non-cash compensation paid to non-employee directors during the last fiscal year.
Non-Management Director Compensation for Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2022
Name |
|
Fees |
|
|
Option |
|
|
All Other |
|
|
Total ($) |
|
||||
John Bitar |
|
|
18,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,000 |
|
Richard D. Butler, Jr. |
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
Nael Hajjar |
|
|
14,400 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
14,400 |
|
68
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED SHAREHOLDER MATTERS
The following table sets forth as of April 12, 2023 the beneficial ownership of common stock by each of the Company’s directors, each of the named executive officers, and all directors and executive officers of the Company as a group, as well as information about beneficial owners of 5.0% or more of the Company’s voting securities. Beneficial ownership includes shares that may be acquired in the next 60 days through the exercise of options or warrants.
Beneficial Owner |
|
Position with |
|
Number of |
|
|
Percent of |
|
||
Directors and executive officers: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Tony Isaac (3) |
|
President, Chief Executive Officer, and Secretary |
|
|
94,000 |
|
|
|
2.6 |
% |
Virland A. Johnson |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
— |
|
|
* |
|
|
Richard D. Butler, Jr. (3) |
|
Director |
|
|
18,000 |
|
|
* |
|
|
John Bitar |
|
Director |
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
* |
|
|
Nael Hajjar |
|
Director |
|
|
— |
|
|
* |
|
|
All directors and executive officers |
|
|
|
|
114,000 |
|
|
|
3.2 |
% |
Other 5% stockholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Isaac Capital Group, LLC (4) |
|
|
|
|
675,761 |
|
|
|
18.7 |
% |
Juan Yunis (5) |
|
|
|
|
460,000 |
|
|
|
12.7 |
% |
Michael Bigger (6) |
|
|
|
|
361,000 |
|
|
|
10.0 |
% |
* Indicates ownership of less than 1% of the outstanding shares
Beneficial Ownership of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
The following table sets forth, as of April 12, 2023, the beneficial ownership of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock by each owner of 5% or more of the Company’s Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock. No officers or directors of the Company have beneficial ownership of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock. There are no options or warrants to purchase shares of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock.
Beneficial Owner |
|
Number of |
|
|
Percent of |
|
||
Gregg Sullivan (3) |
|
|
28,859 |
|
|
|
13.0 |
% |
Juan Yunis (4) |
|
|
193,730 |
|
|
|
87.0 |
% |
69
The following table provides aggregate information under our equity compensation plans as of January 1, 2022:
|
|
(a) |
|
|
(b) |
|
|
(c) |
|
|||
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
Number of |
|
|||
Equity compensation plans approved by |
|
|
110,000 |
|
|
$ |
6.27 |
|
|
|
710,000 |
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total |
|
|
110,000 |
|
|
$ |
6.27 |
|
|
|
710,000 |
|
Review, Approval or Ratification of Transactions with Related Persons
There are no family relationships among any of the directors or executive officers of the Company. Of the current directors, each of Messrs. Butler, Bitar, and Hajjar is an “independent” director, as defined under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market and each has been an independent director since each joined the Board.
In accordance with its charter, the Audit Committee reviews and recommends for approval all related party transactions (as such term is defined for purposes of Item 404 of Regulation S-K). The Audit Committee participated in the approval of the transactions described above.
70
Related Party Transactions
Tony Isaac, our Chief Executive Officer, is the father of Jon Isaac, President and Chief Executive Officer of Live Ventures and managing member of ICG, a greater than 5% stockholder of the Company. Tony Isaac and Richard Butler are also members of the Board of Directors of Live Ventures. We also share certain executive, accounting, and legal services with Live Ventures. The total services shared were approximately $314,000 and approximately $296,000 for fiscal years ending December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, respectively. Connexx rents approximately 9,900 square feet of office space from Live Ventures at its Las Vegas, Nevada office. The total rent and common area expense were approximately $215,000 and approximately $227,000 for fiscal years ending December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022, respectively.
ApplianceSmart Note
As stated in Note 5, on December 30, 2017, the Company sold its retail appliance segment, ApplianceSmart, Inc. (“ApplianceSmart”) to ApplianceSmart Holdings LLC (the “Purchaser”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Live Ventures Incorporated, pursuant to a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”). Pursuant to the Agreement, the Purchaser purchased from the Company all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of ApplianceSmart in exchange for $6.5 million. On April 25, 2018, the Purchaser delivered to the Company a promissory note (the “ApplianceSmart Note”) in the original principal amount of approximately $3.9 million.
On December 9, 2019, ApplianceSmart filed a voluntary petition in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York seeking relief under Chapter 11 of Title 11 of the United States Code. Consequently, the Company recorded an impairment charge of approximately $3.0 million for the amount owed by ApplianceSmart to the Company as of December 28, 2019.
On October 13, 2021, a hearing was held to consider approval of a disclosure statement filed by ApplianceSmart in conjunction with its bankruptcy proceedings. On December 14, 2021, a hearing was held to confirm ApplianceSmart’s plan for reorganization (the “Plan”). On January 10, 2022, ApplianceSmart paid $25,000 to JanOne in settlement of its debt, as provided for in the confirmed Plan, and the ApplianceSmart Note was reversed. A final decree was issued by the court on February 28, 2022, upon the full satisfaction of the Plan, at which time ApplianceSmart emerged from Chapter 11. The outstanding balance of the ApplianceSmart Note at December 31, 2022 and January 1, 2022 was zero and approximately $3.0 million, respectively, exclusive of the impairment charge.
For discussion related to potential obligations and or guarantees under ApplianceSmart Leases, see Note 24.
71
Related Party Note
On August 28, 2019, ARCA Recycling entered into and delivered to ICG a secured revolving line of credit promissory note, whereby ICG agreed to provide ARCA Recycling with a $2.5 million revolving credit facility (the “ICG Note”). The ICG Note originally matured on August 28, 2020. On August 25, 2020, the ICG Note was amended to extend the maturity date to December 31, 2020. On March 30, 2021, ARCA Recycling entered into a Second Amendment and Waiver (the “Second Amendment”) to the ICG Note to further extend the maturity date to August 18, 2021 and waive certain defaults under the ICG Note. The ICG Note bears interest at 8.75% per annum and provides for the payment of interest, monthly in arrears. ARCA Recycling will pay a loan fee of 2.0% on each borrowing made under the ICG Note. In connection with entering into the ICG Note, the Borrower also entered into a security agreement in favor of the Lender, pursuant to which ARCA Recycling granted a security interest in all of its assets to the Lender. The obligations of ARCA Recycling under the ICG Note are guaranteed by the Company. The foregoing transaction did not include the issuance of any shares of the Company’s common stock, warrants, or other derivative securities. As of January 1, 2022, the balance due on ICG note was $1.0 million. Beginning in April 2022, the revolving credit facility was converted to a term note that amortizes ratably through its maturity date of March 2026. The principal amount of the note is $1.0 million, and bears interest at 8.75% per annum. Monthly payments on this note will be approximately $24,767. ICG is a record and beneficial owner of 13.9% of the outstanding common stock of the Company. Jon Isaac is the manager and sole member of ICG, and the son of Tony Isaac, the Chief Executive Officer of JanOne and ARCA Recycling. As of December 31, 2022, the principal balance of the note is approximately $838,000.
ARCA Purchasing Agreement
On April 5, 2022, ARCA entered into a Purchasing Agreement with Live Ventures. Pursuant to the agreement, Live agrees to purchase inventory from time to time for ARCA, as set forth in submitted purchase orders. The inventory is owned by Live until which time payment by ARCA is received. All purchases made by the ARCA shall be paid back to Live in full plus an additional five percent surcharge or broker-type fee. The term of the Agreement is one year, and automatically renews if not terminated by either party, as provided for in the Agreement. As of the year ended December 31, 2022, the amount due to Live Ventures was approximately $624,000. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company paid broker fees of approximately $59,000.
ARCA and Subsidiaries Disposition
On March 19, 2023, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement with VM7 Corporation, a Delaware corporation, under which the Buyer agreed to acquire all of the outstanding equity interests of (a) ARCA Recycling, Inc., a California corporation, (b) Customer Connexx LLC, a Nevada limited liability company, and (c) ARCA Canada Inc., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“ARCA Canada”; and, together with ARCA and Connexx, the “Subsidiaries”). The principal of the Buyer is Virland A. Johnson, our Chief Financial Officer. The sale of all of the outstanding equity interests of the Subsidiaries to the Buyer under the Purchase Agreement was consummated simultaneously with the execution of the Purchase Agreement. The Company's Board of Directors unanimously approved the Purchase Agreement and the Disposition Transaction.
The economic aspects of the Disposition Transaction are: (i) the Company reduced the liabilities on its consolidated balance sheets by approximately $17.6 million, excluding those related to the California Business Fee and Tax Division; (ii) the Company will receive not less than $24.0 million in aggregate monthly payments from the Buyer, which payments are subject to potential increase due to the Subsidiaries’ future performance; and (iii) during the next five years, the Company may request that the Buyer prepay aggregate monthly payments in the aggregate amount of $1 million. The Company also received one thousand dollars for the equity of each of the Subsidiaries at the closing. Each monthly payment is to be the greater of (a) $140,000 (or $100,000 for each January and February during the 15-year payment period) or (b) a monthly percentage-based payment, which is an amount calculated as follows: (i) 5% of the Subsidiaries’ aggregate gross revenues up to $2,000,000 for the relevant month, plus (ii) 4% of the Subsidiaries’ aggregate gross revenues between $2,000,000 and $3,000,000 for the relevant month, plus (iii) 3% of the Subsidiaries aggregate gross revenues over $3,000,000 for the relevant month. The Buyer will receive credit toward the payment of the first monthly payment (March of 2023) for any payments, distributions, or cash dividends paid by any of the Subsidiaries to the Seller on or after March 19, 2023.
72
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Each year, the Audit Committee approves the annual audit engagement in advance. The Audit Committee also has established procedures to pre-approve all non-audit services provided by the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm. All non-audit services for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022, and January 1, 2022 that are listed below were pre-approved.
Audit Fees: Audit fees include fees for the audit of the Corporation’s consolidated financial statements and interim reviews of the Corporation’s quarterly financial statements, comfort letters, consents and other services related to Securities and Exchange Commission matters.
Audit-Related Fees: Audit-related fees primarily include fees for certain audits of subsidiaries not required for purposes of WSRP's audit of the Corporation’s consolidated financial statements or for any other statutory or regulatory requirements, and consultations on various other accounting and reporting matters
Tax Fees: This category consists of professional services rendered by our independent auditors for tax compliance.
All Other Fees consist of fees for services other than the services described above.
The following fees were billed to us by our independent registered public accounting firms , WSRP, LLC (“WSRP”) and Frazier & Deeter, LLC (“Frazier & Deeter”) for 2022 and WSRP in 2021:
Description |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
January 1, 2022 |
|
||
Audit fees |
|
$ |
353,500 |
|
|
$ |
212,725 |
|
Audit-related fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
11,466 |
|
Tax fees |
|
|
40,800 |
|
|
|
48,459 |
|
All other fees |
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total |
|
$ |
398,300 |
|
|
$ |
272,650 |
|
73
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
See Index to Financial Statements under Item 8 of this report.
None.
See Index to Exhibits
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
74
Index to Exhibits
Exhibit No. |
|
Description |
2.1 |
|
Agreement and Plan of Merger dated August 18, 2017, between the Company, Appliance Recycling Acquisition Corp., GeoTraq Inc., and the stockholders of GeoTraq Inc. [filed as Exhibit 10.9 to the Company’s Form 10-Q/A for the quarterly period ended July 1, 2017 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
Stock Purchase Agreement dated December 30, 2017 [filed as Exhibit 10.28 to the Company’s Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 30, 2017 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
2.3 |
|
Asset Purchase Agreement among JanOne Inc., ARCA Recycling, Inc., and Customer Connexx LLC, on the one hand, and ARCA Affiliated Holdings Corporation, ARCA Services Inc., and Connexx Services Inc., on the other hand, dated February 19, 2021 [filed as 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on February 25, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
Articles of Incorporation of Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 3.3 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on March 13, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
Articles of Conversion [filed as Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on March 13, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.3 |
|
Articles of Conversion [filed as Exhibit 3.2 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on March 13, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.4 |
|
Certificate of Correction to Articles of Incorporation [filed as Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2018 (File No 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
Certificate of Change [filed as Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 22, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.6 |
|
Certificate of Correction to Articles of Incorporation of Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 3.7 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 24, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.7 |
|
Certificate of Designation of Powers, Preferences, and Rights of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock of Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 3.8 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 24, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.8(a) |
|
Amended and Restated Certificate of Designation of the Preferences, Rights, and Limitations of the Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock of JanOne Inc., dated October 1, 2020 [filed as Exhibit 3.8(a) to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2020 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.8(b) |
|
Second Amendment and Restated Certificate of Designation of the Preferences, Rights, and Limitations of the Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock of JanOne Inc., dated April 13, 2021 [filed as Exhibit 3.8(b) to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 16, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference] |
|
|
|
3.9 |
|
Articles of Incorporation of JanOne Inc. (the Name Change Subsidiary), filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada on September 6, 2019 [filed as Exhibit 3.9 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 13, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.10 |
|
Certificate of Amendment to Articles of Incorporation, filed with the Secretary of State for the State of Nevada on November 5, 2020 [filed as 3.9 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 26, 2020 filed on November 10, 2020 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
75
3.11 |
|
Articles of Merger for JanOne Inc. into Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc., filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada on September 9, 2019, and effective on September 10, 2019 [filed as Exhibit 3.10 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 13, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.12 |
|
Bylaws of Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 3.4 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on March 13, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.13 |
|
First Amendment to Bylaws of Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on December 31, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
3.14+ |
|
|
|
|
|
4.1+ |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
|
Specimen Stock Certificate [filed as Exhibit 4.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 26, 2020 filed on November 10, 2020 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.1X |
|
Patent and Know How License Agreement dated November 19, 2019, by and among JanOne Inc., and UAB Research Foundation, TheraVasc, Inc., and the Board of Supervisors of Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, acting on behalf of LSU Health Sciences Center at Shreveport [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 25, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.2 X |
|
Master Agreement for Development, Manufacturing and Supply Services dated February 5, 2020 by and between JanOne Inc. and CoreRx Inc. [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 7, 2020 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
Promissory Note between JanOne Inc., as the borrower, and Texas Capital Bank, N.A., as lender [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on May 4, 2020 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
Amended and Restated Promissory Note, effective April 1, 2018, issued by ApplianceSmart Holdings LLC [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on December 31, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
Security Agreement dated December 26, 2018 by and between ApplianceSmart Holdings LLC and Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on December 31, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.6 |
|
Security Agreement dated December 26, 2018 by and between ApplianceSmart, Inc. and Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on December 31, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.7 |
|
Security Agreement dated December 26, 2018 by and between ApplianceSmart Contracting Inc. and Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on December 31, 2018 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.8 |
|
Subordination Agreement, dated March 15, 2019, from Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. to Crossroads Financing, LLC [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on March 21, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.9 |
|
Intercreditor and Subordination Agreement, dated March 18, 2019, by and between Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc. and Crossroads Financing, LLC [filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on March 21, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.10 |
|
Secured Revolving Line of Credit Promissory Note [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 30, 2019 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
76
10.11 |
|
Amendment to Secured Line of Credit Promissory Note dated August 25, 2020 between ARCA Recycling, Inc. and Isaac Capital Group, LLC [filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 10, 2020 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.12 |
|
Second Amendment and Waiver to Secured Line of Credit Promissory Note dated March 30, 2021 between ARCA Recycling, Inc. and Isaac Capital Group, LLC [filed as Exhibit 10.12 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on March 30, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.13 |
|
Securities Purchase Agreement dated November 8, 2016, between Energy Efficiency Investments, LLC and the Company [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 15, 2016 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.14 |
|
Termination Agreement by and between Energy Efficiency Investments, LLC and JanOne Inc [filed as 10.18 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 28, 2019 filed on April 6, 2020 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference] |
|
|
|
10.15 |
|
Form of 3% Original Issue Discount Senior Convertible Promissory Note issuable under Securities Purchase Agreement dated November 8, 2016, between Energy Efficiency Investments, LLC and the Company [filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 15, 2016 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.16 |
|
Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant issuable under Securities Purchase Agreement dated November 8, 2016, between Energy Efficiency Investments, LLC and the Company [filed as Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 15, 2016 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.17* |
|
2011 Stock Compensation Plan [filed with the Company’s Schedule DEF 14A on March 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.18* |
|
2016 Equity Incentive Plan [filed as Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference] |
|
|
|
10.19* |
|
First Amendment to the JanOne Inc. 2016 Equity Incentive Plan [filed with the Company’s Schedule DEF 14A on October 2, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference] |
|
|
|
10.20*× |
|
Master Equipment Finance Agreement dated as of March 25, 2021 between KLC Financial, Inc. and ARCA Recycling, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 10.20 to the Company’s Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 2, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference] |
|
|
|
10.21 |
|
Asset Purchase Agreement among JanOne Inc., ARCA Recycling, Inc., and Customer Connexx LLC, on the one hand, and ARCA Affiliated Holdings Corporation, ARCA Services Inc., and Connexx Services Inc., on the other hand, dated February 19, 2021 [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 25, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.22 |
|
Second Amendment and Waiver to Secured Line of Credit Promissory Note dated March 30, 2021 between ARCA Recycling, Inc. and Isaac Capital Group, LLC. [filed as Exhibit 10.12 to the Company’s Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 2, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference] |
|
|
|
10.23 |
|
Securities Purchase Agreement dated January 29, 2021 by and between JanOne Inc. and the purchasers listed therein. [filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 29, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.24 |
|
Addendum to Master Equipment Finance Agreement dated as of April 14, 2021 between KLC Financial, LLC and ARCA Recycling, Inc. [filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on May 17, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.25 |
|
Settlement Agreement and Mutual Release of Claims dated April 9, 2021 by and among JanOne Inc. (f/k/a Appliance Recycling Centers of America, Inc.); GeoTraq, Inc.; Antonio Isaac; and Gregg Sullivan. [filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on August 16, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
77
10.26 |
|
Amendment No. One to Asset Purchase Agreement among JanOne Inc., ARCA Recycling, Inc. and Customer Connexx LLC, on the one hand, and ARCA Affiliated Holdings Corporation, ARCA Services Inc., and Connexx Services Inc., on the other hand [filed as Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on August 16, 2021 (File No. 0-19621) and incorporated herein by reference]. |
|
|
|
10.27+ |
|
|
|
|
|
10.28 |
|
Asset Purchase Agreement between JanOne Inc. and SPYR Technologies Inc., dated May 24, 2022. |
|
|
|
10.29 |
|
Promissory Note of SPYR Technologies Inc. in favor of JanOne Inc., dated May 24, 2022. |
|
|
|
10.92 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.93 |
|
Guaranty to Gulf Coast Bank and Trust by JanOne Inc., dated as of September 21, 2022. |
|
|
|
10.94 |
|
Debt Subordination Agreement by Isaac Capital Group, dated as of September 21, 2022. |
|
|
|
10.95+ |
|
|
|
|
|
21.1+ |
|
|
|
|
|
23.1+ |
|
Consent of Frazier & Deeter, LLC, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
|
|
23.2+ |
|
Consent of WSRP, LLC, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
|
|
31.1+ |
|
Certification by Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
31.2+ |
|
Certification by Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
32.1† |
|
|
|
|
|
32.2† |
|
|
|
|
|
101+ |
|
The following materials from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2022, formatted in iXBRL (Inline eXtensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity, (v) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, and (vi) document and entity information. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
104 |
|
Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). |
* |
|
Items that are management contracts or compensatory plans or arrangements required to be filed as an exhibit pursuant to Item 14(a)3 of this Form 10-K. |
|
|
|
+ |
|
Filed herewith. |
|
|
|
† |
|
Furnished herewith. |
|
|
|
× |
|
Portions of this exhibit have been redacted in compliance with Regulation S-K Item 601(b)(10)(iv) |
78
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this Report to be signed on our behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
April 17, 2023 |
JANONE INC. |
|
|
|
|
|
By |
/s/ Tony Isaac |
|
|
Tony Isaac |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
Principal Executive Officer |
|
|
|
|
/s/ Tony Isaac |
|
Chief Executive Officer, Treasurer |
|
April 17, 2023 |
Tony Isaac |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Principal Financial and Accounting Officer |
|
|
|
|
/s/ Virland A. Johnson |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
April 17, 2023 |
Virland A. Johnson |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Directors |
|
|
|
|
/s/ Tony Isaac |
|
Director |
|
April 17, 2023 |
Tony Isaac |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Richard Butler |
|
Director |
|
April 17, 2023 |
Richard Butler |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ John Bitar |
|
Director |
|
April 17, 2023 |
John Bitar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Nael Hajjar |
|
Director |
|
April 17, 2023 |
Nael Hajjar |
|
|
|
|
79